JOURNAL 3729
Organic Communications
Year: 2025 Issue: 4 October-December
p.307 - 320
Viewed 229 times.
-
Mohd Khairul Nizam Mazlan

-
Mohamad Nurul Azmi

-
Saiful Azmi Johari

-
Nor Syaidatul Akmal Mohd Yousof

-
Mohammad Tasyriq Che Omar

-
Habibah A. Wahab

-
Mohd Fazli Mohammat

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
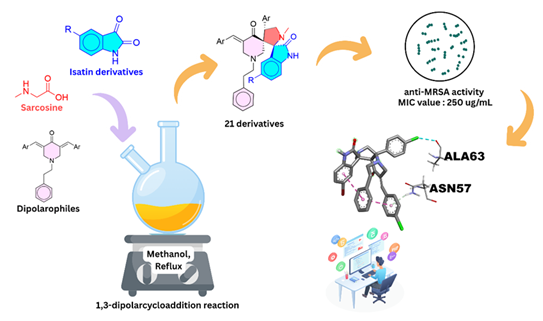
ABSTRACT
A series of new dispiropyrrolidine oxindole derivatives (8-10) were successfully synthesised with yield of 57 to 95% via one-pot 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction of azomethine ylides and characterised by various spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, FT-IR, and HRMS. The compounds were evaluated for their activity against methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Among the compounds, compound 9f and 9g exhibit moderate activity against MRSA with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 250 µg/mL and 325 µg/mL, respectively. The binding energies and interactions of both compounds with S. aureus adhesion proteins such as sdrE, CIfA and FnBPA were further studied through molecular docking studies. Compound 9f (-8.5 ± 0.00 kcal/mol) showed a strong binding affinity than compound 9g (-7.5 ± 0.20 kcal/mol) particularly towards FnBPA adhesion protein. The molecular docking results revealed that the interactions between the compounds 9f and 9g with target proteins correlate with the observed MRSA inhibitory activity, highlighting their potential as promising lead candidates for anti-MRSA drug development.
KEYWORDS- Dispiropyrrolidine oxindole
- anti-bacterial activity
- methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- molecular docking
- in silico study