JOURNAL 3419
Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Available Online: April 25,2025
p.1 - 12
http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.28.2501.3419 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 124 times.
-
Gjoshe Stefkov

-
Filip Todorov

-
Jovana Gjorgjievska

-
Ivana Cvetkovikj Karanfilovaa

-
Marija Karapandzova

-
Daniela Jovanovska

-
Slavcho Hristovski

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
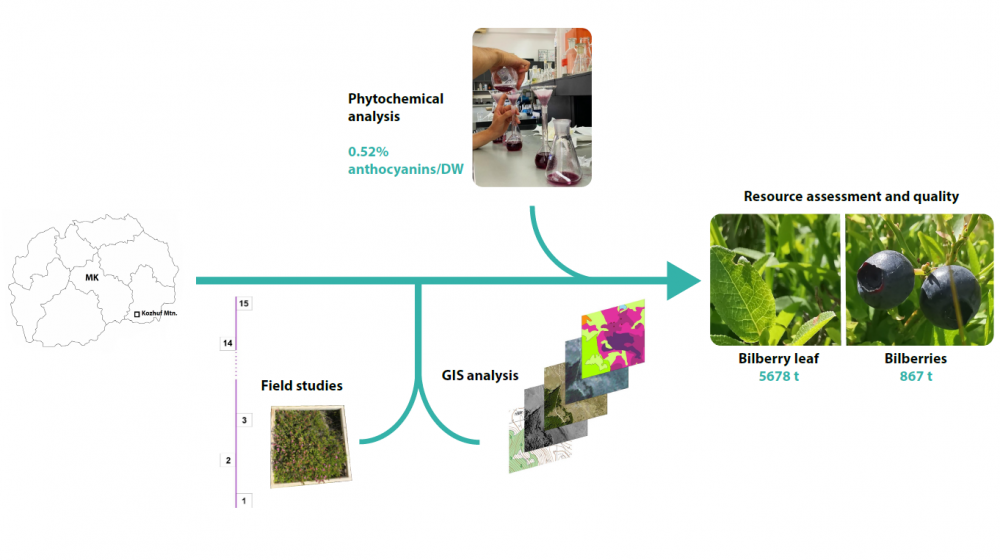
Blueberries are a valuable natural resource in North Macedonia, providing income for many people. However, underdeveloped collection, licensing, and monitoring systems result in unsustainable use. This study integrates GIS and field assessments of blueberry resources on Kozuf Mountain, analyzing annual fruit and leaf production and their chemical composition. Leaf and fresh fruit production averaged 48.30 g/m² and 30.70 g/m², respectively. The total biomass of dry leaves was estimated at 5186.70 t, mainly in heathlands. Anthocyanin content in fresh blueberries, determined according to Ph. Eur. 11, was 0.52%. The total phenolic content in Vaccinium myrtillus leaf extract averaged 174.55 mg GAE/g DW. Sustainable blueberry use could generate 3.55 million EUR from fruit and 5.44 million EUR from leaves. This could support nearly 1400 people based on average Macedonian salaries. To strengthen the licensing and monitoring system, resource management must align with the growing demand for bilberry collection while considering the region’s socioeconomic conditions. Establishing a protected area on Kozuf Mountain, promoting sustainable harvesting, and raising biodiversity awareness are crucial for long-term conservation. These efforts will help preserve natural resources while ensuring continued economic benefits for local communities.
KEYWORDS- Vaccinium myrtillus
- biomass production
- natural resources
- anthocyanins