Organic Communications
A scientific open access journal in the field of synthetic organic chemistry and polymersLATEST ARTICLES
Theoretical investigation of interactions between HIV-1 Tat and p53 proteins

HIV-1 Tat (transactivator of transcription) protein is the main arsenal of HIV, playing numerous roles during viral infection. This protein is intrinsically disordered, lacking well-defined secondary structures. Such structural plasticity allows HIV-1 Tat to interact with a wide range of proteins and biological molecules, ultimately leading to immune system collapse or severe tissue damage. Proteomic studies have previously revealed that p53, often referred to as the “guardian of the genome,” interacts with Tat through its tetramerization domain. Since p53 plays a pivotal role in determining cell fate, its interaction with Tat is of broad interest in the pathogenesis of HIV infection. Therefore, we investigated the complex formation between Tat and the tetramerization domain of p53 using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. We believe that the results presented in this manuscript provide valuable insights for the development of novel therapeutic agents targeting the p53/Tat interaction.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.200.25.08.3618 Keywords HIV-1/2 Tat protein p53 molecular docking MD simulations protein-protein interaction DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Synthesis and molecular docking studies of dispiropyrrolidine oxindole derivatives as a therapeutics agent against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
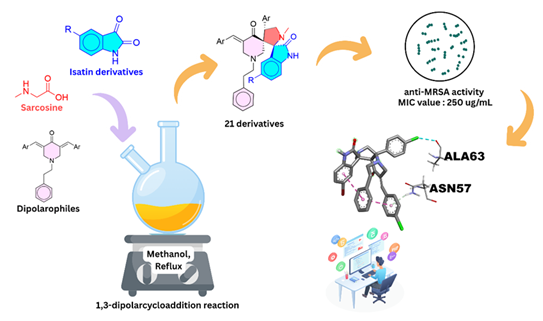
A series of new dispiropyrrolidine oxindole derivatives (8-10) were successfully synthesised with yield of 57 to 95% via one-pot 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction of azomethine ylides and characterised by various spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, FT-IR, and HRMS. The compounds were evaluated for their activity against methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Among the compounds, compound 9f and 9g exhibit moderate activity against MRSA with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 250 µg/mL and 325 µg/mL, respectively. The binding energies and interactions of both compounds with S. aureus adhesion proteins such as sdrE, CIfA and FnBPA were further studied through molecular docking studies. Compound 9f (-8.5 ± 0.00 kcal/mol) showed a strong binding affinity than compound 9g (-7.5 ± 0.20 kcal/mol) particularly towards FnBPA adhesion protein. The molecular docking results revealed that the interactions between the compounds 9f and 9g with target proteins correlate with the observed MRSA inhibitory activity, highlighting their potential as promising lead candidates for anti-MRSA drug development.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.204.2511.3729 Keywords Dispiropyrrolidine oxindole anti-bacterial activity methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus molecular docking in silico study DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.A catalyst-free and eco-friendly approach to synthesis of 1,8-naphthyridines via natural deep eutectic solvents
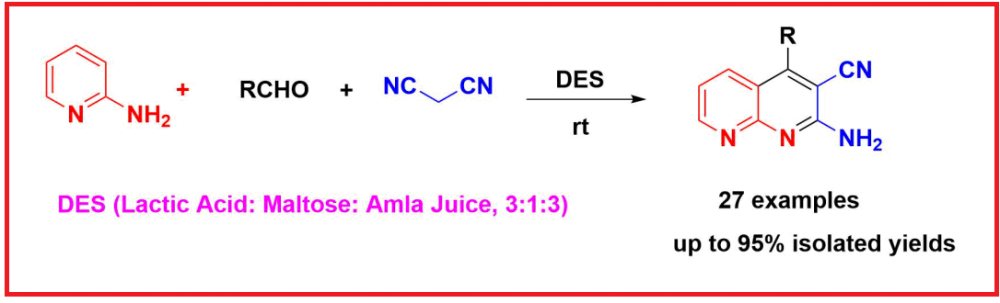
The use of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) not only promotes the reaction but also aligns with green chemistry principles due to their biodegradability, low toxicity, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability. A green and efficient one-pot, three-component synthesis of 2-amino-4-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carbonitrile derivatives has been developed using lactic acid-based DESs. The reaction, involving 2-aminopyridine, aromatic aldehydes, and malononitrile, proceeds under mild conditions in a DES composed of lactic Acid, maltose, and amla (Indian gooseberry) Juice (3:1:3 molar ratio) without the need for any additional catalysts or additives. Among various DESs evaluated, this ternary mixture exhibited the highest catalytic activity, delivering products in good to excellent yields. The methodology offers notable advantages, including high atom economy, reduced reaction time, and elimination of hazardous solvents. The synthesized naphthyridine derivatives were structurally confirmed by FTIR, NMR, and HRMS analyses. This study highlights the potential of natural-product-based DESs as sustainable media for multicomponent heterocycle synthesis, with significant implications for the field of organic synthesis and green chemistry.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.199.2507.3592 Keywords Multicomponent reactions deep eutectic solvents (DESs) 1,8-naphthyridine green synthesis 2-amino pyridine lactic acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Synthesis and antidiabetic assessment of substituted 2-benzylidene-1-indanone derivatives using in vitro and in silico techniques

In search for novel antidiabetic agents, a new series of substituted 2-benzylidene-1-indanone derivatives were synthesized via crossed Adol condensation reaction. The structures of the synthesized compounds were determined using various spectroscopic techniques, including HREIMS, FTIR, and NMR. The enzyme inhibitory activities of the target analogues were assessed using in vitro assays. The tested compounds demonstrated inhibitory potential against α-amylase, as indicated by their IC50 values ranging from 17.7 to 28.2 µM as compared to standard drug acarbose with IC50 value of 30.2 ± 1.9 µM. Furthermore, molecular docking study was conducted to elucidate the binding interactions of the compounds within the α-amylase enzyme binding pocket (PDB ID 2QV4). The results of molecular docking studies indicated that compounds 3m, 3c, 3d has the lowest binding energy (-9.8, -9.3 and -9.4, respectively). The structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis revealed that alteration in the inhibitory activities of α-amylase enzymes was provided by distinct types of substituents attached to either ortho- or para positions of the phenyl group. The combined SAR and docking results highlight the importance of para-position substitution on ring A for optimal activity, particularly when introducing moderately electron-withdrawing groups such as chlorine, fluorine, and bromine. Thus, in the pursuit of developing newer antidiabetic agents, the in silico ADME prediction was carried out with promising physicochemical, drug likeness and ADME properties which indicated that some compounds were considered drug-like as they do not violate any of the rule-based filters of Lipinski.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.202.2508.3626 Keywords 2-benzylidene-1-indanone derivatives Aldol condensation reaction α-amylase inhibitor; molecular docking ADME properties DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.

