Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2025 Volume: 19 Issue:2 July-December
1) Optimisation of temperature for accurate water content determination in plant-derived materials using vaporisation–coulometric Karl Fischer titration
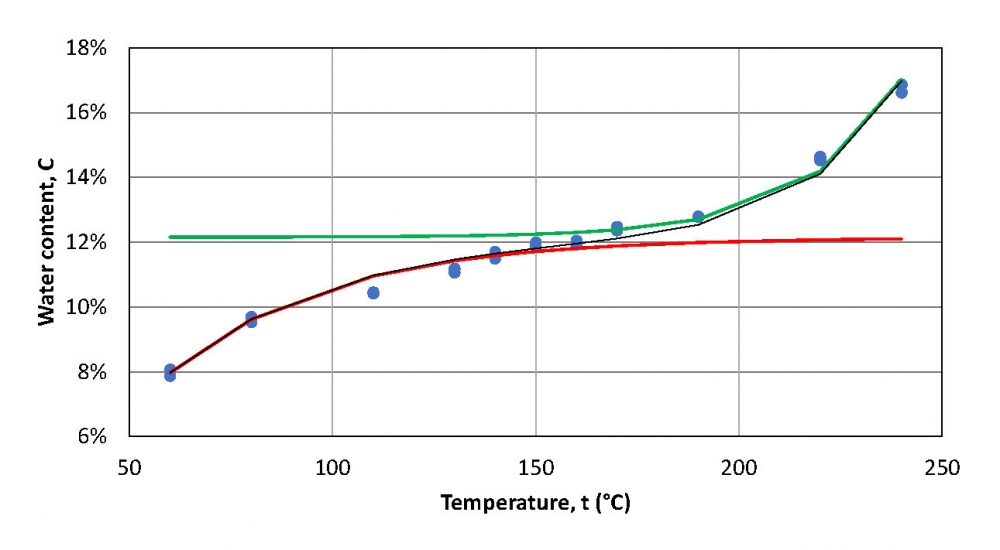
Accurate determination of the water content in plant-derived materials is both crucial and challenging. Most plant-derived materials are not soluble, making conventional coulometric Karl Fischer (KF) titration methods unsuitable for the purpose. The vaporisation–coulometric KF titration (vap-C-KFT) technique offers a more effective alternative for such samples. However, identifying the optimal heating temperature for vaporisation is challenging because at a certain temperature, some components of the material can decompose, while the water released from other components can still be insufficient. In this study, we propose an approach to determine the optimal oven temperature at which insufficient release of water is compensated by the water released due to decomposition, using the vap-C-KFT method. The experimental water content values, depending on KF oven temperature, are approximated by a so-called “sigmoid curve” model that is defined by 5 parameters. This enables to find the optimal analysis temperatures and water content values for different plant-derived materials. The model worked well for barley seeds, wheat seeds, and different types of lignin. However, for crushed rapeseeds the experimental data did not follow the same model, and for non-crushed rapeseeds the water content uncertainty was significantly higher than for other materials.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.126.2511.3730 Keywords Water content vaporisation–coulometric Karl Fischer titration wheat barley lignin DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) UncertCalc: a web-based tool for measurement uncertainty calculation
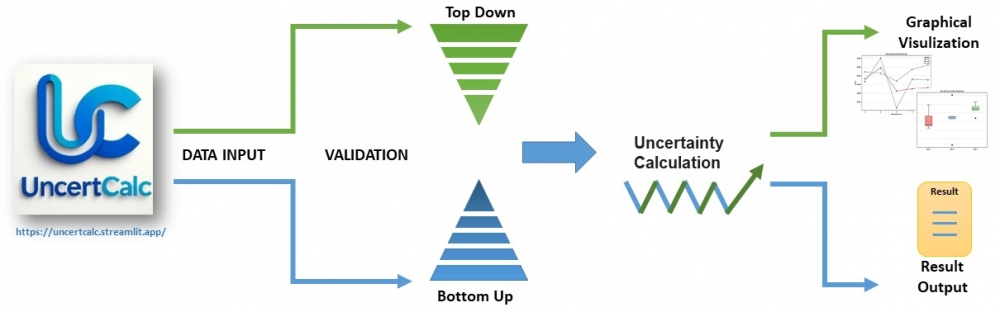
This study presents UncertCalc, a web-based tool developed to facilitate measurement uncertainty calculations in laboratory settings. The application is supporting both Top-Down and Bottom-Up approaches. The Top-Down module performs ANOVA based estimation of within day repeatability and between day intermediate precision using multi day repeated measurements. The Bottom-Up module calculates the combined measurement uncertainty by incorporating user-defined uncertainty components. Both modules have graphical visualization of uncertainty contributions. The computational accuracy of UncertCalc was independently validated using Microsoft Excel and R, using randomly generated representative data for both Top-Down and Bottom-Up approaches. Results from these comparisons proved to be in perfect agreement across the different platforms, confirming that UncertCalc offers statistically reliable and fully traceable calculations, consistent with established analytical tools.
UncertCalc has been developed to provide a practical solution that enables a sound, accessible process of biochemical measurement methods according to ISO/IEC 17025.
3) Contrasting alkaloid and polyphenol-rich plants: LC-MS/MS based characterization and bioactivity assessment of Papaver somniferum and Celtis australis

This study involves a comparative evaluation of Papaver somniferum L. and Celtis australis L., two phytochemically different medicinal plants from Türkiye, by focusing on their phenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and enzyme inhibition properties. Ethanolic and aqueous extracts of both plants were analyzed by LC–MS/MS, and the results revealed different secondary metabolites. P. somniferum was determined to be rich in terms of flavonoids, including luteolin, apigenin, and naringenin. Meanwhile, C. australis was found to be rich in terms of phenolic acids, including rosmarinic, syringic, vanillic, and chlorogenic acids. Antioxidant evaluation through ABTS radical scavenging, CUPRAC, FRAP, and Fe³⁺-reducing assays showed that the aqueous extract of C. australis (WECA) exhibited significant radical scavenging capacity; on the other hand, the ethanolic extract of P. somniferum (EEPS) possessed stronger reducing power, which was evaluated as consistent with their respective phenolic compositions determined by LC-MS/MS analysis. Enzyme inhibition assays of both extracts demonstrated potent α-amylase inhibition by EEPS with an IC50: 5.02±0.73 μg/mL, suggesting potential antidiabetic effects, and remarkable human carbonic anhydrase II isoenzyme (hCA II) inhibition by P. somniferum water extract with IC50: 3.11±1.98 μg/mL, outperforming the standard inhibitor. Both plants also showed moderate anticholinergic effect, indicating a possible neuroprotective property. In conclusion, while the flavonoid-rich P. somniferum showed excellent reducing ability and potent inhibition of key metabolic enzymes, including α-amylase, acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and hCA II, the phenolic acid–dominant C. australis exhibited a stronger radical scavenging efficiency, reflecting distinct yet complementary antioxidant and therapeutic potentials that may be harnessed for functional or pharmacological applications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.125.2510.3703 Keywords Papaver somniferum Celtis australis LC-MS/MS antioxidant activity enzyme inhibition DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Optimization of luteolin derivative extraction conditions of Avicennia officinalis L. leaf extract

Avicennia officinalis L. is a medium-sized evergreen mangrove shrub belonging to the Acanthaceae family. The leaves of this plant are widely used in traditional medicine across Asia. Recently, demand for this herb and its extracts has increased, particularly for herbal product development. This study aimed to optimize the ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of A. officinalis leaves and quantify luteolin-7-O-glucuronide (L7Gn) and luteolin-7-O-rutinoside (L7R) using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The optimal UAE conditions were a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1, extraction with 50% ethanol for 20.4 minutes, as determined by the Box–Behnken design. Under these conditions, the extract contained 124.65 mg of L7Gn and 67.22 mg of L7R per 100 g of dried leaf powder. These optimized parameters were used to validate the quantification method. Bioactive compounds from the A. officinalis leaf extract were identified by ultra-fast liquid chromatography coupled with a diode array detector. The method was then applied to quantify L7Gn and L7R in leaf samples collected from Ngoc Hien District, Ca Mau Province, Vietnam. The ethanol extracts contained L7Gn levels ranging from 2.50 to 2.91 mg/g and L7R levels ranging from 1.58 to 1.73 mg/g. This is the first study to quantify L7Gn and L7R in A. officinalis leaves. The findings provide initial scientific evidence and establish a foundation for further research on this species.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.124.2509.339 Keywords Avicennia officinalis L. luteolin-7-O-glucuronide luteolin-7-O-rutinoside optimization ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Determination of sulfur in topical formulations by GC-MS

A simple, sensitive, and validated gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) method was developed for the quantitative determination of sulfur in topical formulations. The separation was achieved on a TR-5MS capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm film thickness) using helium as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The oven temperature was maintained at 190 °C, and the total analysis time was 13 min. Detection was performed in selective ion monitoring (SIM) mode at m/z 64. The injection volume was 1 µL. The method exhibited excellent linearity within the concentration range of 0.75–15.00 µg/mL. The lower limit of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were found to be 0.25 µg/mL and 0.75 µg/mL, respectively. Mean recovery values ranged from 98% to 102%, with intra- and inter-day precisions (RSD) not exceeding 2%. Method validation was conducted in accordance with the ICH Q2(R1) guidelines. Furthermore, measurement uncertainty was evaluated following the EURACHEM approach. The validated method was successfully applied to the determination of sulfur in commercial topical formulations, demonstrating its suitability for routine quality control analysis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.123.2510.3664 Keywords Sulfur topical formulations method validation GC-MS uncertainty assessment. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) An extensive analysis of trace element content and antioxidant properties of nuts and dried fruits

This study examined the microelement composition and antioxidant activity of nuts and dried fruits that included soya raisin, golden raisin, malayar raisin, dried apricot, dried prune, walnut, peanut, almond, dried mango, dried melon, apricot with stone, cashew, dried kiwi, dried apple, pumpkin seed, pistachio, hazelnut, and rosehip. Ethanol infusions were assessed using the DPPH and ABTS methods to evaluate their ability to eliminate radicals and determine total phenolic content. Among the tested samples, hazelnuts displayed the lowest antioxidant content alongside high toxicity levels, while cashews exhibited the weakest reactivity. To ascertain the trace element content, the samples underwent processing in microwave ovens, and concentrations of various components were measured using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES). The method's accuracy was further validated using a certified sample material (NIST SRM 1515, apple leaves). The concentrations observed in the samples varied as follows: Al: 4.7–172.1 mg/kg, B: 3.3–50 mg/kg, Cu: 5.6–52.6 mg/kg, Fe: 14.1–145.4 mg/kg, Mn: 0.3–51.3 mg/kg, Ni: 1.5–8.7 mg/kg, Sr: 1.75–78.5 mg/kg, and Zn: 5.8–63.9 mg/kg, and the findings were compared with existing literature on similar matrices. Overall, the results underscore the nutritional significance of hazelnuts and dried grapes as natural antioxidant sources, raise concerns about potential health risks associated with potentially toxic metal accumulation, and emphasize the necessity for ongoing analyses to ensure consumer safety. The novelty of this study lies in its analysis of both antioxidants and minerals found in nuts and dried fruits from Kazakhstan, which are significant in everyday diets, festive events, and traditional medicine.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.122.2509.3632 Keywords ICP-OES nuts dried fruits antioxidant capacity trace element DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Microwave-assisted extraction of turkish Aronia melanocarpa fruit: modeling, optimization and characterization of commercial products
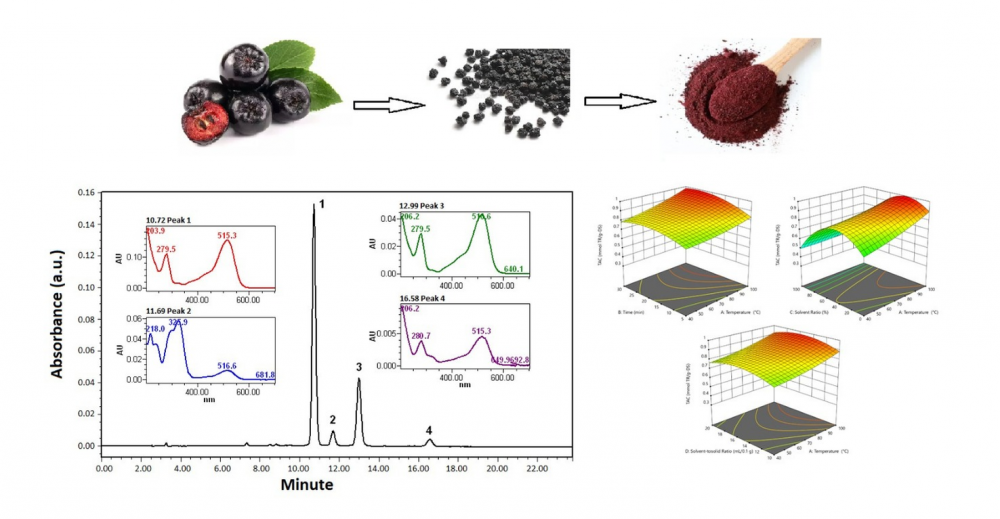
Aronia melanocarpa (black chokeberry) is a fruit rich in phenolic compounds and well-known for its potent antioxidant capacity; however, comparative investigations comparing fresh berries and their processed counterparts remain scarce. In this work, microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) was optimized via response surface methodology (RSM) to enhance the recovery of antioxidant constituents from Aronia fruits cultivated in Türkiye. Extraction time (5–30 min), temperature (40–100 °C), solvent-to-solid ratio (mL/0.1 g dry sample, DS), and solvent composition (20–100%) were systematically modeled, while antioxidant performance was assessed using the CUPRAC assay. The optimal conditions (100 °C, 24 min, 34% ethanol, 14 mL per 0.1 g DS) yielded a maximum TAC value of 0.998 mmol TE/g DS. Both raw fruits and commercial preparations (juice, concentrate, dried fruit, jam, vinegar, gummies, herbal capsules) were then characterized by spectrophotometric assays (CUPRAC, Folin–Ciocalteu, pH differential) and by chromatographic analysis (HPLC-PDA). Major anthocyanins—including cyanidin-3-O-xyloside, cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, and cyanidin-3-O-galactoside—and phenolics such as chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and gallic acid were identified and quantified. Substantial compositional differences were observed between fresh fruit and processed products, with pronounced losses of anthocyanins attributed to industrial processing. This study provides the first integrated assessment of Turkish Aronia fruits and related commercial products, by uniting MAE optimization with comprehensive antioxidant and phytochemical profiling, and offering new insights into their nutritional and functional potential.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.120.2509.3647 Keywords Aronia melanocarpa response surface methodology microwave-assisted extraction antioxidant capacity anthocyanins HPLC-PDA DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Simultaneous determination of pinaverium bromide, medazepam, and their related impurities in combined dosage form by UPLC–QDA
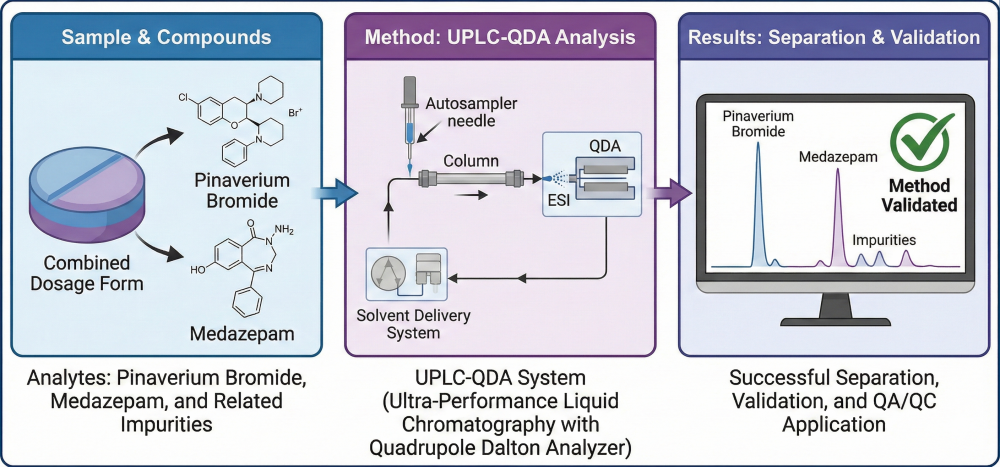
A rapid ultra-performance liquid chromatographic method coupled with a quadrupole detector (UPLC–QDA) was developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of pinaverium bromide, medazepam, and their related substances in a newly developed fixed-dose pharmaceutical formulation. Chromatographic separation was achieved on an Acquity BEH C18 column (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 µm) using a gradient elution of 25 mM ammonium formate buffer (pH 3.5) and acetonitrile at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min and a column temperature of 45 °C. The total run time was 11 min, providing complete resolution of all analytes without interference. Linearity was demonstrated (R² ≥ 0.999) within the ranges of 2–400 ng/mL for medazepam, 10–2000 ng/mL for pinaverium bromide, 5–1000 ng/mL for RS1 (medazepam impurity), and 10–2000 ng/mL for RS3–RS6 (pinaverium bromide impurities). The limits of detection (LOD) and quantitation (LOQ) were 0.17 and 0.50 ng/mL for medazepam and 0.43 and 1.30 ng/mL for pinaverium bromide, respectively, while LOD and LOQ values for related substances ranged between 0.22–0.91 ng/mL and 0.66–2.70 ng/mL. The method was validated in accordance with the ICH Q2(R2) guideline. The validated method was successfully applied for the simultaneous quantification of pinaverium bromide, medazepam, and their respective impurities (RS1–RS6) in commercial film-coated tablets (50 mg/10 mg), demonstrating its applicability for routine quality control and stability testing of fixed-dose combination formulations.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.128.2512.3748 Keywords Pinaverium bromide medazepam related impuriti UPLC–QDA method validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Phenolic acid extraction from Avicennia officinalis L. fruit: An optimized ultrasound-assisted approach with HPLC-DAD
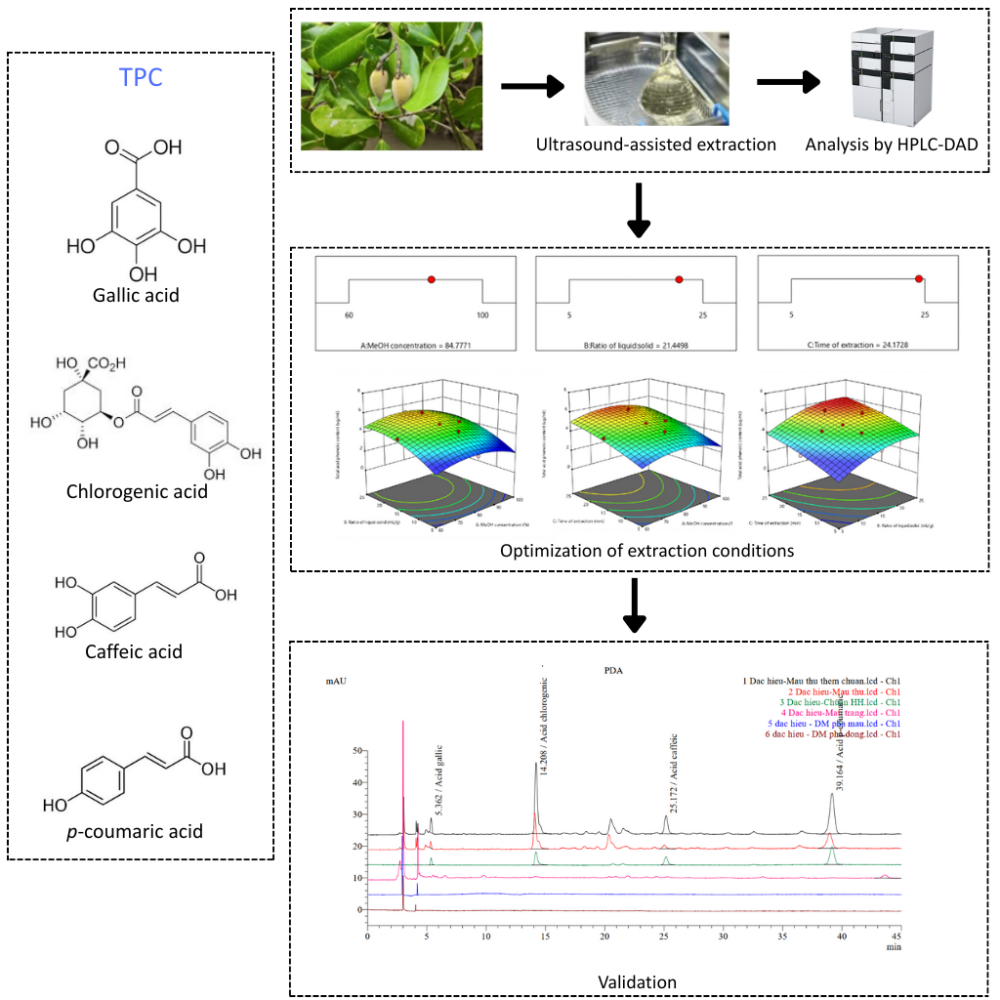
Avicennia officinalis L. is a valuable mangrove species rich in phenolic compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. Despite this, research on extracting these compounds from its fruit is limited. This study focused on developing and optimizing an ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) method to quantify four specific phenolic acids (gallic, chlorogenic, caffeic, and p-coumaric acids) from A. officinalis fruit collected in Ca Mau, Vietnam. The optimized UAE conditions by response surface methodology (RSM) involved methanol concentration of 84.78%, the liquid-to-solid ratio at 21.45 mL/g and extraction time at 24.17 minutes, and three extraction cycles. The method was validated according to AOAC guidelines, demonstrating excellent linearity, precision (RSD <11%), and accuracy (recovery rates 82.68-104.51%). This research marks the first successful quantification of these phenolic acids in A. officinalis fruit in eight location of Ca Mau province, Vietnam, offering a highly efficient (>99%) and repeatable (RSD <6%) method for future studies.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.129.2511.3735 Keywords Avicennia officinalis L. fruit phenolic acid ultrasound-assisted extraction response surface methodology HPLC-DAD DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) A New RP-HPLC method for stability indicating assay of pazopanib hydrochloride in tablet dosage form: method development, validation, and degradation kinetics
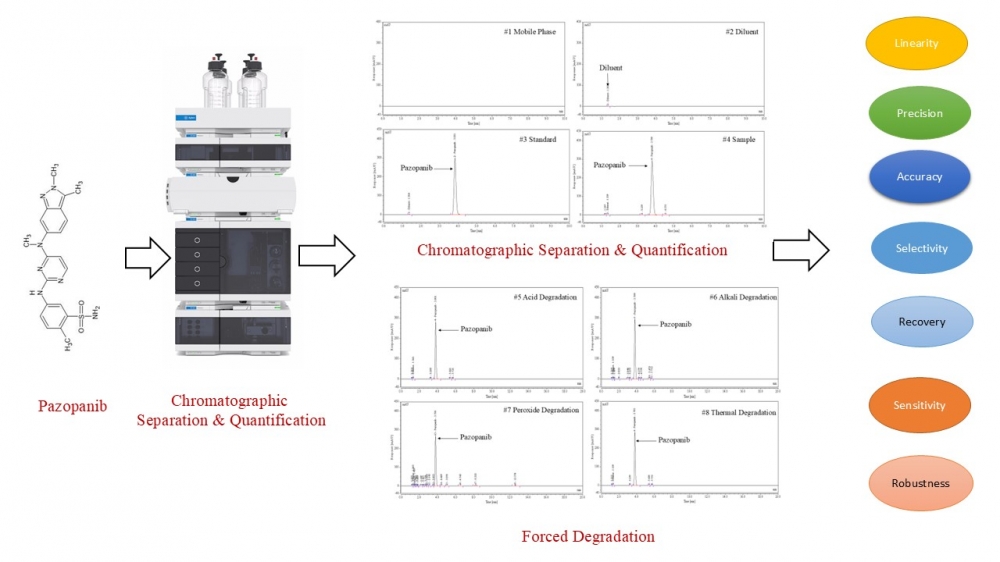
This study reports the development and validation of a novel, rapid, and stability-indicating reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method for the quantification of pazopanib in tablet formulations. Chromatographic separation was achieved on an Inertsil ODS-3V column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) using an isocratic mobile phase of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid and acetonitrile (70:30, v/v) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min with UV detection at 268 nm. The method demonstrated excellent resolution of pazopanib from its degradation products under forced degradation conditions, including acid/base hydrolysis, oxidation, photolysis, thermal, and humidity stress, confirming its stability-indicating capability. Validation in accordance with ICH Q2(R1) guidelines showed linearity over 25.71, 51.41, 82.26, 102.82, 123.38, and 154.23 µg/mL (r² > 0.999), precision with %RSD < 2.0, accuracy with recovery > 99%, and robustness under deliberate variations in chromatographic parameters. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) confirmed high sensitivity, and solution stability studies established analyte stability over 24 hours at 25 °C. With a runtime of 20 minutes and cost-efficient operation, this RP-HPLC method provides accurate, precise, and selective quantification of pazopanib in pharmaceutical dosage forms.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.130.2510.3711 Keywords Pazopanib hydrochloride stability indicating RP-HPLC method forced degradation study assay analytical method validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Determination of phenolic content of Hypericum aucheri Jaub. & Spach by LC-HRMS and its antioxidant capacity
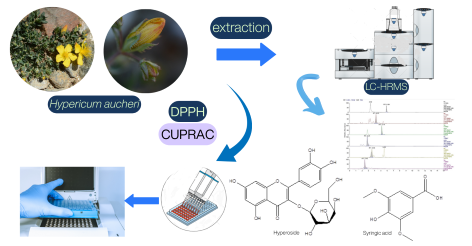
The study aims to identify the secondary metabolites of Hypericum aucheri Jaub. & Spach extracts using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) and to evaluate the plant's antioxidant activity. Antioxidant activity was assessed using DPPH free radical scavenging and CUPRAC assays. The primary secondary metabolite detected was hyperoside, with concentrations of 1059.53 mg/L in acetone (Ac) extract and 389.73 mg/L in methanol (MeOH) extract. Sinapinic acid was the predominant compound in the chloroform (C) extract, with a concentration of 6646.53 mg/L. In addition, Ac extract showed the highest DPPH free radical scavenging activity (85.90±0.26 - 61.19±0.47%) of all the extracts tested. The MeOH extract exhibited the highest value in the CUPRAC assay (2.53±0.05 mmol TR g-1). The study highlights a numerical relationship between phenolic content and antioxidant activity, underscoring the importance of phenolics in their antioxidant functions.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.131.2512.3765 Keywords Hypericaceae Hypericum aucheri antioxidant LC-HRMS phenolic compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) Development of a quality control material for conductivity measurements in food and environmental applications
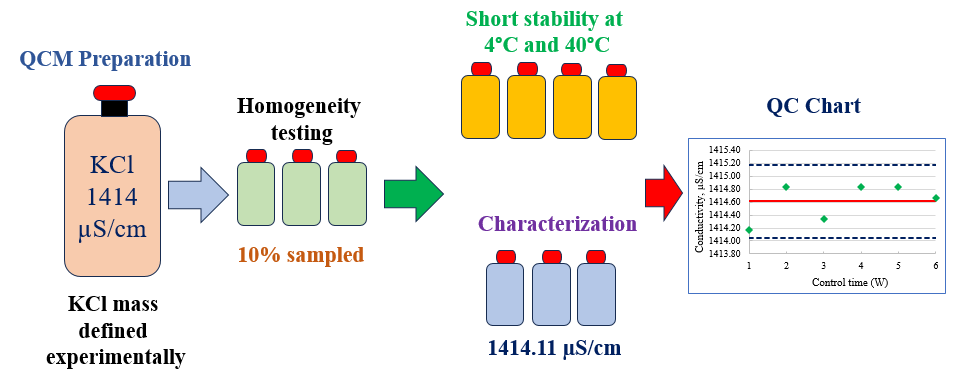
The accuracy and reliability of conductivity measurements in analytical laboratories depend significantly on the availability of quality control materials. This study addresses the preparation, homogeneity, stability and characterization of a potassium chloride (KCl) quality control material (QCM) of 1414 µS/cm based on ISO/TR 33402. OIML R-56 does not contain this conductivity value as a secondary standard, so the mass of KCl required to prepare such a solution was experimentally defined. The conductivity measurements were carried out at 25 °C using a conductivity meter calibrated by a CRM produced by the the Slovak Institute of Metrology (SMU), a signatory to the mutual recognition arrangement (MRA) of the International Committee of Weights and Measures (CIPM). The homogeneity study was carried out in accordance with ISO 33405 using 10% of the batch bottles and the analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that the QCM batch is homogeneous. The short-term stability was carried out over 4 weeks storage time at 4°C and 40°C and the isochronous measurements showed no significant deviations over time. The characterization of the QCM along three days showed that, its conductivity was 1414.11 µS/cm. The uncertainty associated with the conductivity measurements was assessed based on the requirements of the Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement (ISO GUM) and the EURACHEM/CITAC Guide, CG4 (Quantifying uncertainty in analytical measurement). It was found to be 23.10 µS/cm or 1.63%. A control chart was developed using the prepared QCM and the measured values remained within the control limits over the control time of six weeks. The prepared KCl QCM will be useful for use in quality control and instrumental validation in food, drug and environmental conductivity testing.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.119.2508.3607 Keywords Conductivity QCM ISO/TR 33402 homogeneity stability control chart DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Desorption of ethanol from internal surface of the cylinders
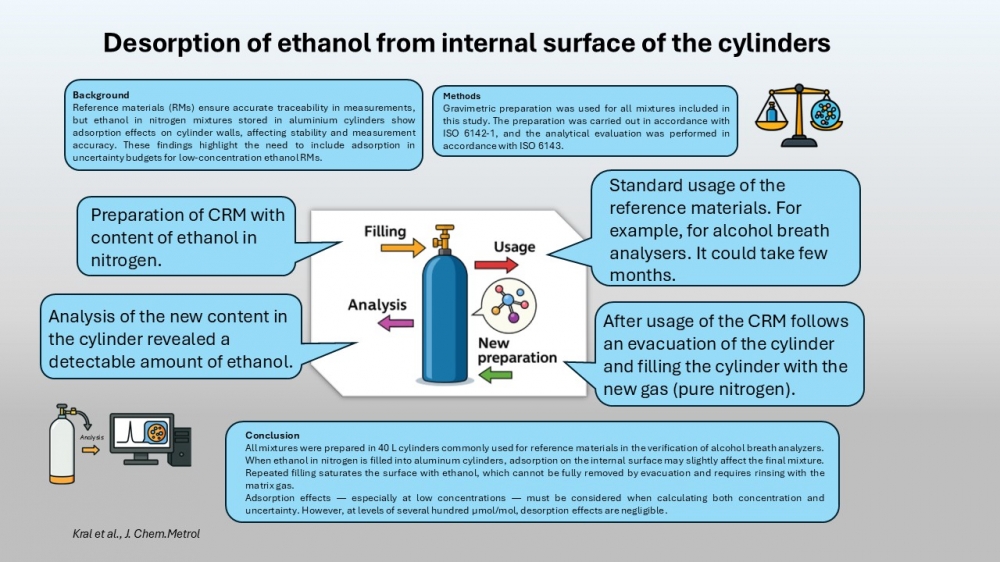
Reference materials (RMs) are essential for ensuring metrological traceability in various fields, including environmental monitoring, chemical analysis, and the verification of alcohol breath analyzers. One critical property of RMs is their long-term stability, particularly for gas mixtures such as ethanol in nitrogen, which are stored in pressurized aluminum cylinders. This paper describes the preparation of such gas mixtures according to ISO 6142-1, utilizing differential weighing to minimize the influence of ambient conditions and ensure accurate composition. The effects of adsorption of ethanol on the internal surfaces of aluminum cylinders were experimentally investigated. Results indicate that ethanol can remain adsorbed on the cylinder walls even after evacuation, leading to measurable ethanol concentrations upon subsequent refilling with nitrogen. Repeated fillings demonstrated a decrease in ethanol levels, confirming the saturation and gradual desorption behavior. These findings underscore the necessity to consider adsorption effects in the uncertainty budget and composition calculations for low-concentration ethanol-in-nitrogen RMs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.121.2507.3596 Keywords Stability reference materials ethanol pressurized cylinders gas chromatography desorption DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.