Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2019 Volume: 13 Issue:2 July-December
1) Proficiency testing for determination of pH and electrolytic conductivity in water and soil samples
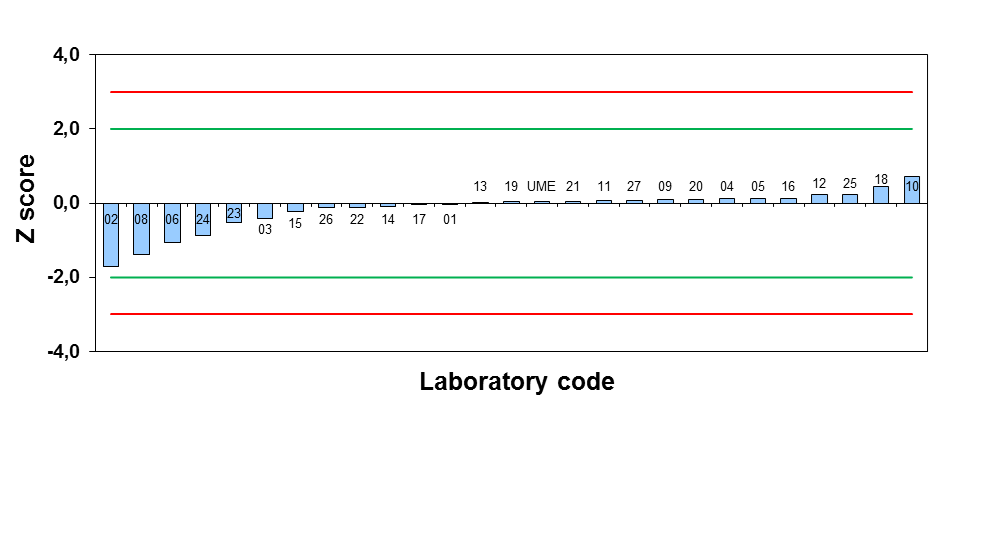
According to ISO 17025:2017, the testing laboratories are required to confirm the measurement accuracy with proficiency testings or international comparisons. For this purpose, the proficiency testings for pH and conductivity measurements in water and soil are organized by TUBITAK UME twice a year. In this study, the preparation and analysis of the samples according to BS EN ISO 10523:2012, ISO 7888:1985, ISO 10390:2005 and ISO 11265:1996 and the evaluation of the results according to ISO 17043:2010 were carried out. pH and electrolytic conductivity (EC) values were determined by a pH meter and a conductivity meter for this study. Based on the results of the participants, they have a chance to improve the accuracy and reliability of their measurement results as observing the performances of other laboratories.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.31.19.11.1439 Keywords Electrolytic conductivity pH drinking water soil proficiency testing DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Ultra-fast liquid chromatographic method for the determination of ticagrelor in pharmaceutical formulations and spiked plasma samples
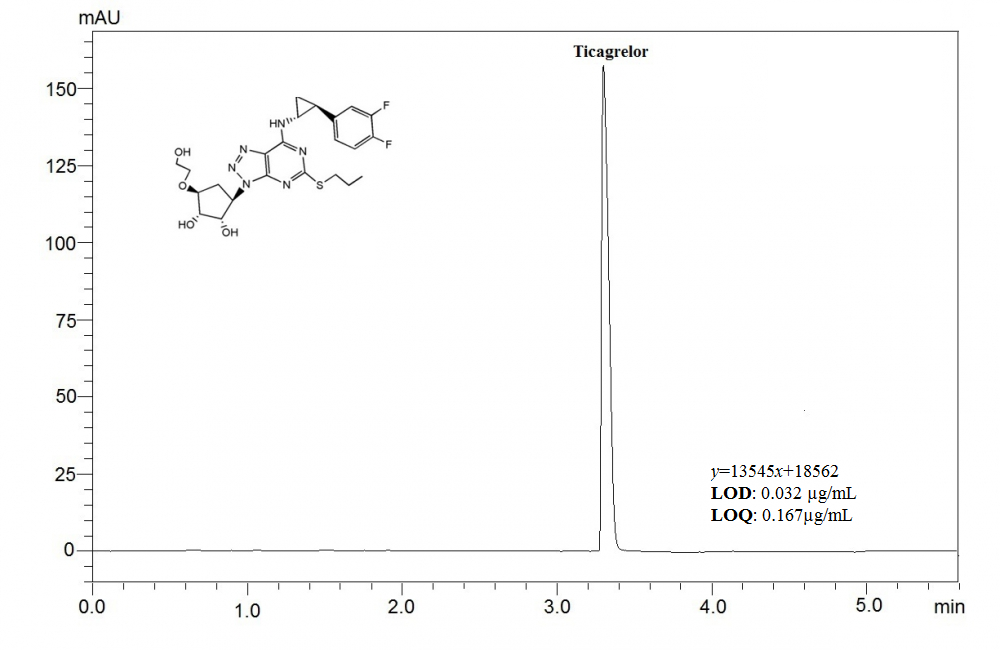
This article aims to present a sensitive, and precise stability-indicating ultra fast liquid chromatographic method, which was developed to determine ticagrelor (TCG) in pharmaceutical formulations and spiked plasma samples. Chromatographic separation was achieved under isocratic elution by using a C18 column (100 × 4mm, 3μm) and a mixture of acetonitrile and phosphoric acid solution (adjusted to pH 3.0 using triethylamine) (55:45, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.7 mL per minute. The analyte was detected at a wavelength of 254 nm, using a photodiode array detector (PDA). The retention time for TCG was found out to be about 3.5 min. As required by the International Conference on Harmonization guidelines, the drug was exposed to different stress conditions; including hydrolysis (acid, alkaline), oxidation, photolysis and thermal degradation. This currently developed method was validated by evaluating the specificity, linearity, precision, accuracy, robustness, and system suitability. The method was determined to be linear in a drug concentration range of 0.5–200 μg/mL with the correlation coefficient of 0.9996. The proposed method was applied successfully to the analysis of TCG in spiked human plasma with good recovery. The method can successfully applied for determination of TCG in pharmaceutical formulation and spiked plasma samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.30.19.11.1465 Keywords Ticagrelor UFLC stability-indicating degradation method validation plasma samples DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Determination of bromate in bottled water marketed in Iran by ion chromatography
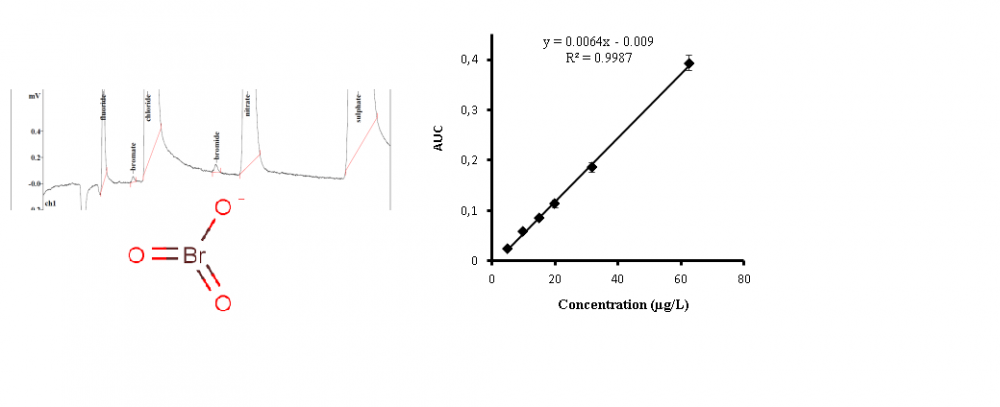
Bottled water is common in most countries in the world. According to high consumption and widely consumers from children to older adults safety of it is very important. Bromate (BrO3) is one of the most important contaminants in bottled water which national and international standards have set permissible level (10 µg/L ). In this study, 168 samples of bottled water (mineral and drinking based on Iranian national standard classification) from Iran’s market were collected and analyzed for bromate content. Ion chromatography with conductivity detector was applied for chemical analysis. 23.8 % of samples had bromate content upper than allowable level. For mineral water 23 samples and for drinking water 17 samples had bromate as 37.04 ± 18.62 µg/L and 33.58 ± 15.12 µg/L , respectively. According to the origin of bottled waters, their bromide content and other related conditions, it is necessary for health authorized organizations to routinely control and also awareness of consumers for hazards of bromate.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.28.19.10.1432 Keywords Bromate bottled water disinfection by-products (DBPs) ion chromatography oxyhalide DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Investigation the fatty acid profile of commercial black cumin seed oils and seed oil capsules: Application to real samples
MMedicinal and aromatic plants are widely used around the world. Today, Black cumin (Nigella sativa L.), one of the most popular medicinal plants, offers numerous benefits for human health. Black cumin oil has known to be used for the treatment of asthma, hypertension, cancer, rheumatism, and headaches over the course of many years. In this study, ten different black cumin seed oils and seed oil capsules, which have been obtained from local markets in Turkey, were investigated for their fatty acid profiles as percentages via gas chromatography and mass spectroscopy (GC-MS). According to the results obtained, the major fatty acids found in capsules and oil samples were similar with small differences in terms of amount; linoleic, oleic and palmitic acids were found as major compounds; 35.27-58.15%, 25.06-51.83%, 7.29-12.88 % in oil samples; 36.67-56.61%, 24.93-46.71%, and 7.90-12.71% in seed oils capsule samples, respectively. This is the first study determining the fatty acid percentages of commercial black cumin seed oil and seed oil capsules.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.26.19.08.1385 Keywords Nigella sativa L. black cumin fatty acid profile seed oil seed oil capsule GC/MS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) A GC-MS method for illegal stimulant drugs from serum: a multi-drug use sample in Turkey
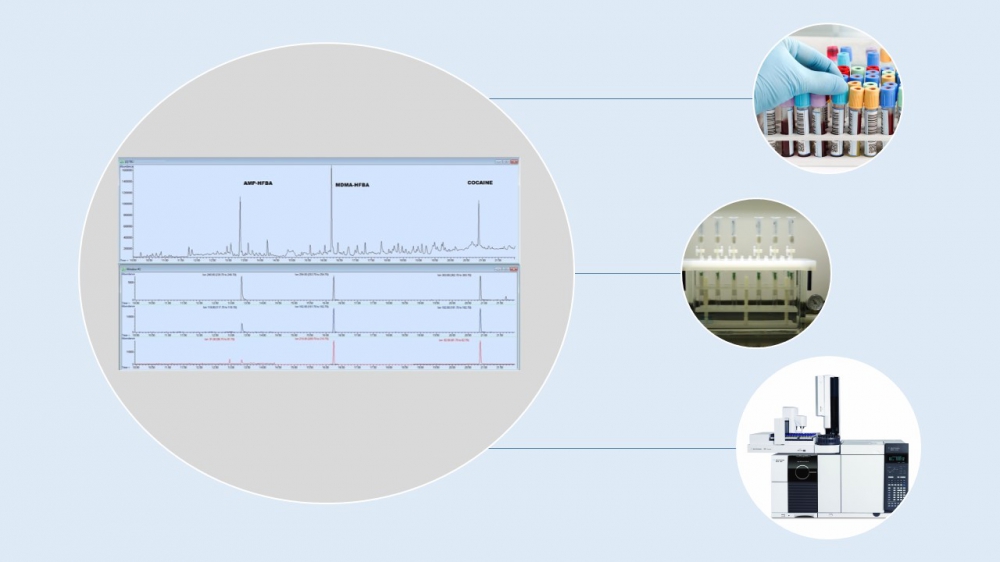
It is rather difficult to determine simultaneously more than one drug from different biological samples and to interpret the clinical picture in the case of multiple drug abuse. All mentioned drugs are life-threatening solely and the risk is becoming higher when they are used together. In this study, a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) method was developed and validated for the simultaneous detection and quantification of amphetamine (AMP), 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and cocaine in serum sample. The analytes were extracted by solid-phase extraction (SPE) cartridges, derivated with heptafluorobutyric anhydride at 60°C for 30 min and analyzed by GC-MS. Correlation coefficient values were found satisfactory. Linearity ranged from 1 to 20 μg/mL for all three substances. After acceptable results were obtained from calibration solutions, the study was conducted to observe matrix-match calibration and linearity parameters. Extraction efficiency of the method was observed in two concentrations spiked to serum matrix (5 and 10 μg/mL) and found over 80% for three illicit drugs. Precision, accuracy, stability evaluation were appropriate as well. The validated analytical method was applied to an authentic sample which obtained from a patient administered to emergency room. The patient was suspected in regard to multi-drug use of stimulants and serum sample was analyzed by the presented method and AMP, MDMA and cocaine use was determined with concentrations of 0.45, 1.03 and 1.98 mg/mL in blood respectively. The developed method proved capable of quantifying simultaneous AMP, MDMA and cocaine use proposed in this study. Multidrug abuse is not a novel phenomenon but has to be determined as soon as possible by forensic toxicology laboratories because of potential severe health risks.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.32.19.11.1499 Keywords Forensic toxicology Multi drug abuse Amphetamine MDMA Cocaine GC-MS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Development and validation of a practical analytical method for Zolpidem as a drug facilitated crime tool
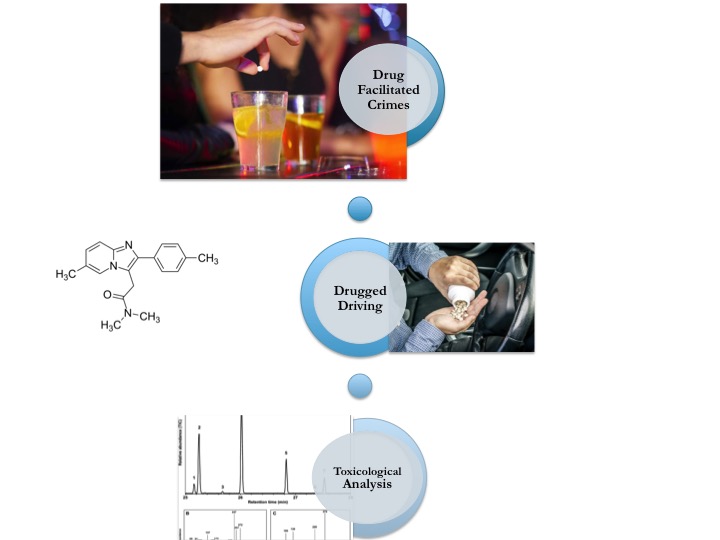
Zolpidem, as a member of Z-drugs, is a non-benzodiazepine, imidazopyridine derivative chemical substance used in the treatment of insomnia. This substance is frequently reported as a tool of drug facilitated crimes such as date rape, robbery, extortion etc besides drugged driving. A Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) method by a one step extraction method with ethyl acetate from urine using HP-5MS capillary column was developed for the determination of zolpidem. Clozapine was used as internal standard. Linearity range was between 10-200 μg mL -1. Limit of detection was 0.28 μg mL -1 , limit of quantification was 0.35 μg mL -1, the mean range of recoveries was between 93.40-94.41% for three spiked concentrations (15, 20 and 50 μg mL -1). The difference of concentrations for same samples analyzed at 7-day intervals was found 0.02 CV% for stability study. The reported method was found cheap, sensitive, rapid, and suitable for the analysis of the spiked beverages and foods as well as urine as evidences of sexual assault, robbery or intentional/ non-intentional intoxication phenomena.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.33.19.12.1498 Keywords Zolpidem drug facilitated crimes gas chromatography–mass spectrometry forensic toxicology Z-Drugs DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Determination of gymnemic acid level in Gymnema inodorum leaves using multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry
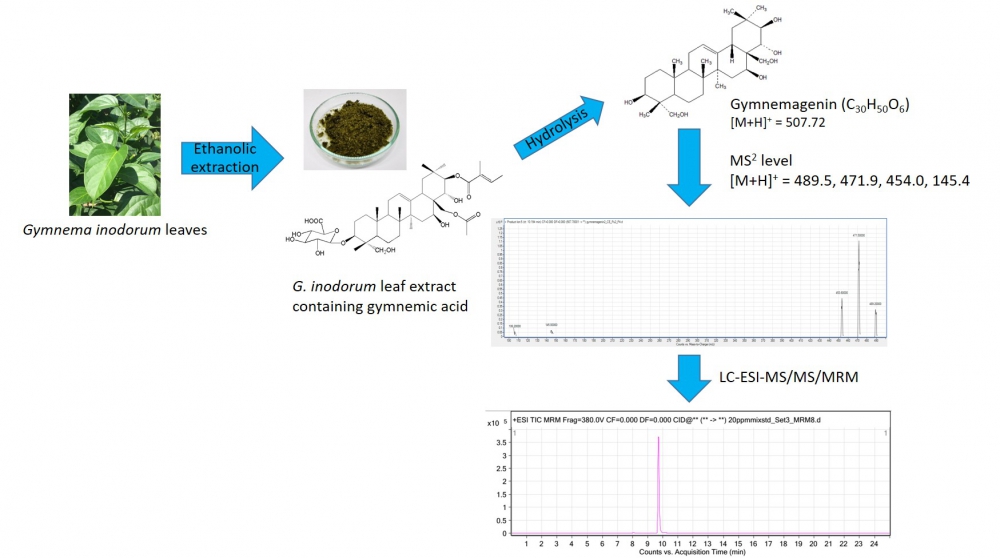
Gymnemic acid (GA) is known as the antidiabetic phytoconstituent in Gymnema species, and is used for quality control and standardization of Gymnema products. In Thailand, a number of nutraceutical products of Gymnema inodorum (Lour.) Decne. (GI) are commercially available and this number is increasing. However, standardized GA content information and safety usage guidelines for GI have not been published. The aim of this study was to investigate the amount of GA constituent in GI leaves using mass spectrometry. Leaf samples were randomly collected in the Northern part of Thailand. Total GA was extracted using an ethanolic solution. The calculation of total GA was based on the detection of aglycone gymnemagenin using the liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with multiple reaction monitoring. The results showed that GI contained total GA content in range of 0.20-1.44 mg per one kilogram dry leaves.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.29.19.10.1438 Keywords Gymnema inodorum gymnemic acid gymnemagenin mass spectrometry electrospray ionization multiple reaction monitoring DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Stability-indicating ultra-fast liquid chromatographic analysis of maprotiline in pharmaceutical formulations
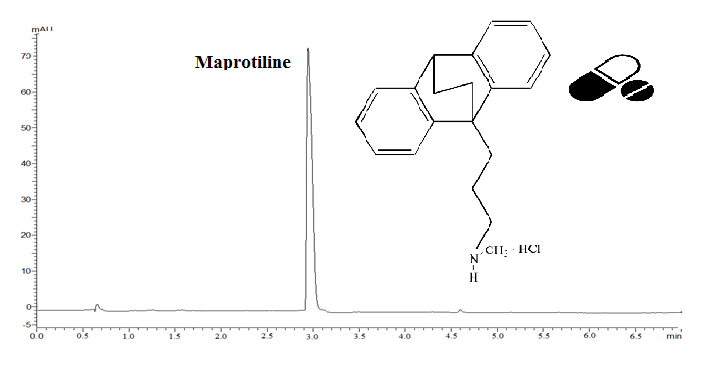
This current study aimed to develop a simple, fast, and reproducible isocratic reverse-phase ultra-fast liquid chromatographic (RP-UFLC) method to detect and quantify maprotiline hydrochloride (MAP) in bulk drug and pharmaceutical formulations. Chromatographic separation was accomplished on a C18 column (100 × 4mm, 3 μm) under isocratic elution with the use of a binary solution of acetonitrile and phosphate buffer at a pH of 7 (75 : 25, v/v) and a flow rate of 0.4 mL per minute at 215 nm. The linearity was excellent in the concentration range of MAP from 0.1 to 1.5 µg/mL with a regression coefficient of 0.9996. The proposed method was validated with the respective ICH guidelines. The drug was subjected to hydrolytic, acidic, basic, thermal, photolytic, and oxidative stress conditions as required by the ICH regulation. The method was found to be suitable for use in routine practice to analyze MAP in the pharmaceutical dosage form.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.27.19.07.1349 Keywords Maprotiline, UFLC method alidation stability Indicating tablets quality control analysis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.