JOURNAL 2691
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Issue: 4 July-August
p.664 - 670
Viewed 3226 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
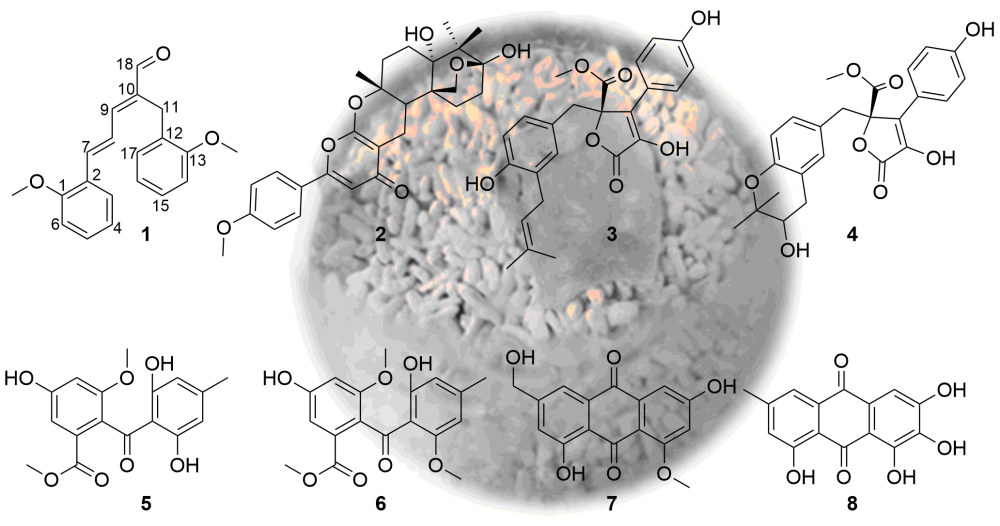
Abstract: The fungal strain Aspergillus sp. LPFH-6 was cultured on solid rice medium with the addition of artificial salt. The culture medium was extracted with the solvent EtOAc to afford an extract, which was separated by various chromatographic techniques to give 8 compounds (1-8). The structures were determined by extensive analyses of the spectroscopic data including 1D (1H and 13C NMR), 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, NOESY), and the MS data. Compound 1 was identified to be a highly conjugated compound that contained a rare 5-(2-methoxyphenyl)penta-2,4-dienal moiety. The known compounds were identified as yaminterritrem B (2), butyrolactone I (3), butyrolactone V (4), sulochrin (5), monomethylsulochrin (6), questinol (7), and 7-hydroxyemodin (8). Bioasasy showed that compounds 2-4 and 8 displayed better a-glucosidase inhibitory activity than the positive control acarbose with IC50 values of 0.25, 0.09, 0.12, and 0.27 mM, respectively.
KEYWORDS- Aspergillus sp.
- marine-derived fungus
- asperaldehyde