JOURNAL 3633
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2026 Issue: 1
p.11 - 11
Viewed 346 times.
-
Gunes Ak

-
Sakina Yagi

-
Mehmet Veysi Cetiz

-
Ramazan Tutuş

-
Evren Yildiztugay

-
Luisa Custodio

-
Eliana Fernandes

-
Maria J. Rodrigues

-
Shaza H. Aly

-
Omayma A. Eldahshan

-
Abdel Nasser B . Singab

-
Gökhan Zengin

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
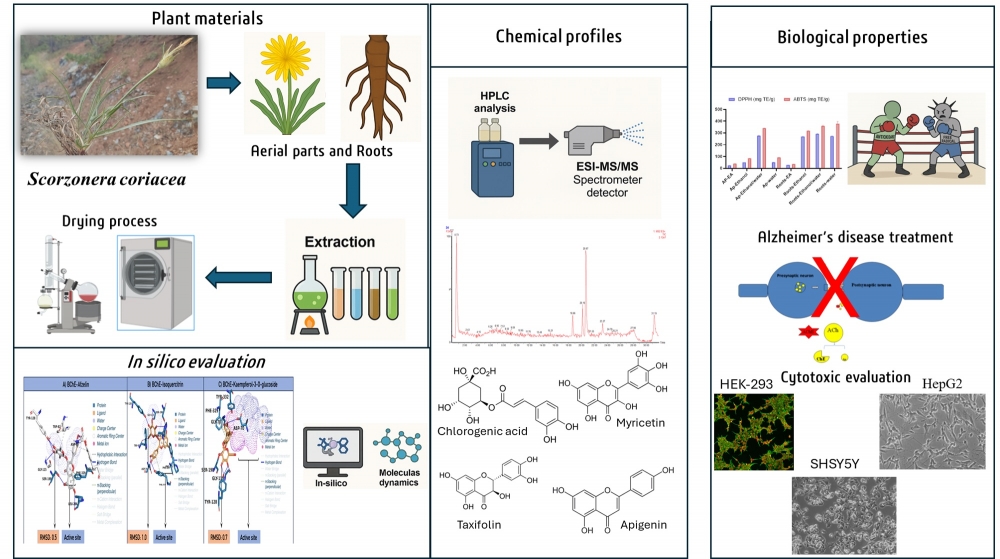
The current study was designed to investigate the chemical composition, antioxidant, enzyme inhibitory, and cytotoxic activities of Scorzonera coriacea A.Duran & Aksoy. Both organs were rich in total phenolic content, with the highest content recorded from the 70% EtOH (48.41 mg GAE/g) and aqueous (47.11 mg GAE/g) extracts of the roots. All aerial parts extracts accumulated higher total flavonoid content than their respective roots extracts, with the highest amount found in their EtOH extract (36.44 mg RE/g). Chemical analysis revealed the presence of 86 compounds belonging to organic acids, phenolic acids, flavonoids, coumarins, anthocyanins, terpenes, saponins, and fatty acids and their derivatives, with the aerial parts accumulating the highest number. The roots displayed the strongest antiradical and ion-reducing capacities. EtOH extract of both organs recorded the highest acetylcholinesterase activity (2.77 and 3.02 mg GALAE/g; p≥0.05), while that of the root showed the best butyrylcholinesterase activity (3.49 mg GALAE/g) and that of the aerial parts the best tyrosinase inhibitory (59.07 mg KAE/g). EtOAc of the root exhibited the best cytotoxicity towards the HepG2 cell line (cell viability = 29.30%), but was also toxic towards HEK293 cells (cell viability = 11.72%). In silico screening supported these findings by identifying multiple strong ligand–protein interactions. Molecular dynamics simulations further confirmed the structural stability of selected complexes. In silico profiling docked 26 phytochemicals against 14 therapeutic targets, generating 364 complexes, of which 62% showed ΔG ≤ −7.0 kcal·mol⁻¹. Binding energies ranged from −1.4 to −10.7 kcal·mol⁻¹, with PD-1–Eriodictyol-7-O-neohesperidoside the best. For metabolic enzymes, Eriodictyol-7-O-neohesperidoside yielded the top α-amylase score and Diosmetin-7-O-glucoside the top α-glucosidase score, while several flavonoids bound AChE/BChE strongly; in contrast, tyrosinase displayed poor affinity overall. 100-ns MD simulations on five top complexes indicated stable behavior for C1 and C4, whereas C2/C3/C5 showed loosening interactions over time. These findings showed that S. coriacea could be a promising source of bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic applications.
KEYWORDS- Scorzonera coriacea
- molecular docking
- molecular dynamics
- antioxidant
- enzyme inhibition
- cytotoxicity