JOURNAL 3592
Organic Communications
Available Online: October 20,2025
p.1 - 12
http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.199.2507.3592 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 33 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
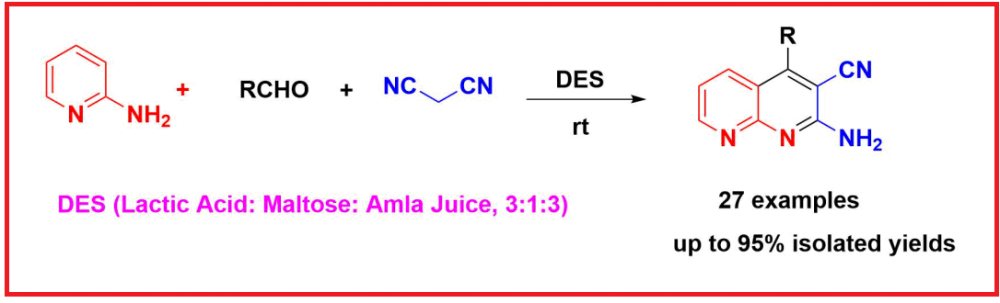
ABSTRACT
The use of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) not only promotes the reaction but also aligns with green chemistry principles due to their biodegradability, low toxicity, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability. A green and efficient one-pot, three-component synthesis of 2-amino-4-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carbonitrile derivatives has been developed using lactic acid-based DESs. The reaction, involving 2-aminopyridine, aromatic aldehydes, and malononitrile, proceeds under mild conditions in a DES composed of lactic Acid, maltose, and amla (Indian gooseberry) Juice (3:1:3 molar ratio) without the need for any additional catalysts or additives. Among various DESs evaluated, this ternary mixture exhibited the highest catalytic activity, delivering products in good to excellent yields. The methodology offers notable advantages, including high atom economy, reduced reaction time, and elimination of hazardous solvents. The synthesized naphthyridine derivatives were structurally confirmed by FTIR, NMR, and HRMS analyses. This study highlights the potential of natural-product-based DESs as sustainable media for multicomponent heterocycle synthesis, with significant implications for the field of organic synthesis and green chemistry
KEYWORDS- Multicomponent reactions
- deep eutectic solvents (DESs)
- 1,8-naphthyridine
- green synthesis
- 2-amino pyridine
- lactic acid