JOURNAL 3484
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: July 11,2025
p.1 - 6
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.531.2504.3484 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 119 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
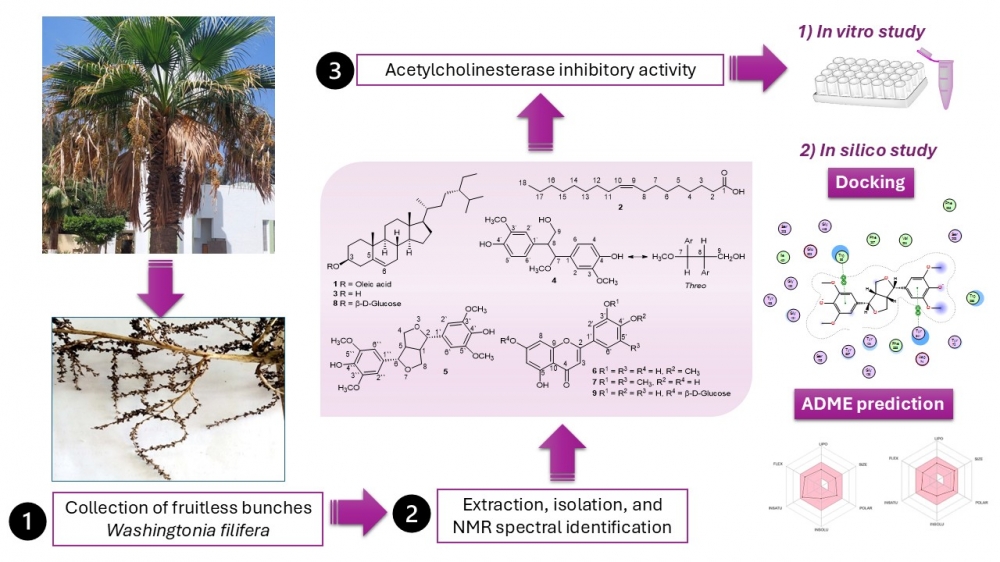
ABSTRACT
Nine known compounds were isolated from the fruitless bunches of Washingtonia filifera, an underutilized agricultural waste, using NMR and mass spectrometry. The identified compounds included β-sitosteryl oleate (1), oleic acid (2), β-sitosterol (3), threo-2,3-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-methoxypropanol (4), syringaresinol (5), diosmetin (6), tricin (7), daucosterol (8), and luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucoside (cynaroside) (9). In vitro acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition assays revealed that compound 5 exhibited the strongest activity (IC50 = 29.75 µM), followed by compounds 4 and 6. Docking studies indicated significant interactions of the active compounds with key AChE residues, particularly Trp86 and Tyr341. ADME predictions further supported the drug-likeness of compounds 4 and 5. These results highlight the significance of W. filifera agricultural waste as a source of bioactive compounds, particularly with neuroprotective effects.
KEYWORDS- Washingtonia filifera
- California fan plam
- fruitless bunch
- acetylcholinesterase
- phenolics
- lignan