Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2020 Volume: 14 Issue:2 July-December
1) Metrology in chemistry: some questions and answers

This article presents some typical questions from practitioners, trying to implement metrological concepts in their everyday chemical analysis work, and answers to them by the authors, in the context of the authors’ pragmatic view on applying the metrological principles to chemical analysis. Several of the presented questions are staples at training seminars and during on-line courses. The answers to the questions reflect the authors’ opinions and are not always fully in line with the generally accepted positions.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.50.20.10.1838 Keywords Metrology in chemistry reference values repeatability intermediate precision constant improvement DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Certification of sodium benzoate solution reference material by HPLC-UV, LC-MS/MS and UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometry for food and drug analysis
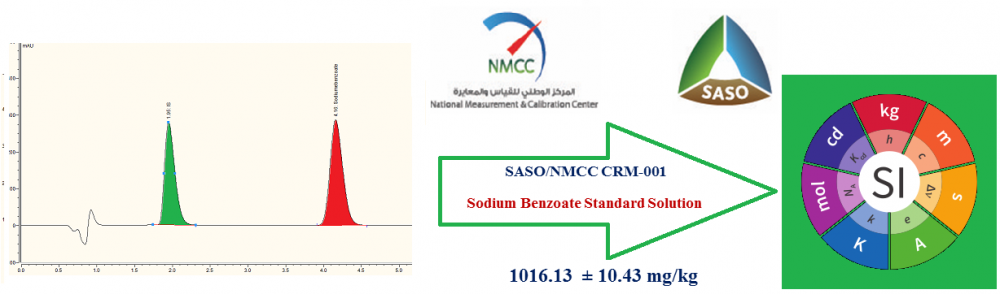
Sodium benzoate is one of the most widely used food perseverates and has to be used in regulated amounts to avoid its harmful health effects. Reviewing the scientific literature for traceability of the analytical measurement results of sodium benzoate in various food and drug applications to the SI units, it has been found that no scientific details of certification of sodium benzoate CRMs used for the calibration of measuring equipment are published. For this reason, the national metrology institute of Saudi Arabia (SASO/NMCC) certifies a sodium benzoate solution reference material. In this work, sodium benzoate was synthesized, purified and a batch solution reference material was prepared as 1014.47 mg/kg then homogenized and bottled. Homogeneity and stability of the candidate RM were assessed and the results obtained showed that the material is sufficiently homogeneous and stable. Characterization of the reference material was carried out by HPLC-UV, LC-MS/MS and UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer as three independent methods. The certified value was derived by combining data from the three methods using the weighted mean approach and was found 1016.13 mg/kg. The certified uncertainty was calculated as weighted uncertainty and was found 10.47 mg/kg (1.03%). Sources of this uncertainty were identified from the characterization, uchar, homogeneity, uhom, and long-term stability, ults, as well as the bias allowance, B.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.48.20.08.1780 Keywords CRM sodium benzoate homogeneity stability characterization certified value DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) UV-spectrophotometry-assisted chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of ambroxol hydrochloride and doxofylline in pharmaceutical formulation
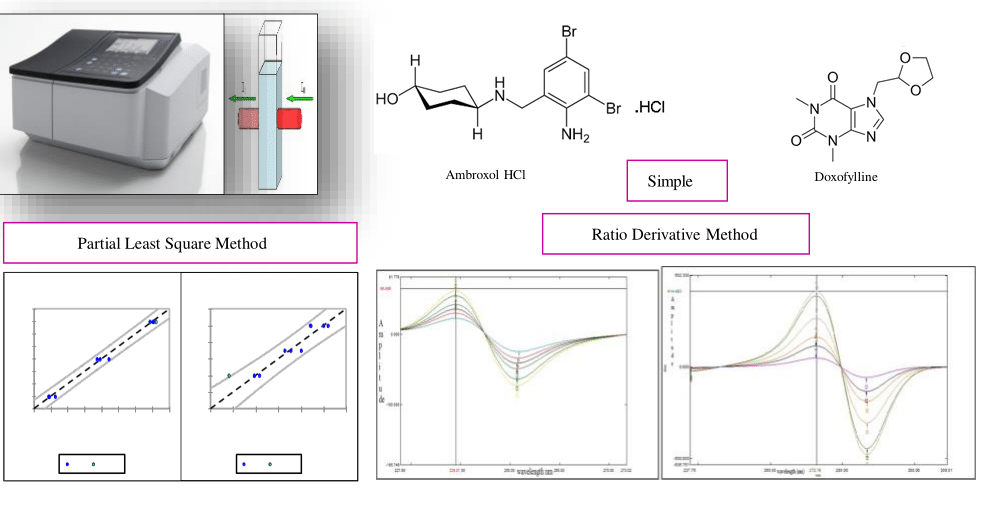
Two methods, ratio spectra derivative method and partial least squares regression (PLS) were developed for the simultaneous estimation of ambroxol hydrochloride and doxofylline in combined dosage form. In the first method, ratio spectra derivative method, analytical signals were measured at the wavelengths corresponding to either maximums or minimums for both drugs in the first derivative spectra of the ratio spectra obtained by dividing the standard spectrum of one of two drugs in water. Partial least squares regression (PLS) was used for data analysis of and the parameters of the chemometry procedures were optimized. In this study, the simultaneous determination of ambroxol hydrochloride and doxofylline in pharmaceuticals by chemometric approaches using UV spectrophotometry has been reported. Spectra of ABH and DOX were recorded at several concentrations within their linear ranges between 2-12 μg/mL and 15-40 μg/mL respectively and applied to pharmaceutical formulation, tablet, with no interference with excipients as indicated by the results of the recovery study. The proposed methods are simple, rapid and can be easily used in the quality control of drugs as alternative analytical tools.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.47.20.05.1638 Keywords Ambroxol hydrochloride doxofylline partial least squares ratio derivative spectrophotometry validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Impact of test conditions on the bacterial bioassay in the presence of TiO2 nanoparticles
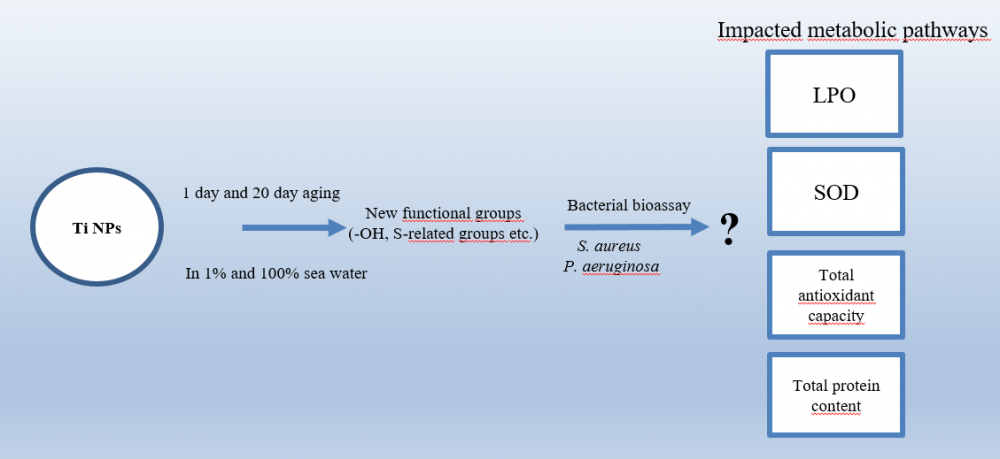
To assess the fate and behavior of engineered nanoparticles in the aquatic environment, it is crucial to conduct appropriate bacterial bioassay procedure. However, test conditions of bacterial bioassay are limitedly investigated; especially in the field of environmental media chemistry or aging of nanoparticles which interfere the procedure. For this purpose, TiO2 nanoparticles were treated with different test conditions by keeping them in 1% and 100% seawater for one day and 20 days. The bacterial bioassay of treated nanoparticles towards gram-negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) bacteria were examined, as well as the mechanism by biochemical responses of bacteria and physicochemical properties of TiO2 nanoparticles. The viability response of tested bacteria reduced remarkably in seawater concentration, while treatment (aging) duration of tested nanoparticles slightly affected the viability response of tested bacteria. Moreover, key events which affected the bioassay response were changed with the treatment duration and media concentration. The results also showed that aging duration and concentration of the media influenced the main physicochemical properties due to the alterations in surface from aging media compared to unaged ones.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.42.20.05.1648 Keywords Nanoparticles bacteria bioassay interference nanometrology surface analysis ecotoxocology DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Stability indicating liquid chromatographic method for the estimation of remogliflozin etabonate
Accurate and precise reverse phase liquid chromatographic method has been developed for the estimation Remogliflozin etabonate in bulk and tablet dosage form. Reverse phase C18 column was used as stationary phase along with mixture of methanol:water (70:30%, v/v) as a mobile phase. Mobile phase flow rate was maintained at 1mL/min and analysis was performed at 229 nm. The method was linear in the concentration range of 1 – 25 μg/mL with correlation coefficient (r2) 0.997. The proposed method was validated with respect to linearity, accuracy, precision and robustness as per ICH Q2 (R1) guideline. To find out the possible degradation pathway, forced degradation studies were performed. The degraded product peaks were well resolved from the pure drug peak with significant difference in their retention time value. The drug was found to be highly susceptible to acid and base hydrolysis. The developed method can be used for analysis of stability samples and routing quality control evaluation of Remogliflozin etabonate in tablet formulation.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.46.20.07.1734 Keywords Forced Degradation validation remogliflozin liquid chromatography DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Oleuropein levels of Anatolian olive leaves and correlated antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory activities
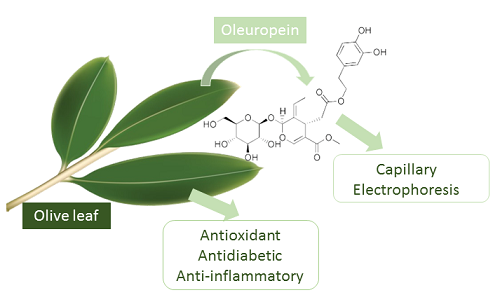
Oleuropein, the major active compound in olive leaf, has been of considerable interest for its many health benefits. This work aims the determination of oleuropein in olive leaves from Turkey by a rapid and simple capillary electrophoretic method, and then to correlate the oleuropein amounts and the bioactivities of olive leaf extracts. The optimal separation medium was composed of 30 mmol/L borate (pH: 9.6), 25 mmol/L2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (2-HP-β-CD), 10% (v/v) methanol. Moreover, olive leaf extracts were examined for antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory activities. The antioxidant activities were determined by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity. The antidiabetic activities were predicted using α-glucosidase inhibitory effects. For the anti-inflammatory activities of the extracts, their reduction power of pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha were measured. Oleuropein concentration ranged between 11.7-106 mg/g dry leaf. Strong correlations were detected between each biological activity and the oleuropein content of olive leaves
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.51.20.04.1632 Keywords Capillary electrophoresis Olive leaf Oleuropein Antioxidant activity Anti-inflammatory activity Antidiabetic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
7) Development of TLC method for simultaneous estimation of novel combination of amlodipine besylate, rosuvastatin calcium, and fimasartan potassium in synthetic mixture
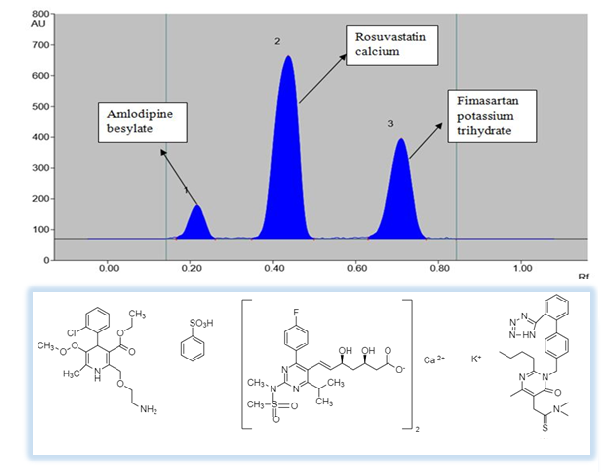
An accurate, sensitive, robust and precise high performance thin layer liquid chromatography method was developed based on ICH Q2 (R1) guidelines for estimation of novel combination of Amlodipine besylate, Rosuvastatin calcium and Fimasartan potassium in bulk and its synthetic mixture. Pre-coated silica gel aluminum plate 60 F254 was selected as the stationary phase and n-hexane, n-butanol, methanol, and Glacial Acetic Acid (5.7:2:2.3:0.1, v/v/v/v) was selected as mobile phase. All three drugs showing appreciable absorbance at the common wavelength of 242 nm were selected for quantification of Amlodipine besylate, Rosuvastatin calcium, and Fimasartan potassium, respectively. The method was validated for linearity, precision, accuracy, and robustness, limit of detection and limit of quantitation as per ICH parameters. The regression coefficients (r2) were found to be 0.9986, 0.9975 and 0.9988 for Amlodipine besylate, Rosuvastatin calcium, and Fimasartan potassium, respectively. The average percentage recovery of Amlodipine besylate, Rosuvastatin calcium and Fimasartan potassium were found to be 99.38-100-60%, 99.75-100.63%, 99.39-100%, respectively. Thin Layer Chromatographic method has prospective qualitative as well as quantitative applications for concurrent estimation of Amlodipine besylate, Rosuvastatin calcium and Fimasartan potassium in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.45.20.07.1744 Keywords HPTLC; amlodipine besylate (AML); rosuvastatin calcium(ROS); fimasartan potassium (FIM); validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Determination of simethicone in different drug formulations by gravimetry and comparison with the FTIR method
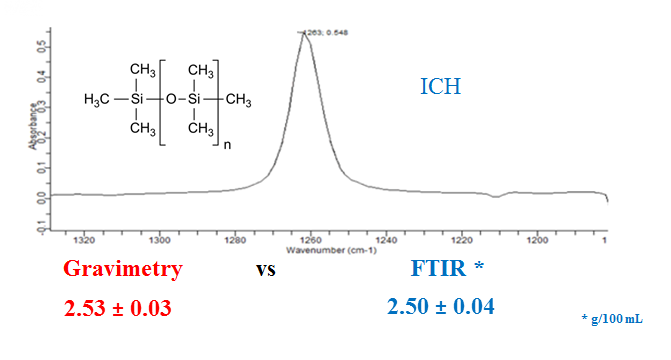
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was mostly used in both pharmacopeia and literature studies to determine the assay of simethicone (SMT) in pharmaceuticals. It should be noted that HPLC is used less frequently. As an alternative to the mentioned methods a new, simple, fast, easy-to-apply and very cheap gravimetric method was developed and validated according to ICH guidance entitled Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology for the quantification analysis of simethicone in different pharmaceutical forms. For the simethicone suspension product provided to alleviate too much gas in the gastrointestinal tract, the simethicone amount was determined both by the validated gravimetric method and by the FTIR method defined in the USP and BP monographs, and the results were within the acceptance criteria. It is emphasized that there is no significant difference between the results of gravimetric and FTIR methods according to the calculated F- and t-test results.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.44.20.07.1701 Keywords Simethicone gravimetry F- and t-test method validation assay DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Achievement of antioxidants from Abelmoschus esculentus L. seeds using ultrasound-assisted extraction optimized by the help of experimental design approach
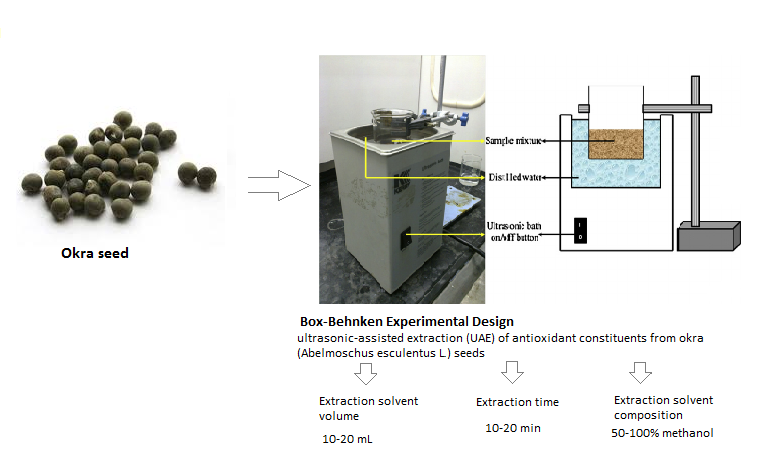
Developments of food supplements and nutraceuticals from different natural origins require the use of some extraction methods. The success of the procedure relies on theefficiency of the extraction methods. Therefore, extraction methods need to be optimized. This work aimed for the determination of optimal conditions of ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) of antioxidant constituents from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) seeds which contain high contents of polysaccharides, polyphenols and flavonoids using response-surface methodology based on Box-Behnken experimental design (BBD). The independent variables of UAE were extraction time (Et, 10-20 min), extraction solvent composition (EC, 50-100% methanol) and extraction solvent volume (EV, 10-20 mL). 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging activity, 2,2'-azinobis- (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activity and N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (DMPD) radical-scavenging activity were dependent variables. Optimal extraction conditions for UAE from okra seed were: 20 mL volume of 70% methanol at 10 min extraction time for DPPH inhibition; 20 mL volume of 50% methanol at 20 min for ABTS inhibition; 15 mL volume of 55% methanol at 12 min for DMPD inhibition. Under these optimum extraction conditions, the effectiveness of UAE of okra seed was successfully revealed. So, this practical extraction technique can be widely used for the achievement of dietary supplements and nutraceuticals.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.49.20.07.1742 Keywords Abelmoschus esculentus L. seed okra ultrasound-assisted extraction box-Behnken Design response surface methodology DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Assessment of the relationship between some physico-chemical properties of soil and soil algae in micro basin scale in Kocaeli
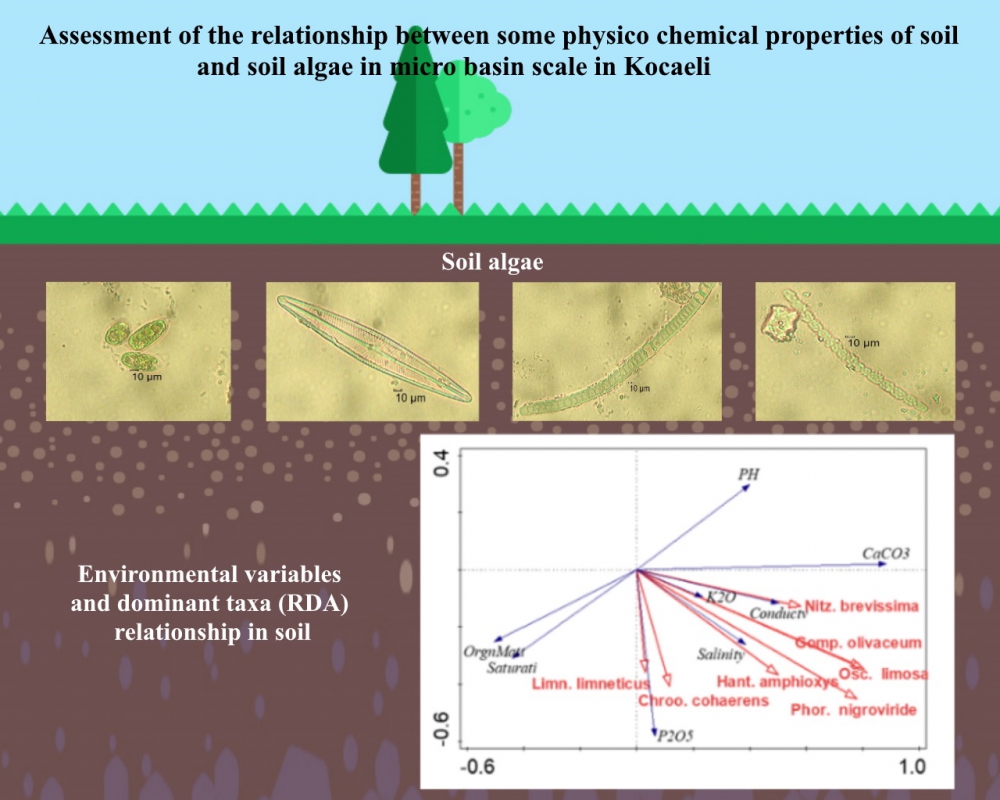
In this study, it was aimed to determine the relationship between soil algae and physico-chemical structure of soil. Algae composition and some soil quality parameters from 12 sampling stations were investigated between March 2019 and May 2019 in Kocaeli. Physico-chemical properties that reflect soil nutrient content and fertility status (pH, conductivity, salinity, CaCO3, organic matter, saturation, P2O5 and K2O) were determined using standard physicochemical techniques. Average in soil parameters were determined as pH: 8.06, conductivity: 5.79 µmhos / cm, salinity: 0.22 ‰, CaCO3: 9.98%, organic matter: 1.70%, saturation: 59.55%, P2O5: 3.16 kg / da, K2O: 93.92 kg / da. Algal flora of Kocaeli province was a total of 30 taxa, 14 taxa of Bacillariophyta, 3 taxa of Chlorophyta, 1 taxa of Charophyta and 12 taxa of Cyanobacteria were identified. The determined as the Chroococcus cohaerens, Limnococcus limneticus, Phormidium nigroviride, Oscillatoria limosa, Gomphonema olivaceum, Hantzschia amphioxys and Nitzschia brevissima most dominant taxa. These taxa have been identified in stations with high industrial activity. Bacillariophyta taxa were found in all months due to their ecological tolerance, while other species belong to spring. In this study, the species diversity were found similar in research stations.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.43.2005.1652 Keywords Soil epipelic algae ecology micro basin physico-chemical parameters DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
11) A year - round monitoring of ambient volatile organic compounds across Dardanelles strait
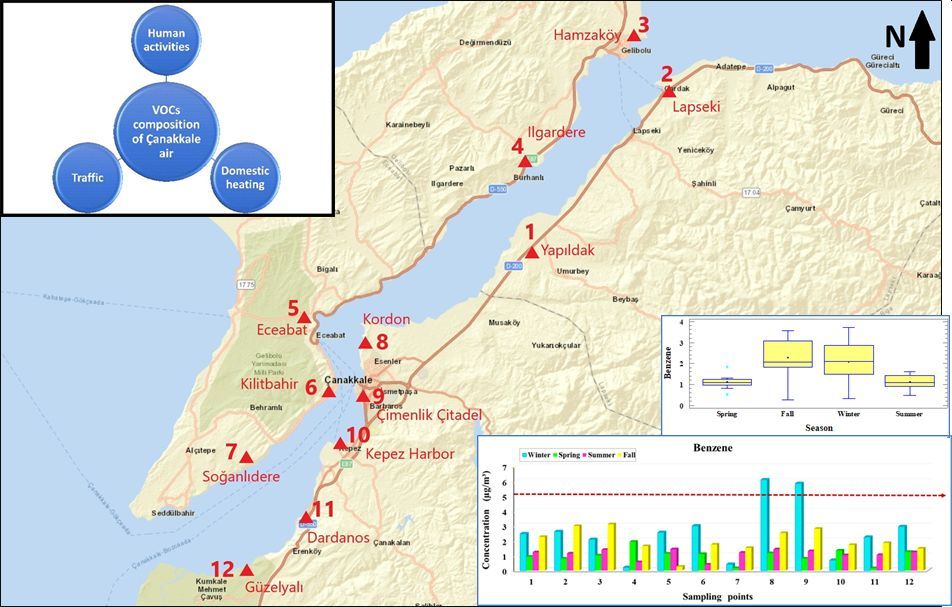
Dardanelles strait has a crucial importance on marine transport, splitting Çanakkale city. Combustion-related anthropogenic sources emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air and they have public concern due to adverse health effects. In this study, composition of ambient VOCs across Dardanelles strait was monitored for 4 seasons over the year of 2018. A total of 12 sampling locations, including 5 locations on the European and 7 locations on the Asian seashores of Dardanelles strait were determined as sampling points. Standard methods were followed during the sampling and analysis of VOCs. VOCs samples were collected on thermal desorber tubes, containing sorbents of Tenax TA and Carbograph 1TD. Active VOC samples were collected by an air sampling pump and passive VOCs samples were exposed to air for 2 weeks. VOCs samples were analyzed by Thermal Desorber followed by Gas Chromatography – Flame Ionization Detector. Target VOCs in this study were paraffins and aromatic hydrocarbons. Limit of quantification was assessed as ≤ 0.1 µg/m3. According to the results of the study, VOCs concentrations varied both spatially and seasonally. The most abundant VOCs in the air were n-pentane, n-hexane, toluene, benzene, and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene throughout the study. Furthermore, the highest VOCs levels mostly occurred at the locations that were close to the traffic sources and/or residential areas.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.51.20.09.1816 Keywords Ambient air pollution Çanakkale Dardanelles strait gas chromatography thermal desorber volatile organic compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.