JOURNAL 3593
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2026 Issue: 1
p.2 - 2
Viewed 660 times.
-
Huy Truong Nguyen

-
Phuong Mai To

-
Tri Nhan Pham

-
Dinh-minh-tu Nguyen

-
Le Van Nguyen

-
Thuc-Huy Duong

-
Thi-Hoai-Thu Nguyen

-
Jirapast Sichaem

-
Ngoc-Hong Nguyen

-
Nutthapol Funnimid

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
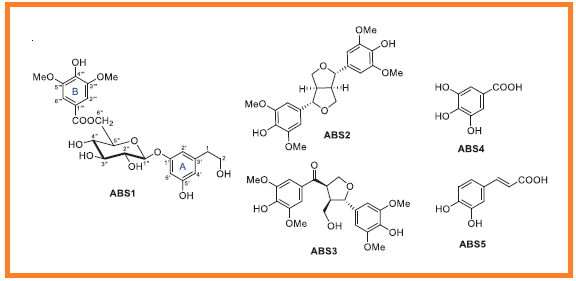
ABSTRACT
Nitric oxide (NO) overproduction by activated macrophages drives inflammatory responses via iNOS activation, prompting the search for natural NO inhibitors. A bioassay-guided investigation targeting NO inhibition was conducted on Averrhoa bilimbi and Schinus terebinthifolia, two Thai medicinal plants. The most active fractions, derived from the branches of A. bilimbi and the stems of S. terebinthifolia, were subjected to chemical analysis. Seventeen compounds were isolated, five (ABS1–ABS5) from A. bilimbi and twelve (ST1–ST12) from S. terebinthifolia, with bilimoside A (ABS1) identified as a new compound. Structural elucidation of all isolated compounds was accomplished through detailed spectroscopic analysis, including NMR and HRESIMS. Their in vitro NO inhibitory activity was evaluated, revealing 3-oxoursolic acid (ST2) as the most potent compound (IC50 28.00 µg/mL), surpassing the positive control L-NMMA (IC50 41.30 µg/mL), while exhibiting minimal cytotoxicity. These findings suggest that ST2 could serve as a promising candidate for further development as an anti-inflammatory agent.
KEYWORDS- Averrhoa bilimbi
- Schinus terebinthifolia
- bilimoside A
- nitric oxide inhibition.