JOURNAL 3507
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2025 Issue: 5 September-October
p.571 - 595
Viewed 1102 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
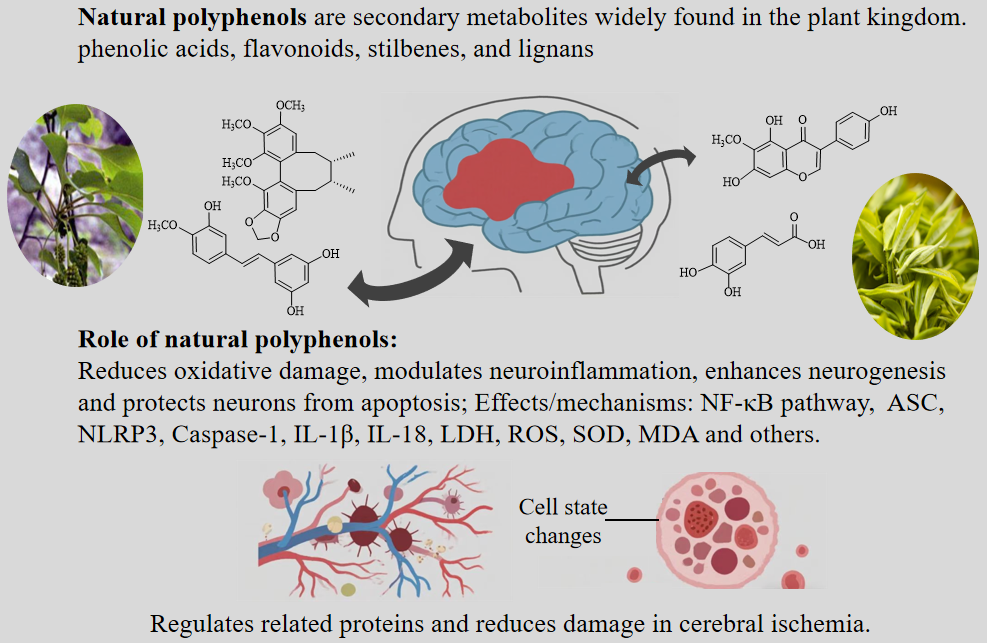
ABSTRACT
Cerebral ischemia is a disorder characterized by insufficient blood flow to the brain, which can lead to severe neurological deficits and brain damage. Given the complexity of cerebral ischemia and the limitations of current pharmacological treatments, there is a growing scholarly interest in natural polyphenols. Polyphenols are a diverse group of secondary metabolites, and these compounds have a strong antioxidant capacity, and oxidative stress is one of the main causes of post-ischemic brain damage. A major consequence of ischemia is the interruption of normal cellular processes due to oxygen and glucose deprivation, resulting in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS damage cellular structures, trigger an inflammatory response, and exacerbate neuronal death. In addition, some polyphenols have a direct effect on the cerebral vasculature; they improve endothelial function and enhance microcirculation, which is essential for restoring blood flow and oxygenation to ischemic brain tissue. Polyphenols can also affect mitochondrial function by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and reducing mitochondrial dysfunction, which plays a key role in cell death during ischemic episodes. Therefore, this paper reviews the potential therapeutic effects of natural polyphenols on cerebral ischemia, focusing on their anti-ischemic effects and related mechanisms.
KEYWORDS- Natural polyphenols
- antiischemic
- phytochemistry
- pharmacology