JOURNAL 2676
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2023 Issue: 1 January-June
p.25 - 41
Viewed 3172 times.
-
Alejandro Monserrat GarcÍa Alegria

-
Ivan Anduro-Corona

-
Cinthia Jhovanna Perez-Martinez

-
Trinidad Quizan-Plata

-
Lorena Armenta-Villegas

-
Maria Lucila Rascon-Duran

-
Humberto Astiazaran-Garcia

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
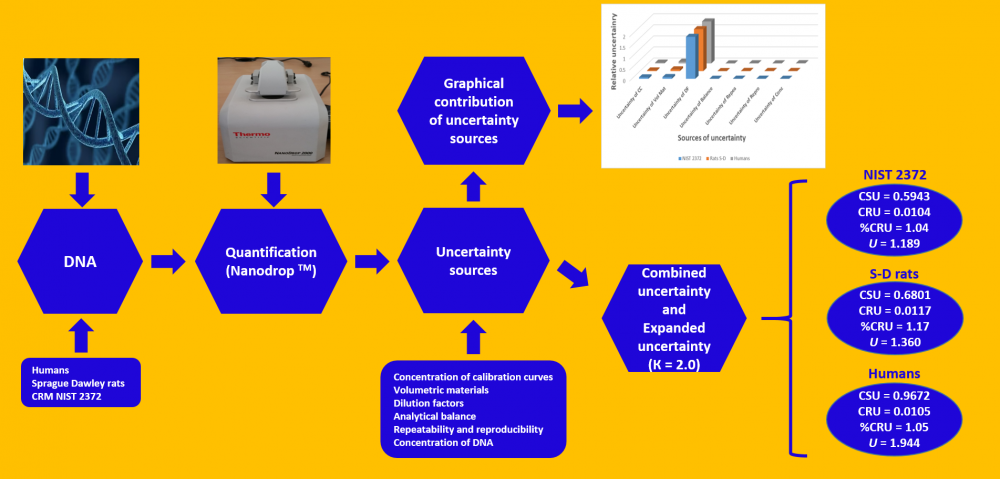
Although the uncertainty calculation proposed by ISO was initially applied to physical quantities, it now also applies to chemical measurements. Therefore, uncertainty estimation contributes to the reliability of the results obtained in analytical chemical measurements, among other parameters. This work seeks to estimate the uncertainty of the analytical method for DNA quantification through a Nanodrop spectrophotometer, using DNA from certified reference materials (NIST 2372), Sprague Dawley rats, and humans. For these purposes, the sources of uncertainty were established and evaluated. Some of these sources are concentration uncertainty from the calibration curves, volumetric materials, dilution factors, analytical balance, repeatability, and reproducibility, as well as DNA concentrations used. The results obtained indicate that the expanded uncertainty was 1.189, 1.360, and 1.944 ng/µL of DNA for the reference material (NIST 2372), Sprague Dawley rats, and humans, thus representing 2.08%, 2.34%, and 2.12%, respectively, for the DNA concentrations from each source (57.0, 57.9, and 91.5 ng/µL DNA, respectively). The uncertainty source that contributes most to these calculations is the dilution factor uncertainty, although it should be noted that the dilution factor uncertainty also considers the volumetric material uncertainty, as well as the fact that five dilutions were used for the calibration curves. Hence, these results may be overestimated.
KEYWORDS- DNA
- Nanodrop spectrophotometer
- Uncertainty