JOURNAL 3455
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: April 30,2025
p.1 - 8
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.517.2503.3455 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 330 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
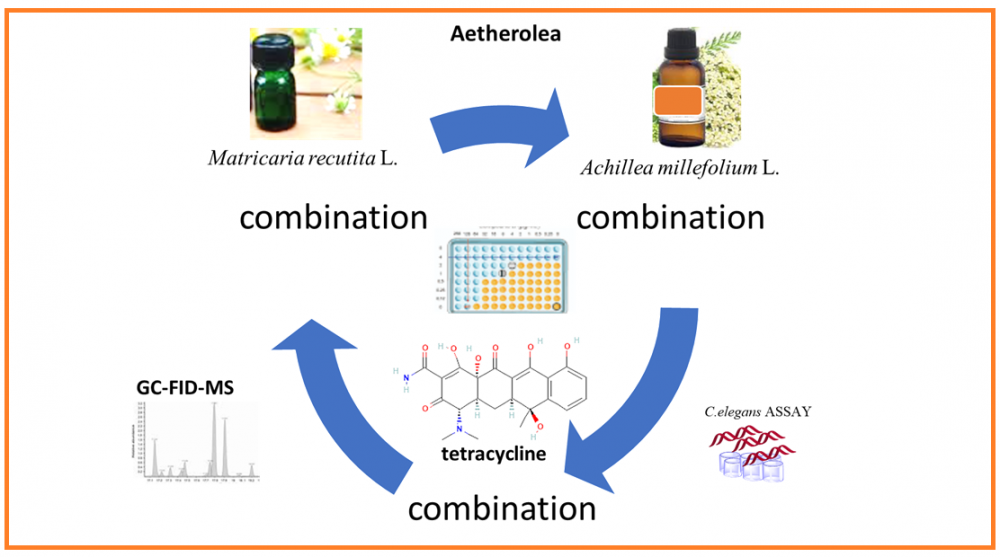
ABSTRACT
Matricaria recutita L. and Achillea millefolium L. (Astereacea) aetherolea are among the herbal drug preparations used due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects. The present study aimed to evaluate the in vitro antibacterial activity of M. recutita and A. millefolium oils individually combined with tetracycline. Followed by safety/toxicity evaluation using an in vivo animal alternative experimental model, namely Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemical verification of Pharmacopoeia quality essential oils was performed both by GC-FID and GC-MS systems, simultaneously. β-Caryophyllene (17%), β-pinene (13.2%), camphor (10%), and sabinene (9.7%) were identified as major components for A. millefolium essential oil; whereas, bisabolol oxide A (41.6%), α-bisabolol (19.4%), (E)-β-farnesene (17%), α-bisabolol oxide B (5.2%), α-bisabolon oxide A (5%), chamazulene (1.6%), and germacrene D (1.2%) were determined as major components for M. recutita essential oil, respectively, in line with the international standards. Antibacterial activities of essential oils and tetracycline were evaluated by microdilution methods against the standard pathogenic strains Bacillus cereus NRRL B3711, Corynebacterium striatum ATCC BAA-1293, Streptococcus sanguinis ATCC 10556, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 700699. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were determined followed by the checkerboard combination studies. A. millefolium and M. recutita essential oils showed in vitro inhibitory activity against all tested microorganisms (MIC= 48.7-6250 μg/mL). The oil combinations with tetracycline showed varying inhibitory antibacterial activity, where M. recutita essential oil with tetracycline resulted in synergism against S.aureus. In vivo toxicity tests on C. elegans nematodes resulted in a non-acute toxicity, indicating the relatively safe use of the tetracycline combinations.
KEYWORDS- Matricaria recutita L
- Achillea millefolium L.
- Caenorhabditis elegans
- synergy
- antimicrobial activity.