Records of Natural Products
A scientific open access journal in the field of natural products.LATEST ARTICLES
Two new cucurbitane-type triterpenoids fromthe peel of Trichosanthes kirilowii

Two new cucurbitane-type triterpenoids (1-2) and one known compound (3) were obtained from the ethyl acetate extract of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. The structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data analysis and comparison with spectroscopic data in the literature. All compounds were evaluated for anti-inflammatory activity in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Compounds 1 and 2 could inhibit the secretion of IL-6, TNF-α, and NO, with IC50 values ranging from 34.82±1.54 to 86.14±1.94 μM
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2512.3776 Keywords Trichosanthes kirilowii triterpenoids anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.An experimental and in silico study on the antifungal activity of guaianolides isolated from Centaurea polypodiifolia Boiss. against resistant Candida strains
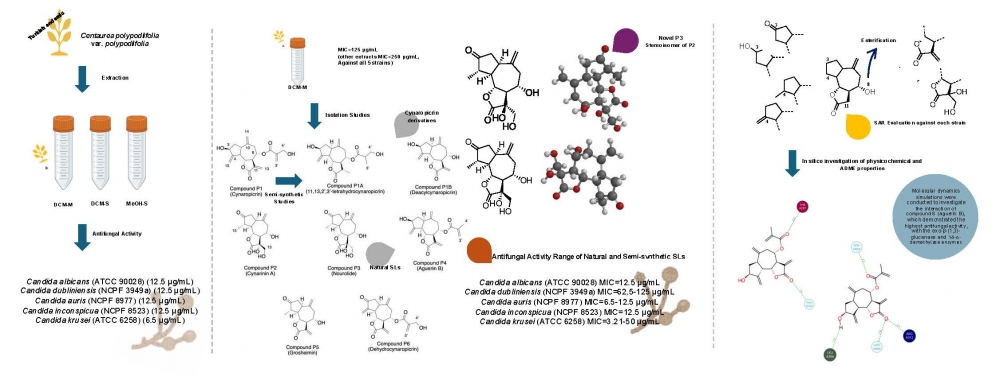
The emergence of multidrug-resistant Candida strains especially, Candida auris, C. dubliniensis, and C. inconspicua has accelerated the research on antifungal novel molecules. Sesquiterpene lactones, abundant in the Asteraceae family, have drawn attention with their antifungal activity. Therefore, three extracts obtained from the aerial part of Turkish endemic Centaurea polypodiifolia were investigated against Candida albicans (ATCC 90028), C. krusei (ATCC 6258), C. dubliniensis (NCPF 3949a), C. inconspicua (NCPF 8523), and C. auris (NCPF 8977) and gave MIC values between 6.25 and 12.5 µg/mL. Dichloromethane (DCM-M) extract yielded five known (cynaropicrin, cynarinin A, aguerin B, grosheimin, and dehydrocynaropicrin) and one novel (nourolide) guaianolide-type sesquiterpene lactones. Two semi-synthetic cynaropicrin derivatives were obtained to enhance the molecular diversity of the present study. 1D (1H and 13C APT) and 2D (COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY) NMR experiments were employed for structure elucidation. MIC values of the tested sesquiterpene lactones against the above-mentioned strains ranged between 3.12 and 50 µg/mL. Molecular dynamics simulations were conducted to investigate the interaction of 4 (aguerin B), which demonstrated the highest antifungal activity, with the exo-β-(1,3)-glucanase and 14-α-demethylase enzymes. These findings revealed stable binding interactions, suggesting that aguerin B has potential as a lead for further antifungal drug development.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2512.3763 Keywords antifungal Candida Centaurea sesquiterpene lactone fungal resistance DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.New polyketide and chromene derivative isolated froman endophytic Diaporthe Phaseolorum associated with Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua
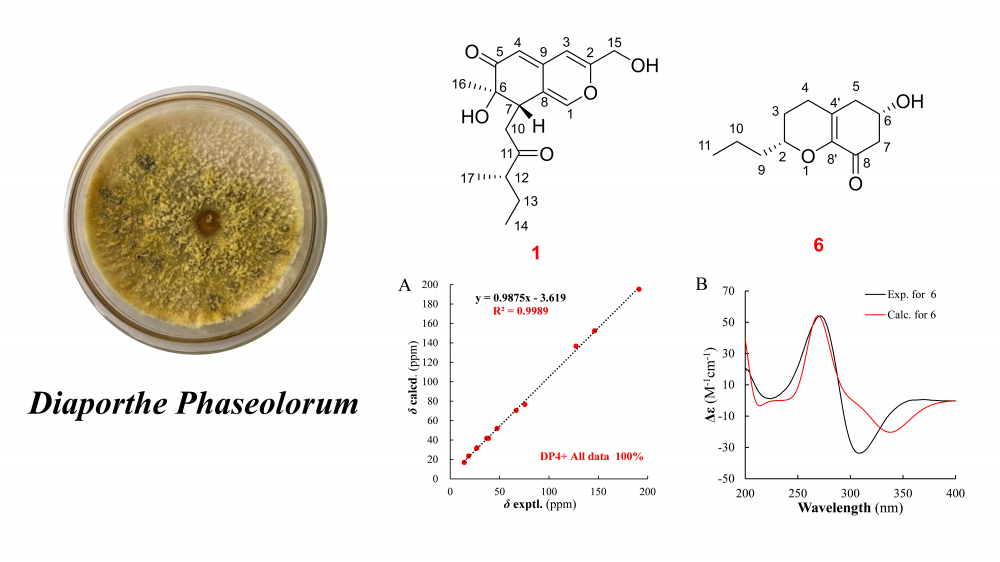
Eight compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of the Diaporthe phaseolorum fermentation products, comprising five polyketide derivatives (1–5), one chromene (6), one chromone (7), and one tetralone (8). Among these, compounds 1 and 6 were identified as previously undescribed. Notably, compound 6 features a unique C12 chromone skeleton, representing only the second reported example of such a framework. The structures and spatial configurations of all compounds were elucidated through comprehensive analysis of HR-MS, NMR, and quantum chemical calculations supported by DP4+ analysis. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity screening revealed that none of the isolated compounds (1–8) inhibited nitric oxide (NO) production in mononuclear macrophages.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2601.3781 Keywords Diaporthe phaseolorum Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua polyketide chromene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.GC-MS characterization of the essential oil fromTeucrium kotschyanum Poech (Lamiaceae) and its antimicrobial assessment
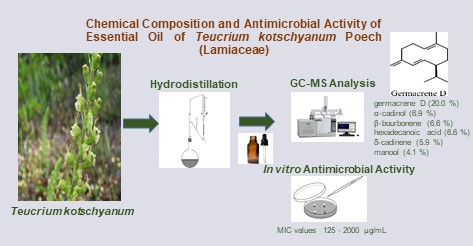
The genus Teucrium L., a member of the Lamiaceae family, is represented by approximately 36 species in Türkiye. In this study, the essential oil composition of the aerial parts of Teucrium kotschyanum Poech collected from ˙Izmir (Ödemi¸s) was investigated by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for the first time. The major compounds were identified as germacrene D (20.0%), α-cadinol (6.9%), β-bourbonene (6.6%), hexadecanoic acid (6.6%), δ-cadinene (5.9%) and manool (4.1%). The antibacterial and antifungal activities of the essential oil were evaluated against six bacteria and six fungi using the microdilution broth method. The essential oil exhibited limited antimicrobial activity, with the highest efficacy observed against Candida utilis (MIC:125 μg/mL) and the lowest against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Salmonella typhimurium (MIC: 2000 μg/mL).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2512.3750 Keywords Teucrium kotschyanum Poech Lamiaceae essential oil GC-MS antimicrobial activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
