JOURNAL 3735
Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2025 Issue: 2 July-December
p.209 - 222
Viewed 200 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
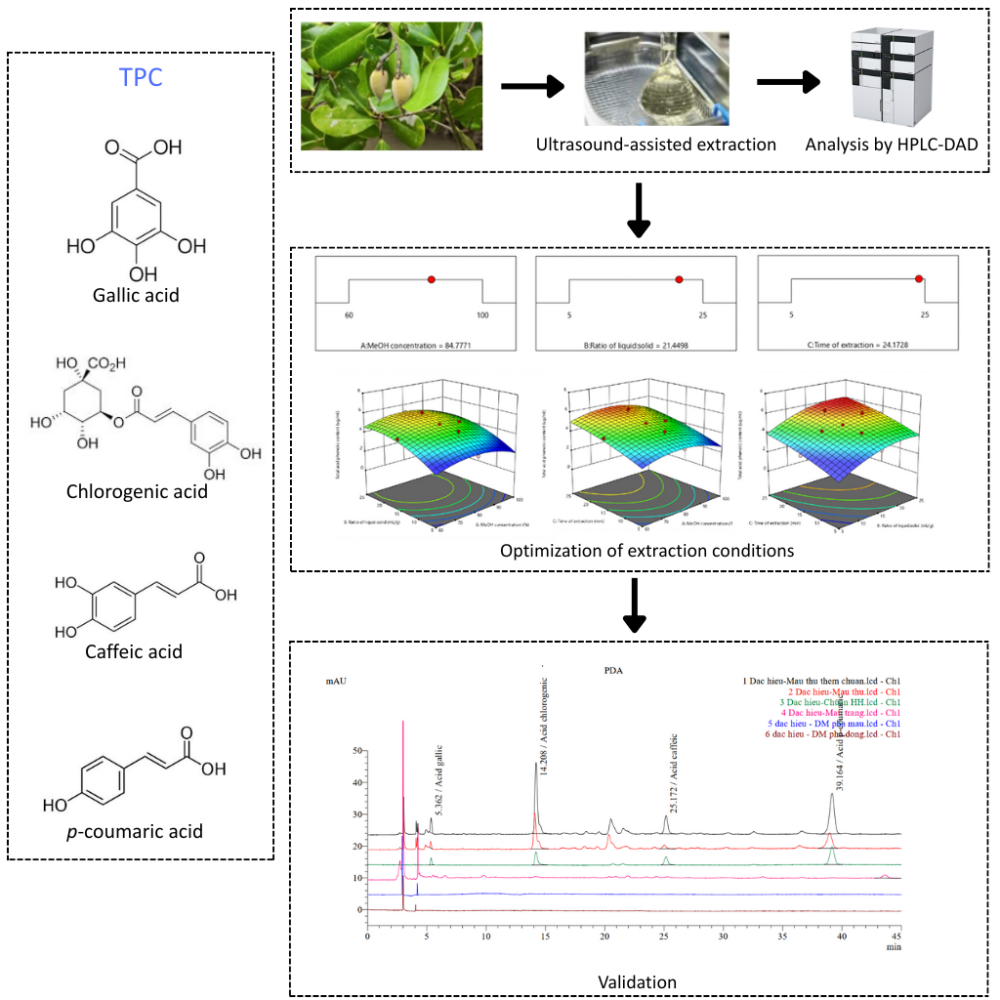
ABSTRACT
Avicennia officinalis L. is a valuable mangrove species rich in phenolic compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. Despite this, research on extracting these compounds from its fruit is limited. This study focused on developing and optimizing an ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) method to quantify four specific phenolic acids (gallic, chlorogenic, caffeic, and p-coumaric acids) from A. officinalis fruit collected in Ca Mau, Vietnam. The optimized UAE conditions by response surface methodology (RSM) involved methanol concentration of 84.78%, the liquid-to-solid ratio at 21.45 mL/g and extraction time at 24.17 minutes, and three extraction cycles. The method was validated according to AOAC guidelines, demonstrating excellent linearity, precision (RSD <11%), and accuracy (recovery rates 82.68-104.51%). This research marks the first successful quantification of these phenolic acids in A. officinalis fruit in eight location of Ca Mau province, Vietnam, offering a highly efficient (>99%) and repeatable (RSD <6%) method for future studies.
KEYWORDS- Avicennia officinalis L. fruit
- phenolic acid
- ultrasound-assisted extraction
- response surface methodology
- HPLC-DAD