JOURNAL 1615
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Issue: 6 November-December (Special Issue Dedicated to the Memory of Professor Ayhan Ulubelen)
p.593 - 601
Viewed 2486 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
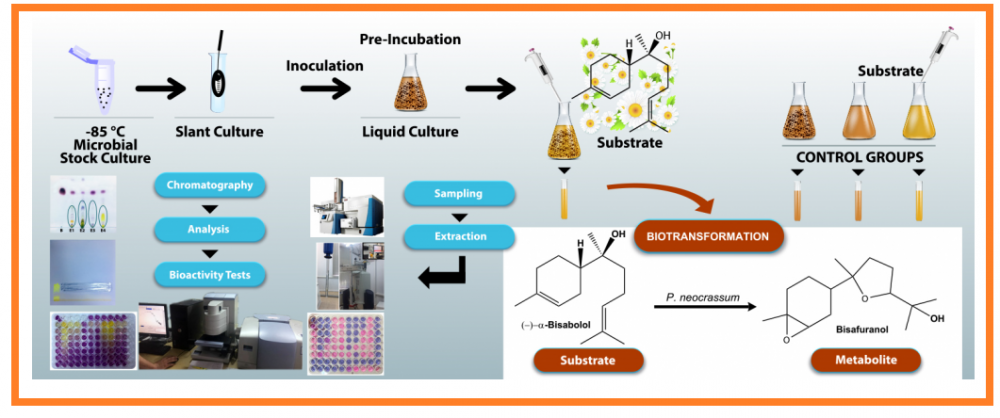
ABSTRACT
Bisabolol is one of the bioactive constituents of chamomile. It was aimed to biotransform (–)-α-bisabolol by different fungi for the production of new bioactive metabolites, which was converted to α-bisabolol oxide A and B by Thamnidium elegans. Additionally, the biotransformation by Penicillium neocrassum yielded a new metabolite, which was characterized as 2-(5-methyl-5-(6-methyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-3-yl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)propan-2-ol = bisafuranol. The substrate and its metabolite mixtures were tested using antioxidant DPPH• scavenging assay. Antimicrobial activity was evaluated by an in vitro microdilution assay against a panel of human pathogenic bacteria and yeasts resulting in the lowest MIC and MFC values of 150 μg/mL. (–)-α-Bisabolol was effective against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis (75, 37.5 μg/mL, respectively). The antioxidant activity of the metabolites was found to be more effective in scavenging free radicals.
KEYWORDS- microbial transformation
- Matricaria recutita L.
- bisabolol
- antimicrobial
- antioxidant
- Penicillium neocrassum