JOURNAL 2767
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2023 Issue: 1 January-June
p.79 - 52
Viewed 1859 times.
-
Cherukula Srinivasa Reddy

-
Chilakabattina Naga Narasimha Babu

-
Bhagya Kumar Tatavarti

-
Nalleboyina Vijaya

-
Venkateswara Rao Anna

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
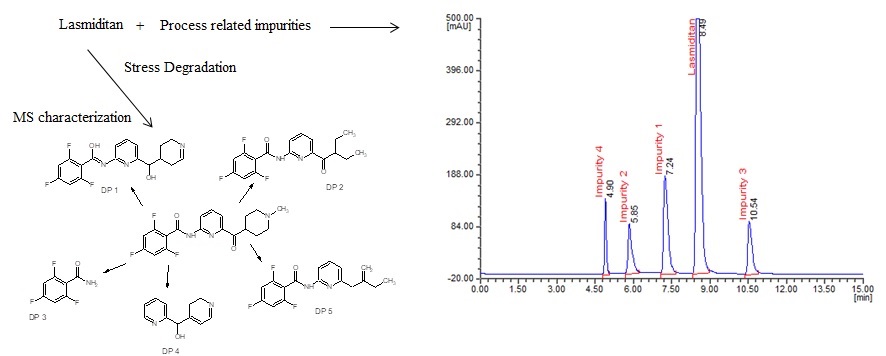
The present investigation aimed to investigate a novel approach involving the utility of liquid chromatography (LC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC–MS) to resolve, identify and characterize very nominal quantities of degradation products (DPs) of lasmiditan without isolation from their reaction mixtures. The process related impurities along with lasmiditan were resolved on Inertsil ODS-3 (250×4.6 mm, 5.0 μm) column at room temperature using 0.1 M phosphate buffer with pH 3.6 and acetonitrile 65:35 (v/v) as mobile phase A, 0.1 M phosphate buffer with pH 3.6 and methanol in the ratio of 20:80 (v/v) as mobile phase B. The mobile phase solvent A and B were mixed at 50:50 (v/v) and the mixture was pumped isocratically at 1.0 mL/min and UV detection at 246 nm. The method shows sensitive detection limit of 0.003 µg/mL, 0.008 µg/mL, 0.008 µg/mL and 0.005 µg/mL respectively for impurity 1, 2, 3 and 4 with calibration curve liner in the range of 25-150 µg/mL and 0.025-0.15 respectively for lasmiditan and its studied impurities. The validation including system suitability, specificity, accuracy, recovery, ruggedness and robustness were noticed to be acceptable. The lasmiditan pure compound was subjected to stress studies as per International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guideline. Among all the stress conditions the drug was found to be labile in acid, base and UV light conditions, while it was stable in thernak abd peroxide conditions. A total of five degradation products (DPs) were formed. All the DPs were characterized with the help of their fragmentation pattern and the masses obtained upon LC–MS/MS. All the hitherto unknown degradation products were identified 2,4,6-trifluoro-N-{6-[hydroxy(2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)methyl]pyridin-2-l}benzenecarboximidic acid (DP 1), N-[6-(2-ethylbutanoyl)pyridin-2-yl]-2,4,6-trifluorobenzamide (DP 2), 2,4,6-trifluorobenzamide (DP 3), 2,3-dihydropyridin-4-yl(pyridin-2-yl)methanol (DP 4) and 2,4,6-trifluoro-N-[6-(2-methylidenebutyl) pyridin-2-yl]benzamide (DP 5). The proposed method was successfully applicable for routine analysis of lasmiditan and its process related impurities in pure drug and formulations and also applicable for identification of known and unknown impurities of lasmiditan.
KEYWORDS- Lasmiditan
- Impurities
- HPLC method
- stress degradation studies
- LCMS characterization
- degradation products