Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2018 Volume: 12 Issue:2 July-December
1) Effect of priming on thymoquinone content and in vitro plant regeneration with tissue culture of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seeds
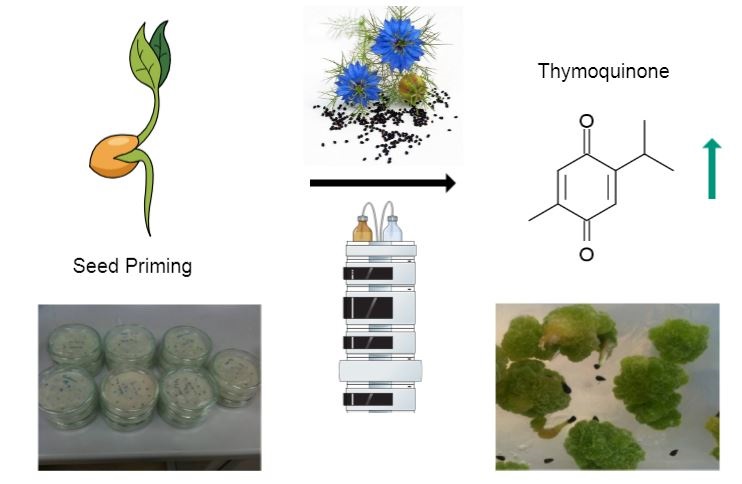
The aim of this study is to analyze the changes on thymoquinone content, which is the major constituent of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seeds, by using priming methods. For the priming studies, seeds placed in distilled water (18 - 20 hours), PEG (Polyethylene glycol 10%, 20%) and mannitol (4% and 6%) for 20 hours and subsequently dried for 24 hours on blotting paper at room temperature (24 ºC ± 1 ºC). The best priming results were obtained in the 4% of mannitol treatment. Control (not primed) Nigella seeds and 4% of mannitol primed seeds were planted in both greenhouse and farm conditions. Seed extracts were analyzed with HPLC to compare the amount of thymoquinone. The results reveal that seed priming with 4% of mannitol increases the amount of thymoquinone in Nigella sativa. In addition, the effects of plant growth hormones on callus regeneration of these primed seeds were investigated herein.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.18.18.09.950 Keywords Black cumin HPLC Nigella sativa priming thymoquinone tissue culture DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Validation of ultrasonic extraction method for the quantification of phthalates in poly (vinyl chloride) and polypropylene matrices at low concentrations by gas-chromatography time of flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOFMS)

Phthalates are used as plasticizers in the manufacturing of plastics to increase their flexibility. Phthalates are endocrine disruptors and given their potential toxicity and widespread use, many countries have implemented strict regulations on their usage. A rapid gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOFMS) analytical method was developed for the determination and quantification of six regulated phthalates. Three extraction methods were investigated including two standard techniques; a dissolution method and a Soxhlet method (EN 14372:2004E). These two standard methods were compared to a simpler ultrasonic extraction method. The recoveries and accuracy of the measurements were assessed by analyzing a polypropylene (PP) certified reference material (matrix CRM) and spiked polyvinyl chloride (PVC) samples. The ultrasonic extraction method resulted in better recoveries (>80%) when compared to the dissolution method. The results obtained from extracting the CRM using the ultrasonic, dissolution and Soxhlet extraction methods were within the certified ranges. The dissolution method occasionally retains the phthalates during precipitation, leading to lower recoveries and inconsistent performance. The ultrasonic extraction method is simpler, uses less solvent and is less time consuming when compared to the conventional Soxhlet extraction method. The ultrasonic extraction method can confidently be used for the accurate quantification of the regulated phthalates in plastics at concentration levels ten times below the European Union regulated limits.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.18.12.1094 Keywords Phthalates Poly (vinyl chloride) Polypropylene Ultrasonic extraction Gas chromatography - time-of-flight mass spectrometry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Determination of Boron in hazelnut varieties with the addition of sorbitol by using ICP-OES and ultrasonic nebulization after microwave digestion system
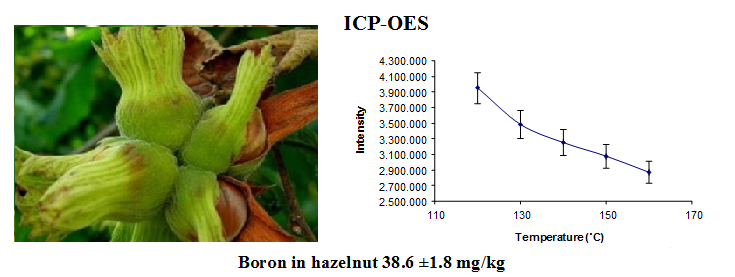
Boron is an essential nutrient for plants and an essential element for many organisms, but can be toxic to aquatic and terrestrial organisms above certain concentrations. The aim of this research is determining the Boron content of four varieties of Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from Sakarya. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) with ultrasonic nebulization (USN) was used for the determination of Boron contents. This method is based on microwave digestion system and reduced memory effect of Boron by using sorbitol. Different conditions were optimized for this method. Four hazelnut varieties, eight soil samples and certificated reference material (NIM-GBW10012) were analyzed. The Boron contents were found as 18.27, 28.3, 38.6, 17.6 mg kg-1 in Kara, Sivri, Delisava and Tombul hazelnut varieties, respectively. And Boron contents of soil samples were between 30.44 to 196.79 mg/kg. The results revealed that the Turkish hazelnut is a good natural source of Boron.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.20.18.11.1076 Keywords Boron microwave digestion hazelnut memory effect ICP-OES USN DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Quantitative determination of some phenolics in Origanum laevigatum Boiss. extracts via validated LC-MS/MS metod and antioxidant activity
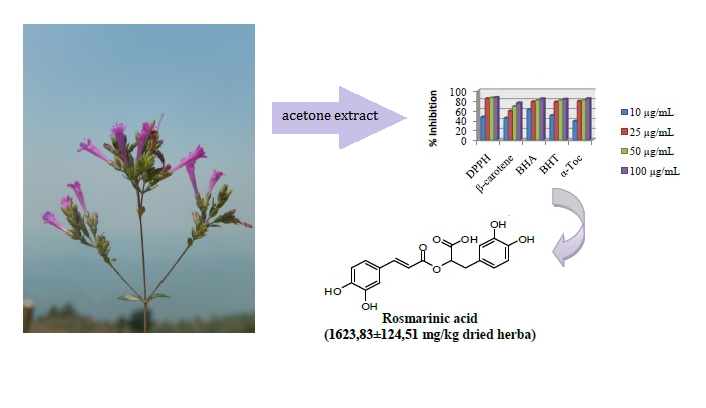
In this study, quantities of some phenolics; caffeic acid, (E)-ferulic acid, rosmarinic acid, chlorogenic acid, fumaric acid, gallic acid, pyrogallol and vanillin in the directly methanol (M1), chloroform (C), acetone (Ac) and methanol (M2) extratcs obtained from Origanum laevigatum Boiss. from Turkey were investigated via liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Curcumin was used as an internal standard. Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, rosmarinic acid and gallic acid were determined as the most abundant phenolic acids in the studied extracts using LC-MS/MS. In LC-MS/MS measurements relative standard deviations (RSD %) for caffeic acid, (E)-ferulic acid, rosmarinic acid, chlorogenic acid, fumaric acid, gallic acid, pyrogallol and vanillin were found to be 8.04, 5.21, 5.45, 3.73, 5.44, 4.85, 5.47 and 6.57 % respectively. For the investigated analytes, the correlation coefficient was found in the range of 0.9803 to 0.9981. Furthermore, antioxidant properties of the extracts were determined based on 2,2-diphenyl-1- picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), β-carotene linoleic acid and cupric (Cu2+) ion reducing power assay (CUPRAC). Acetone (Ac) and methanol (M2) extracts showed high activity in all test assays due to their high concentration of rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid and gallic acid in the extracts.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.21.18.11.1115 Keywords Origanum phenolics LC-MS/MS validation antioxidant activity rosmarinic acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Determination of some major and trace elements in the lower Sakarya River by using ICP-MS
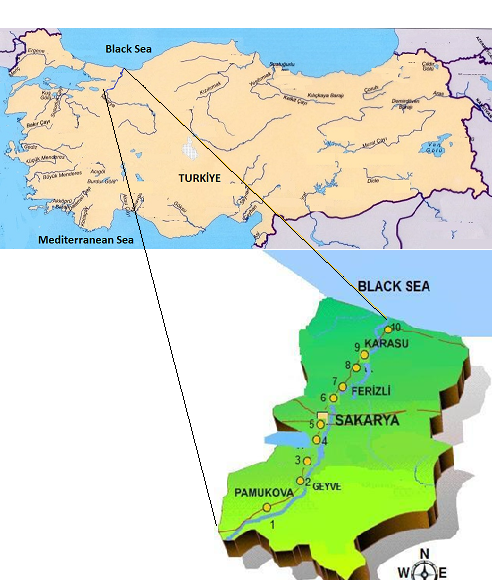
Excessive use of herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers in agricultural activities, anthropogenic discharges and industrial effluents are known to be sources of pollution for the living environment, in water and sediments. Water shows short term effects and sediment shows a long term indication of heavy metal accumulation. It is well known that industries which do not have a water treatment utility have a direct effect on water pollution and an indirect effect on soil and plant contamination. In this paper, water and sediment samples were collected along the Lower Sakarya River basin for a twelve month period between February 2007 and January 2008. The samples were analysed for trace elements (31 elements in sediment and 33 elements in water) using the ICP-MS technique as pollution indicators. The results indicated that the Sakarya River water was polluted by sources of beryllium and thallium which exceeded the limits set by US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA 2003). Sediments were polluted by Antimony, Tin, Rhodium and Selenium. The results also provide useful data for the conservation of the Black Sea where it is joined by the Sakarya River.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.22.18.11.1073 Keywords Sakarya river river water sediment heavy metal ICP-MS environmental DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2018 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.