JOURNAL 2975
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2023 Issue: 2 July-December
p.181 - 198
Viewed 2847 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
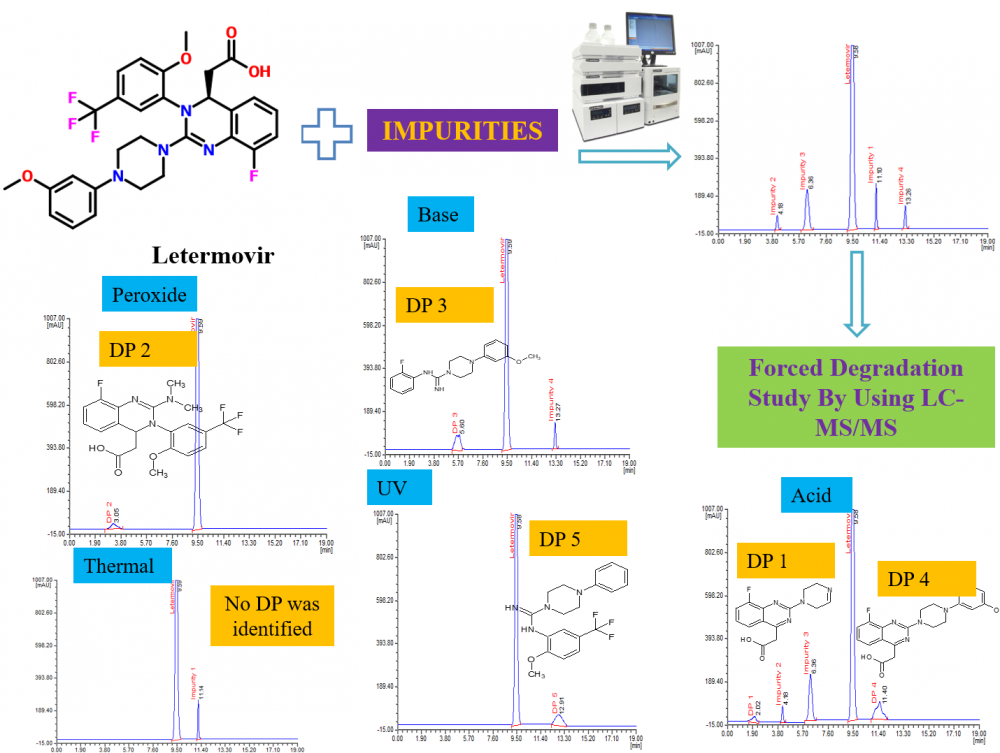
This study aimed to propose a straightforward and highly sensitive HPLC method for the evaluation of letermovir, coupled with an examination of the stress degradation nature of letermovir. Chromatographic separation analytes were attained using a Phenomenex Luna C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm; 5 µm id) maintained at 35 °C. The mobile phase comprises 0.1% phosphoric acid, methanol, and acetonitrile in 45:25:30 (v/v) facilitated isocratic elution at 0.8 mL/min with 234 nm wavelength. Under the proposed conditions, retention times were determined to be 9.58 min for letermovir and 11.10 min, 4.18 min, 6.30 min, and 13.26 min for impurities 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. The method achieved a sensitive detection limit of 0.009 with 0.05–0.2 µg/mL as the linear range for impurities. Other validation tests met acceptable criteria for letermovir and impurities. Additionally, stress degradation tests were conducted following ICH Q1A (R2) guidelines, subjecting the drug to various stress conditions. LC-MS/MS analysis identified five degradation products (DPs), of which DP 1, 4, and 5 were formed due to acid stress, whereas DP 2, 3 and 5 were formed due to peroxide, base and UV stress respectively. The possible structure of DPs was assessed by the interpretation and correlation of mass fragment data. The validation test produces satisfactory results supporting the suitability of the method for regular analysis of letermovir and its impurities. Moreover, the method is applicable for evaluating the degradation mechanism of letermovir.
KEYWORDS- Letermovir
- impurities
- HPLC method optimization
- stress degradation products
- LC-MS/MS characterization