JOURNAL 1686
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2020 Issue: 1 January-June
p.1 - 14
Viewed 3283 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
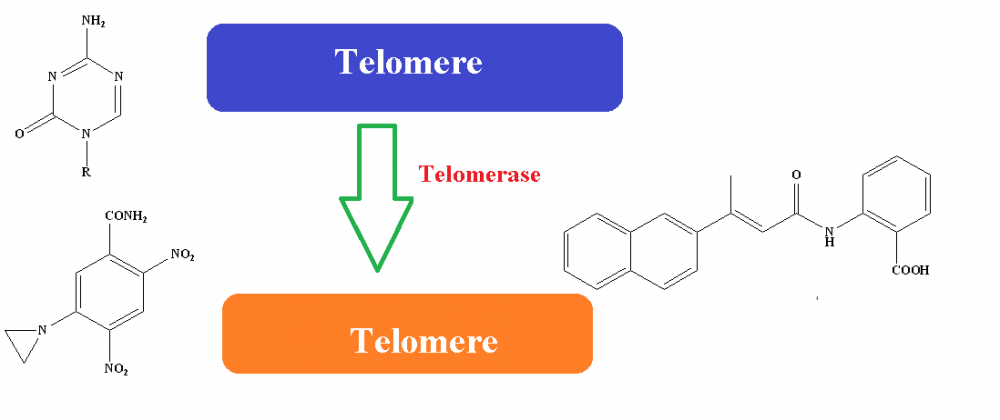
ABSTRACT
Telomeres are DNA sequences with protective structure which are located at the ends of chromosomes. It is known that the telomere length is shortening after all cleavage in somatic cells, whereas in tumor cells this shortening does not occur, and the telomere length is protected. Telomerase is a DNA polymerase with a special structure. The components of its structure are hTR, hTERT and TP1. hTR and hTERT are the components that play a major role in providing continuity to the chromosome. In normal cells, there is almost no telomerase enzyme activity, except for germ cells and stem cells. On the other hand, 85-90 % of cancer cell and cancer cell lines highly express telomerase. Expression of telomerase enzyme contributes to the development of cancer cells. This situation makes telomerase an interesting structure for cancer treatment and it is also supposed that the compounds that target telomerase could be effective in anticancer treatment. Telomerase inhibitors cause apoptosis and cell aging as a result of the shortening of telomere length in telomerase positive cancer cells. In this study, together with the function of the telomerase enzyme, hTERT target inhibitors, hTR target inhibitors, gene and immune treatments directed to telomerase, as well as other telomerase inhibitor strategies in treatment were investigated.
KEYWORDS- Telomere
- telomerase
- telomerase inhibitor
- hTERT
- hTR
- anticancer