Organic Communications
Year: 2022 Volume: 15 Issue:2 April-June
1) Discovering the potential of natural remedies in the post COVID-19 complications based on in silico techniques
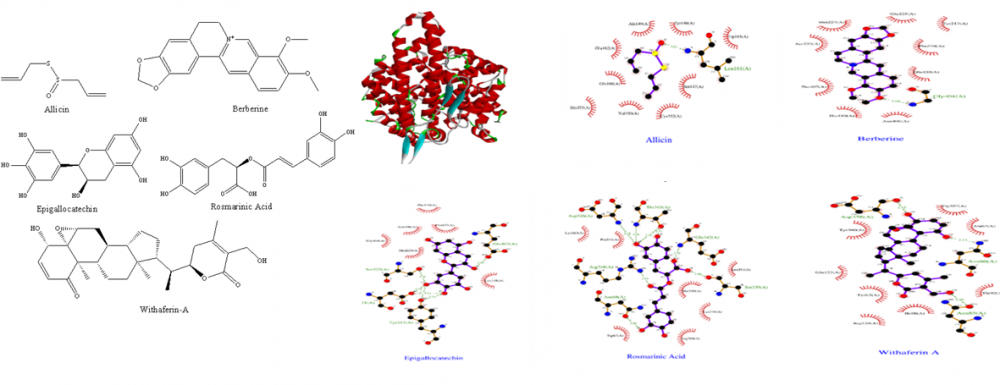
The first incidence of corona virus was reported in China in December of 2019, and the virus quickly spread over the world, eventually being designated a pandemic in March of 2020. It has had a disastrous impact on the global healthcare system. Virus has claimed the lives of 5,298,933 people through December 2021. As a result of the pandemic, there was a boost of research into diagnostic and therapeutic methods to infection. Gradually, the world has discovered new vaccine candidates and medicinal repurposing strategies that have a significant influence on mortality, by which there has been a drop-in death rates over the world since July, 2021. Many patients, particularly those who have been hospitalized due to a viral infection, experience complications beyond discharge that have a significant influence on their lives. Post COVID-19 complications are problems that last longer than 3-4 weeks following a viral infection. There is currently no specific treatment accessible for post COVID-19 problems because whatever medications are available or repurposed are limited to disease prophylaxis and therapeutics. As a result, we're looking for a remedy employing natural substances using the In-Silico technique (molecular docking) and recent research from reputable journals. Allicin, Berberine, Epigallocatechin, Rosmarinic acid and Withaferin-A were docked against ACE (PDB ID: 1O8A), IL-6 (PDB ID: 1ALU), NADPH Oxidase (PDB ID: 2CDU) and TNF- α (PDB ID: 2AZ5) using Autodock.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.128.2202.2356 Keywords Natural remedies post COVID-19 hyper inflammation cytokine storm Autodock DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Synthesis of new heterocycles via methylenebis(2-(2-methoxyphenyl)thiazolidin-4-one) as potential anticancer agents
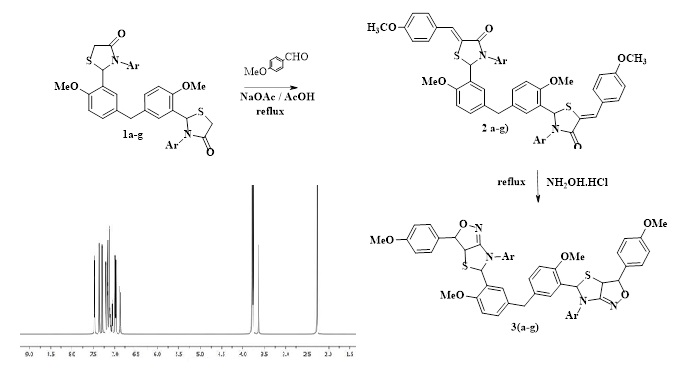
NaOAc catalyzed condensation of bis(2-(2-methoxyphenyl)thiazolidin-4-one) with p-methoxybenzaldehyde in AcOH gave the corresponding chalcones. Cyclization of the synthesized chalcones with NH2OH by refluxing in AcOH afforded the related isoxazoles fused with thiazoles. All the synthesized isoxazoles were evaluated against different tumor cell lines. Almost all compounds showed activity against prostate cancer cell lines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.130.2202.2353 Keywords Bis thiazolo isoxazoles cytotoxic activity Knovenagal condensation cyclisation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Synthesis and reactivity of novel trityl-type protecting groups
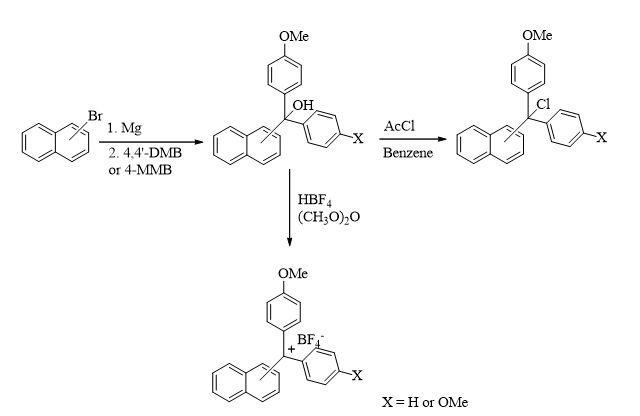
Trityl-type new protecting groups were easily prepared from the reaction of 1-bromonaphthalene or 2-bromonaphthalene and 4-methoxy substituted benzophenones following the Grignard reaction. Aryl-methyl alcohols were transferred to tetrafluoroborate salts using tetrafluoroboric acid. The alcohols also reacted with acetyl chloride to give halides of the protecting groups. The selective protection of amine, sulfur, and hydroxyl groups was obtained by the reaction of the newly synthesized protecting groups (halides and tetrafluoroborate salts). Slightly aqueous acidic conditions were used for deprotection reactions to give alcohols. It can be said that the new protective groups synthesized in this study can be a good alternative to other protecting groups in terms of low solvent use, simple procedures, economic advantages, and environmental protection.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.131.2204.2420 Keywords Protecting groups selective protection kinetic deprotection DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Design, synthesis, in silico and biological evaluation of biotin-pyrazole derivatives as anti-cancer activity

Modified biotin derivatives are effective in killing cancer. Herein we describe the design and synthesis of conjugated biotin-pyrazole derivatives 3a-3h to evaluate as potential anticancer agents. A set of compounds has been prepared by palladium catalysed aminocarbonylation using carbon monoxide in an autoclave. They were well characterized by various spectroscopic techniques and screened for anticancer activity. A cell viability assay (MTT assay) was performed on U251, A549, and HepG2 cell lines and determined their IC50 value. Among target agents, 3a had a considerable activity against human brain cancer cell line U251 (IC50 3.5 µM). 3a could be a promising candidate for the development of new drugs to treat tumours, particularly for brain cancer.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.132.2203.2370 Keywords Anti-proliferative aminocarbonylation biotin cancer pyrazole Swissadme DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Molecular docking, synthesis and biological evaluation (enzyme inhibition, antimicrobial and antioxidant) of methoxy benzoin/benzil/stilbenoid derivatives

In this study, methoxy benzoin compounds (1-10) were synthesized from the corresponding aromatic aldehydes based on a screening of biological activity. Oxidation and reduction of benzoins (1-10) yielded the corresponding benzils (11-20) and stilbenoids (21-29), respectively. The enzyme inhibition, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities of 1-29 were evaluated. 1, 14, 19, and 28 against α-amylase, 15 and 19 against α-glucosidase, 2, 4, 14, 18, 25 and 26 against tyrosinase, 2, 7, and 23 against AChE, and 7, and 13 against BChE showed similar activity to the standard used. Among the methoxy benzoin derivatives, 4 proved to be the most active compound against E.coli, Y.pseudotuberculosis, M. smegmatis, and C.albicans in the range of 41-82 µg/mL MIC values. All benzil derivatives displayed bioactivity against M.smegmatis and C. albicans. Compounds 18 and 11 were found to be most effective against M.smegmatis, and compounds 11 and 17 were found to be the most effective against C.albicans. All stilbenoid type compounds showed selective activity against B.cereus. Compounds 21 and 22 were the most effective stilbenoid compounds against M. smegmatis. Benzoins (1-10) were the most effective antioxidants among all three groups compared to the tested methods, which can be attributed to the free hydroxyl at the benzylic position. As a result, the change of carbon skeleton and substitution at different positions of synthesized organic compounds also caused the variation of biological activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.125.2203.2407 Keywords Methoxy benzoin/benzil/stilbenoid molecular docking enzyme inhibition antimicrobial; antioxidant DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyrans in the presence of WEWFPA and their electrochemical studies
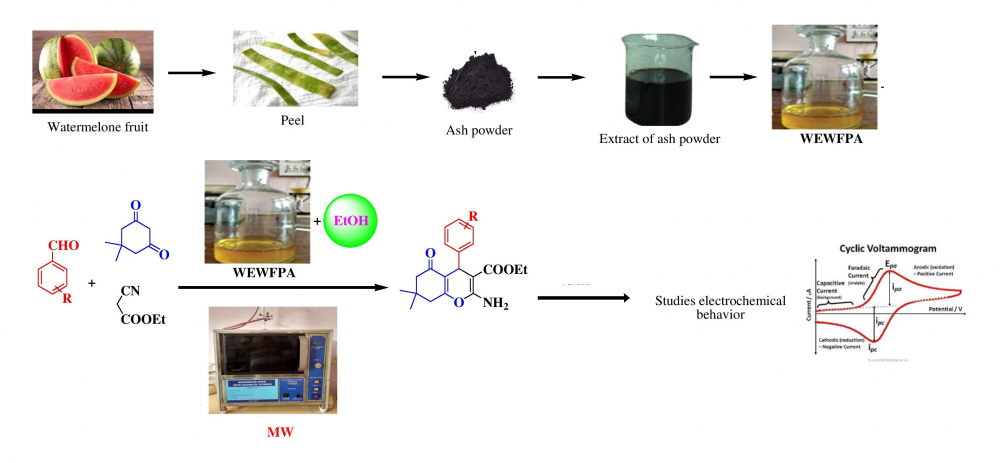
IThe present work described one-pot three-component synthesis of tetrahydro benzo[b]pyran derivatives using Water Extract of Watermelon Fruit Peel Ash (WEWFPA) as a inexpensive grener catalyst. The title compounds were synthesized via the condensation reaction of aromatic aldehyde, dimedone, and ethyl cyanoacetate under microwave irradiation in agro-waste solvent medium and ethanol as a co-solvent. The developed method is simple, rapidity, high yields, pure, low cost, mild reaction condition, evading use of toxic metals and solvent, and the catalyst reusability are the main advantages. The resulting products were isolated by simple workup and recrystallization gave pure compounds. Further, the oxidation and reduction potential of the selected tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran derivatives were studied using cyclic voltammetry.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.124.2111.2263 Keywords Tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyrans ethyl cyanoacetate microwave irradiation agro-waste cyclic voltametry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Nano TiO2.SiO2 catalyzed, microwave assisted synthesis of new α-aminophosphonates as potential anti-diabetic agents: In silico ADMET and molecular docking study

Using microwave irradiation, an effective and greener method for the synthesis of α-aminophosphonates via Kabachinic-Fields reaction in a solvent-free environment is devised. An in silico ADMET and molecular docking analysis was performed on all of the compounds to get insight into their drug likeliness behaviour as well as their capacity to block the enzyme α-amylase (PDB ID: 3IJ8). The compounds with the highest binding affinity and pharmacokinetic properties were developed. The newly created compounds were spectroscopically examined to establish their structure, and all of them were tested for in vitro α-amylase inhibitory action. The compounds 7j (IC50: 99.9±0.3 μg/mL) and 7e (IC50: 102.0±0.7 μg/mL) showed stronger inhibitory efficacy than acarbose, the reference medication. The compounds 7g (IC50, 106.7±0.4 μg/mL), 7d (IC50, 108.4±0.3 μg/mL), 7h (IC50, 115.0±0.4 μg/mL), and 7f (IC50, 119.2±0.4 μg/mL) have shown to inhibit the target enzyme significantly.When compared to the reference drug, Acarbose (IC50, 102.6±0.8 μg/mL), all of the remaining compounds showed modest to good inhibition with IC50 values ranging from 125.6±0.6 to 152.7±0.2 μg/mL. The findings revealed that the vast majority of these drugs have strong α-amylase inhibitory action.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.123.2112.2279 Keywords α-aminophosphonates ADMET molecular docking α-amylase Acarbose DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Chemical descriptors, PASS, molecular docking, molecular dynamics and ADMET predictions of glucopyranoside derivatives as inhibitors to bacteria and fungi growth

The methyl α-D-glucopyranoside and its derivatives have been estimated as the antimicrobial agents against numerous human pathogens, which is constantly amplifying the attention of medicinal chemists to design new bioactive molecules and their structure-activity relationship (SAR) while the computational tools are the most lucid and trustable avenue to perform their theoretical profile building up. Firstly, the predictionof activity spectra for substances (PASS) value has illustrated initially information about the antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, and anticancer potential. It was observed that the PASS predicted pathogens supported their score higher in fungal species than bacteria. However, the “Lipinski five rule” has been monitored for drug-likeness properties. After confirming their biological significance, molecular docking has been completed against both the bacteria and fungi and these docked complexes have been optimized for molecular dynamics through the water system. A molecular docking study against nine bacterial and fungal pathogens revealed promising binding affinity and non-bonding interaction mostly for derivatives (5-8). The chemical descriptors have been obtained using the density functional theory (DFT) and predict their chemical stability and softness in the biological system. The molecular dynamics study was found to be the best stability of all docked complexes. At last, the ADMET properties have been calculated and provide the safe use and non-carcinogenic fact with low toxicity for both aquatic and non-aquatic species. Finally, it is concluded that these selected derivatives (5-8) are highly antifungal potential molecules than antibacterial potential which has been varied with respect to their structural side chain in the D-glucopyranoside sequence.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.122.2203.2397 Keywords Chemical stability pass prediction molecular dynamics DFT calculation ADMET DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Solvent-free synthesis, molecular simulation and cytotoxicity of 1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-diones
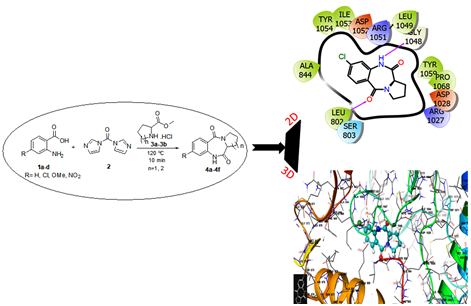
he reaction of anthranilic acid with proline or pipecolinic methyl ester hydrochloride in presence of 1,1’-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) on oil bath heating under solvent-free condition afforded 1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-dione (BZD) derivatives in moderate to good yields. Operational simplicity, absence of hazardous solvents, utility of an inexpensive coupling reagent (CDI) and mild reaction conditions are the significant advantages of this methodology. The cytotoxic activity of six BZDs were evaluated against HCT15 (Human Colon adenocarcinoma), SKMel2 (Human Skin Melanoma) and SKOV3 (Human Ovarian adenocarcinoma) cell lines. Compound 4b with para substituted chlorine atom showed moderate cytotoxicity against HCT15, SKMel2 and SKOV3 with IC50 values 37.04 ± 1.13, 39.45 ± 0.77 and 36.61 ± 0.10 µg/mL respectively. The comprehensive analysis of the interaction between 4a to 4f with receptor VEGFR-2 kinase, the result shows compound 4b have higher molecular docking score with receptor. These result well matched with the result of cytotoxicity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.133.2203.2388 Keywords 1,4-Benzodiazepine-2,5-diones solvent-free synthesis cytotoxicity molecular simulation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Green synthesis and antimicrobial activities of diphenyl substituted aryl phosphoramidates
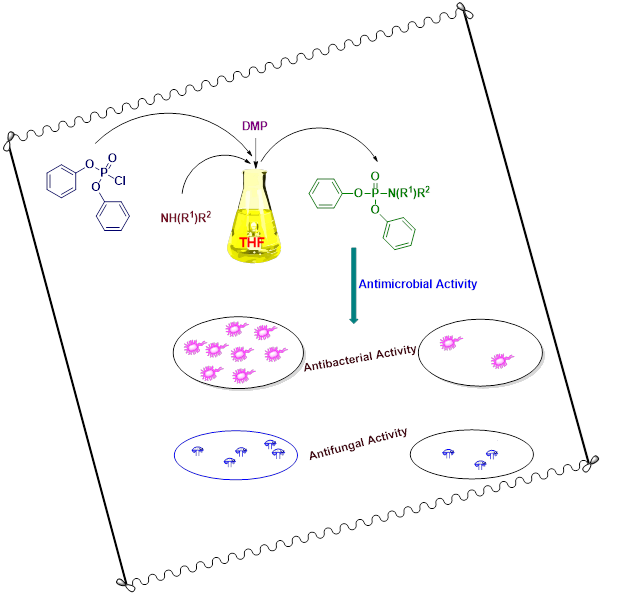
A green, facile and an efficient protocol has been used for the synthesis of new series of diphenyl substituted aryl phosphoramidates by the reaction of diphenyl phosphoryl chloride and various primary/secondary amines using THF as solvent. 1,4-dimethylpiperazine (DMP) was entrenched as a suitable base for catalysing the formation of a P−N linkage. 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, 31P-NMR and mass spectral studies were used to characterize all the title compounds. The newly synthesized phosphoramidates were screened for their antimicrobial activity. Most of the compounds depicted good to moderate antimicrobial activity when compared to the standard.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.134.2204.2410 Keywords Phosphoramidates P−N linkage 1,4-dimethylpiperazine antimicrobial activity synthesis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.