JOURNAL 3383
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: May 04,2025
p.1 - 16
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.1505.2412.3383 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 300 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
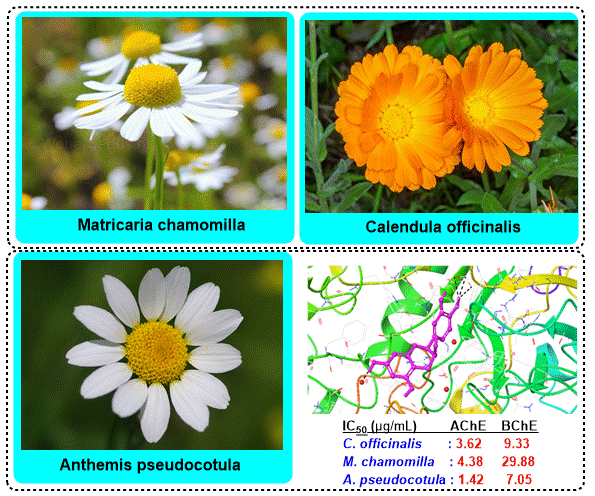
ABSTRACT
This study determined the enzyme inhibition potential of three species (Calendula officinalis, Matricaria chamomilla, and Anthemis pseudocotula) from the Asteraceae family through in silico, followed by in vitro studies. Quinic acid, fumaric acid, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, vanillic acid, quercetin, apigenin, and isorhamnetin were determined by LC-MS/MS in all of the species. Metabolic enzymes are essential catalysts regulating biochemical reactions within living organisms, facilitating energy production, detoxification, and biosynthesis. These enzymes play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and are tightly regulated to ensure optimal metabolic function. High docking scores were also obtained for butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), α-glycosidase, α-amylase, and human carbonic anhydrase I and II enzymes (hCA I and hCA II). Among the extracts, Anthemis pseudocotula was concluded to be the best inhibitor for the enzymes, which was further determined by in vitro enzyme inhibition tests. Besides, it was concluded that all extracts showed anti-cholinergic, anti-diabetic, and anti-glaucoma properties. This is the first study determining the enzyme inhibition property of Anthemis pseudocotula and the three species' hCA I and hCA II inhibition activities.
KEYWORDS- Enzyme inhibition
- Matricaria chamomilla
- Anthemis pseudocotula
- Calendula officinalis
- LC-MS/MS