JOURNAL 3460
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: July 11,2025
p.1 - 6
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.527.2503.3460 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 95 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
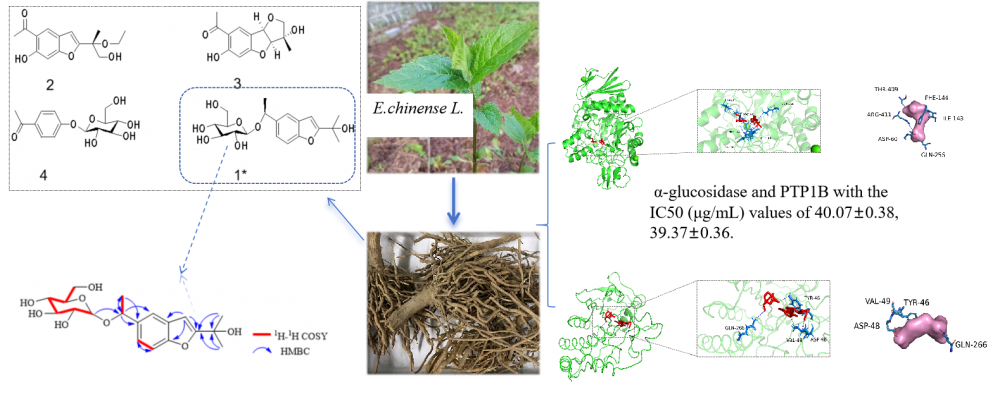
ABSTRACT
A new benzofuranside compound (eupbenzofuranside C) was isolated from the n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Eupatorium chinense L. along with three known compounds. The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR techniques, mass spectrometry and circular dichromism (CD). The isolated compounds were investigated for their α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory activities by p-nitrophenyl-β-galactopyranoside method and p-nitrophenyl phosphate method, respectively. Although eupbenzofuranside C showed potential dual inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase and PTP1B with IC50 values of 40.07±0.38 μg/mL and 39.37±0.36 μg/mL, respectively, these values were determined to be far from the data of the positive control acarbose. In contrast, compound 2 showed inhibitory activities against both α-glucosidase and PTP1B with IC50 (μg/mL) values of 4.83±0.29 and 17.29±0.17, which were closer to acarbose. Compounds 3 and 4 showed no inhibition in both tests (IC50 > 50 μg/mL). In addition, the interactions of compound 1 with α-glucosidase and PTP1B were analyzed using the active site analysis for computer-aided drug design.
KEYWORDS- Eupatorium chinense L
- bioactive components
- inhibitory activity
- α-glucosidase
- PTP1B