JOURNAL 3583
Organic Communications
Available Online: September 08,2025
p.1 - 11
http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc196.2507-3583 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 208 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
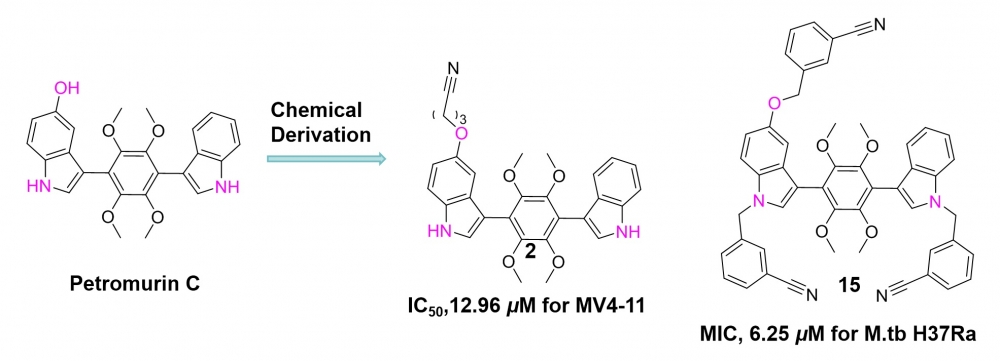
ABSTRACT
A series of nitrile derivatives of Petromurin C were synthesized and assessed for their cytotoxic effects on tumor cell lines and inhibitory activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb H37Ra). Bromoalkyl nitriles (Br(CH2)nCN; n=1-5) and (o-, m-, p-) bromomethyl benzonitriles were used as alkylating reagents. The majority of the syntheses consisted of O-alkylated derivatives in which the two NH group were not alkylated, as expected from the treatment of petromurin C with K2CO3 in DMF followed by treatment with alkylating reagents. Similarly, treatment of Petromurin C with NaH in DMF and the treatment with alkylating reagents yielded both OR and bis-NR alkylated structures. In the first method, 7 different O-alkyl Petromurin C derivatives were obtained. The second method yielded 7 different Petromurin-C derivatives containing both O-alkyl and bis-N-alkyl groups. Notably, compounds 1-4 and 7-10 demonstrated selective inhibitory activity against the acute myeloid leukemia cell line MV4-11, with IC50 values ranging from 12.96 to 20.00 μM. Compound 15 exhibited a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 6.25 μM against M.tb H37Ra. Importantly, all synthesized compounds showed negligible inhibition (below 50%) against human normal cell lines L-02 and 293T at a concentration of 100 μM. These findings suggest that the compounds possess high efficacy and low toxicity, indicating their potential as novel therapeutic agents for the treatment of leukemia and tuberculosis.
KEYWORDS- Petromurin C
- structural modification
- nitrile groups
- cytotoxic activity
- anti-tubercular activity