JOURNAL 3584
Organic Communications
Year: 2025 Issue: 3 July-September
p.177 - 188
Viewed 588 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
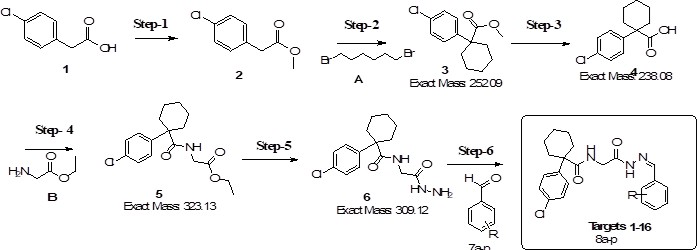
ABSTRACT
Cyclohexanecarboxamido hydrazones constitute a promising new class of therapeutic candidates exhibiting notable antioxidant, antibacterial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory activities. In contrast to conventional hydrazones, these compounds combine the versatile hydrazone pharmacophore with a drug-like cyclohexyl amide moiety, a structural feature that may improve bioavailability, metabolic stability, and overall therapeutic performance. This study shows that, a series of sixteen novel derivatives. 2-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-carboxamido)-N′-arylidenoacetohydrazides (8a–8p), were synthesized through a six-step pathway starting from 2-(4-chlorophenyl)acetic acid. The key hydrazide intermediate was condensed with various substituted aromatic aldehydes, affording the target hydrazones in good to excellent yields (72–86%). Structures of all compounds were confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, LC-MS, and elemental analysis. The synthetic methodology demonstrated broad functional group tolerance, thus providing a reliable platform for generating structurally diverse analogues in consistently high yields.
KEYWORDS- Hydrazones
- substituted aldehydes
- multistep synthesis
- cyclohexane carboxamides