Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2020 Volume: 14 Issue:1 January-June
1) Rapid and easy method for simultaneous measurement of widespread 27 compounds in natural products and foods
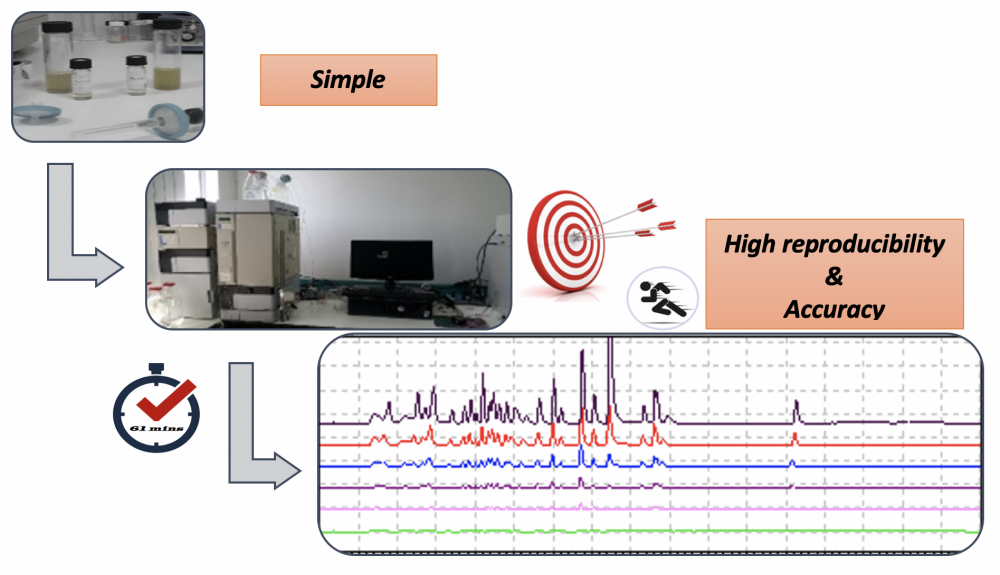
Phenolic compounds are dietary bioactive compounds that are available in foods and beverages. They are produced by the plant and/or by the mushrooms, naturally. Some of the natural phenolic compounds were also used in dietary supplements in the pharmaceutical or food industries. For simultaneous analyses of phenolic compounds in one injection, a rapid and sensitive method was developed for twenty-seven natural compounds using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) coupled with diode array detector (DAD). The linear gradient elution systems of 0.1% acetic acid-methanol were used, and the analyzing time was 61 minutes. The method was validated with linearity, relative error, reproducibility, LOD values. Relative standard deviation between (n = 7) within and between days for reproducibility is less than 10%, and relative error (or recovery) is less than 5%. The method exhibited excellent linearity (R2>0.999), good precision (RSD<6.1%), recovery (97.6–104.1%) and limits of detection (0.23–28.81 µg/m1) and quantification (1.62– 87.29 µg/m1). The detection of compounds was performed at 220 nm, 280 nm, and 330 nm. The developed method for the rapid determination of phenolic compounds using RP-HPLC can be used to identify the availability of these phenolic compounds in natural and commercial products.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.38.20.03.1589 Keywords RP-HPLC phenolic compounds food dietary supplements natural products DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Importance of sample pretreatment step on the bacterial toxicity bioassay of ZnO nanoparticles
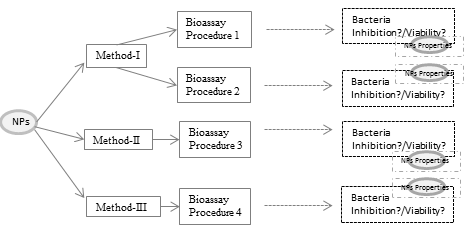
(Eco)toxicological assessment of engineered nanoparticles has largely restricted to laboratory conditions, and contribution to the environmental matrix mostly ignored. Thus, the lack of reflection of the environmental matrix makes it harder to evaluate the ecotoxicity of nanoparticles and its mechanism. Therefore, sample pretreatment has a vital role for appropriate (eco)toxicological assessment and reflection of the environmental matrix. The present study aims to investigate the effect of different sample pretreatment strategies on the (eco)toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles and its mechanism. For this purpose, three sample pretreatments and related bacterial bioassay procedure was examined. Moreover, the impact of the sample pretreatment on the toxicity mechanism was investigated using the physicochemical parameters of ZnO nanoparticles and antioxidant responses of bacteria. The results showed that the sample pretreatment affected the physicochemical properties of ZnO nanoparticles, inhibition level and inhibition pathway.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.37.20.03.1583 Keywords Sample preparation nanoparticles bacterial bioassay matrix effect seawater DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Determination of secondary metabolites of Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum and O. vulgare subsp. vulgare by LC-MS/MS
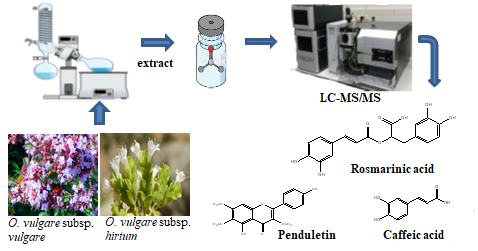
Secondary metabolites of solvent extracts of Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum and O. vulgare subsp. vulgare were determined using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Curcumin was used as an internal standard. Rosmarinic acid was determined as the main compound of studied extracts together with other phenolic acid derivatives. In LC-MS/MS analyses, relative standard deviations (RSD %) ranged between 0.11-9.47. The correlation values were found to be greater than 0.97 for each investigated analyte.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.33.20.04.1610 Keywords Origanum phenolic compounds LC-MS/MS method validation uncertainty assessment rosmarinic acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Liquid chromatographic analysis for the determination of deferasirox in pharmaceutical formulations and spiked plasma samples using dansyl chloride reagent
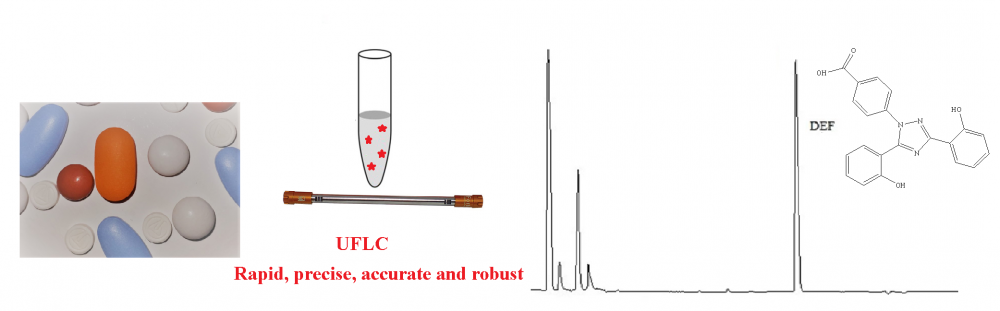
In the current study, a new sensitive and precise method based on HPLC and derivatization with dansyl chloride was developed for quantification of deferasirox (DEF) in pharmaceutical dosage forms and spiked plasma samples. Separation procedure in the chromatographic system was performed using a mobile phase consisting of the mixture of methanol and acetic acid solution (0.5 M, pH adjusted to 7.0 with NaOH) with a ratio of 70:30 v/v at flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute under isocratic elution on a C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm I.D.). The excitation wavelength was selected as 340 nm and emission wavelength was selected as 480 nm for the measurement of the analyte signal. The retention time for DEF is approximately 3.5 min. ICH Guidelines were taken into account for method validation. For the deferasirox concentration range of 20–2000 ng/mL, the proposed analytical method exhibited a linear relationship between the drug concentration and measured fluorescence with a correlation coefficient of 0.9994.The currently developed method can be implemented efficiently for the quantification of DEF in pharmaceutical dosage forms and spiked plasma samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.35.20.01.1518 Keywords Deferasirox HPLC method validation pharmaceutical formulation spiked plasma DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Primary level electrolytic conductivity measurements at National Metrology Institute of Turkey (TUBITAK UME)

TUBITAK UME (National Metrology Institute of Turkey) Electrochemistry Laboratory established the primary level electrolytic conductivity measurement system in 2018. The objective of this work is to prove the accuracy of the established system with an acceptable uncertainty and to disseminate the traceability for electrolytic conductivity measurements. While the accuracy of the system was tested with the certified conductivity solutions, the accuracy of the software developed at TUBITAK UME was also tested. The cell constant was determined as 0.57986 cm-1 at 25 °C by using certified conductivity solutions. The accuracy of the system was evaluated using the measurement of certified conductivity solutions and it was found that there was no significant difference between the results at 95% confidence level. Finally, “Evaluation of measurement data - Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement” and “EA-4/02 M: 2013 Evaluation of the Uncertainty of Measurement in Calibration” guides were used to form the uncertainty budget for primary level electrolytic conductivity measurements.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.34.20.01.1524 Keywords Electrolytic conductivity jones cell CRM traceability DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Development of a densitometric HPTLC method for determination of 5-HMF in fruit-based baby foods in Turkey
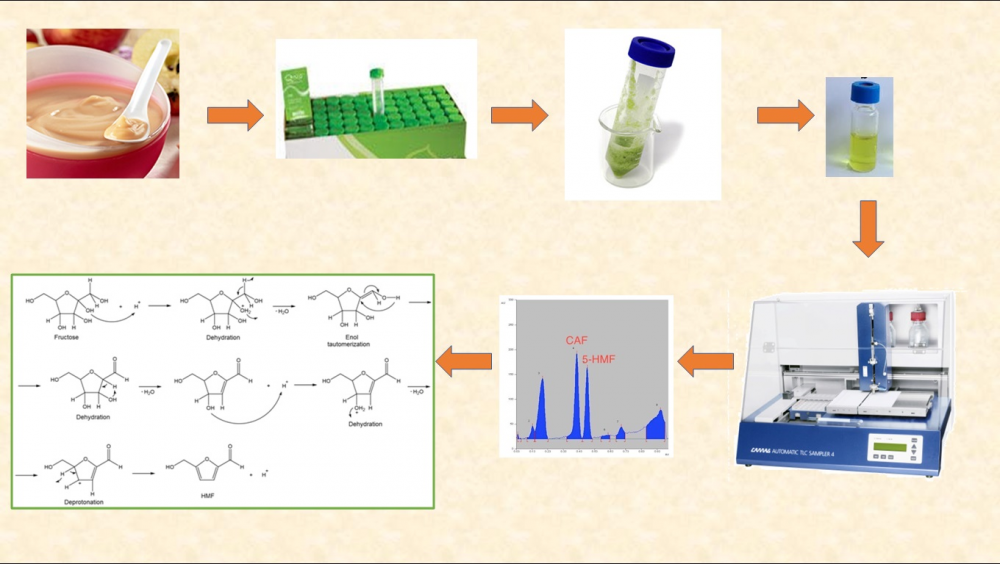
This study reports the determination of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF) by HPTLC in fruit-basedbaby food products and compares the other techniques. The performance of QuEChERS method was evaluated for the measurement of 5-HMF. The mean recovery and RSD% at the two-fortification level of 25 and 250 ng/spot were 83.65% and 2.0%, and 96.02% and 3.0%, respectively. LOD and LOQ levels for 5-HMF were found 1.54 ng/spot and 4.67 ng/spot in fruit-based baby foods, respectively. Fifty eight commercial products on the Istanbul market were evaluated by developed and validated HPTLC method and, 5-HMF were determined in 48 (82.76%) in the range of 13.12-28.90 mg/kg. Although the concentration of 82.76% of the 5-HMF detected products was found to be below the legal limit, the results revealed that a new regulation should be made in fruit-based food considering the baby exposure limit. The analytical performance of this method verifies its potential applicability with particularly low cost and simple sample pretreatment.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.39.20.05.1653 Keywords Baby food 5-hydroxymethylfurfural HPTLC method validation QuEChERS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Determination of doxylamine from a tea sample: A claim of drug facilitated crime
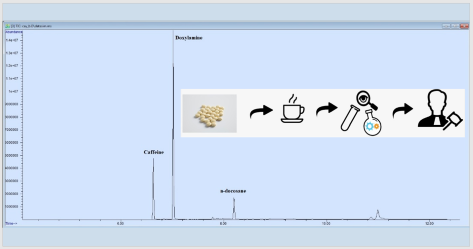
Doxylamine, which is an active drug ingredient used for insomnia, is an antihistaminic with sedative effect and can be received without a prescription. Although doxylamine succinate intoxication is encountered quite frequently, there is no data that shows the drug is used for intentional injury. This study was conducted to unravel a suspected case of intentional poisoning facilitated with the use of doxylamine, using a fast, accurate and reliable method. The complainant realized that she had fallen asleep after drinking the tea given to her by her colleague, who has been treating her badly for some time. After experiencing a second similar situation, she asked for toxicological analysis. The analysis revealed the presence of 69.3μg/mL (13.9mg/cup) of doxylamine in the sample, and it was concluded that this amount was sufficient to produce the symptoms the complainant mentioned. However, this study reveals that the complainant’s claim is quite difficult to prove, and toxicological analysis alone are not enough to prove her claim. Considering the possibility of crimes of intentional injury, aspersion and torment on a legal basis, this study thought to be remarkable as it presents a case of suspected crime facilitated with the use of an active drug ingredient.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.40.20.04.1634 Keywords Analytical chemistry GC-MS doxylamine drug-facilitated crime forensic toxicology intentional injury DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of Donepezil HCl in pharmaceutical formulations
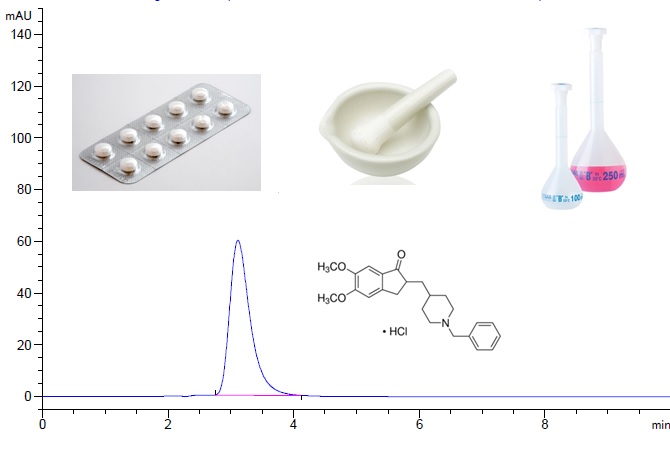
Donepezil HCl is a hydrochloride salt of a piperidine derivative acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and, it uses in treatment demantia of Alzheimer’s disease. In this study, a sensitive and rapid HPLC-UV method was developed and validated for determination of Donepezil HCl in API and tablet dosage forms. Chromatographic separation was performed using a Ace 5 C18 (5 μm, 250 x 4.6 mm) by using isocratic phosphate buffer at pH:2.0 and acetonitrile (55:45, v/v) mobile phase was used at the rate of 1.2 mL/min. The column temperature was set at 30 °C and the UV detection was recorded at 268 nm. The method was validated with respect to specificity, precision, accuracy, linearity, repeatability and reproducibility parameters in a concentration range of 25-125 µg/mL. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were determined as 1.40 and4.20 µg/mL, respectively. The uncertainty budget of the measurement for Donepezil HCl was estiamted as 5.80 % at 95% confidence level (k = 2).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.41.20.04.1622 Keywords Donepezil HCl HPLC-UV pharmaceuticals method validation measurement uncertainty DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Determination of dihydrocapsaicin adulteration in dietary supplements using LC-MS/MS
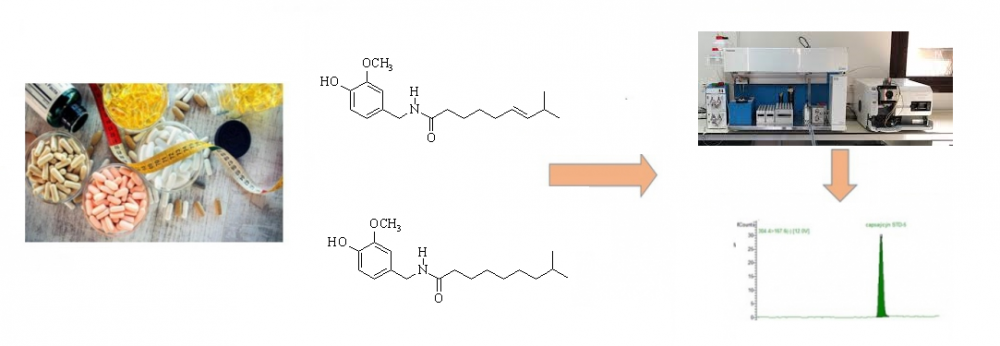
Adulterations of dietary supplements are serious threats to public health in all around of world. Nowadays, in order to obtain the intended effect from natural remedies, the adulteration of natural products via artificial or harmful chemicals are increasing. A rapid LC-MS/MS method for determination of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin in dietary supplements via Fortis C18 (150 x 3 mm; 3 µm) column at 25 °C was developed and validated in a mixture of mobile phase A (1 % formic acid solution and 0.1 % ammonium formate in water) and B (1 % formic acid solution and 0.1 % ammonium formate in methanol) with gradient program at a flow rate of 0.35 mL/min. The recoveries of developed methods weytre obtained in the range of % 95.4-106.3 for capsaicin and % 96.3-108.9 for dihydrocapsaicin. This study shows that synthetic compound dihydrocapsaicin is widely use in dietary supplements products for adulteration to increase the effects of product without any declaration.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.36.20.01.1532 Keywords Capsaicin dihydrocapsaicin LC-MS/MS adulteration lose weight dietary supplements DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.