JOURNAL 3561
Records of Natural Products
Available Online: August 03,2025
p.1 - 6
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.541.2506.3561 (DOI number will be activated after the manuscript has been available in an issue.)
Viewed 44 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
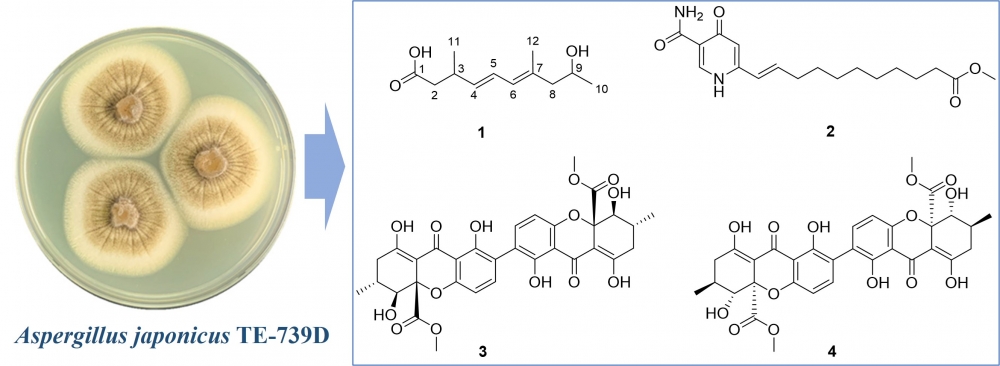
ABSTRACT
Filamentous fungi are very well known for producing a wide variety of secondary metabolites with important biological effects. In our study chemical exploration of the Nicotiana tabacum symbiotic fungus Aspergillus japonicus TE-739D led to the discovery of a new polyketide derivative, namely (3S,4E,6E,9S)-9-hydroxy-3,7-dimethyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid (1), along with three previously reported compounds 2−4. The structures of these compounds were elucidated by using HRESIMS, NMR spectroscopic analyses, and quantum chemical calculations. Compounds 3 and 4 showed strong antibacterial activity against four representative bacterial strains including two Gram-negative species (Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Xanthomonas oryzae) and two Gram-positive Bacillus species (B. cereus and B. subtilis), with MIC values range from 1 to 16 μg/mL, respectively.
KEYWORDS- secondary metabolites
- Aspergillus japonicus
- polyketides
- antibacterial activity