Records of Natural Products
Year: 2025 Volume: 19 Issue:Special Issue:Lamiaceae Family: Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Ethnopaharmacology, Ethnobotany and as Food Soruce
1) Editorial

We have previously announced that we have started working to publish a "Special Review Article Issue" every year in Records of Natural Products starting from this year. In this context, we are happy to have published our first Special Issue under the title "Lamiaceae Family: Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Ethnopharmacology, Ethnobotany, Food and Clinical Application" with 7 wonderful review articles as the 2025 Special Issue of Records of Natural Products. Our authors who contributed to this issue shared their highly qualified and comprehensive studies on the ethnobotanical properties, ethnopharmacological uses, biological activities, phytochemical studies and applications in various fields of the Lamiaceae family with our readers. Each of them has already taken its place in the scientific literature as highly qualified studies that will support young researchers, scientists looking for new research areas and valuable scientists teaching in these fields at universities. We will continue this new application that we started to implement in 2025 in the coming years. In this regard, we would like to state that we are waiting for your suggestions on topics that are suitable for the scope of the Records of NAtural Products journal. Finally, we would like to thank all the authors who contributed to our journal in this issue and our referee board and editorial board members who took part in the work. As we always say, our main purpose is to offer an unbiased research portal to the scientific world, natural products chemistry and pharmacognosy research, and we have never stepped back. And we will not. “This is your journal, support yourself”.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.540.2506.3573 Keywords Special issue Lamiaceae DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) An Updated Review of Research into Carvacrol and Its Biological Activities
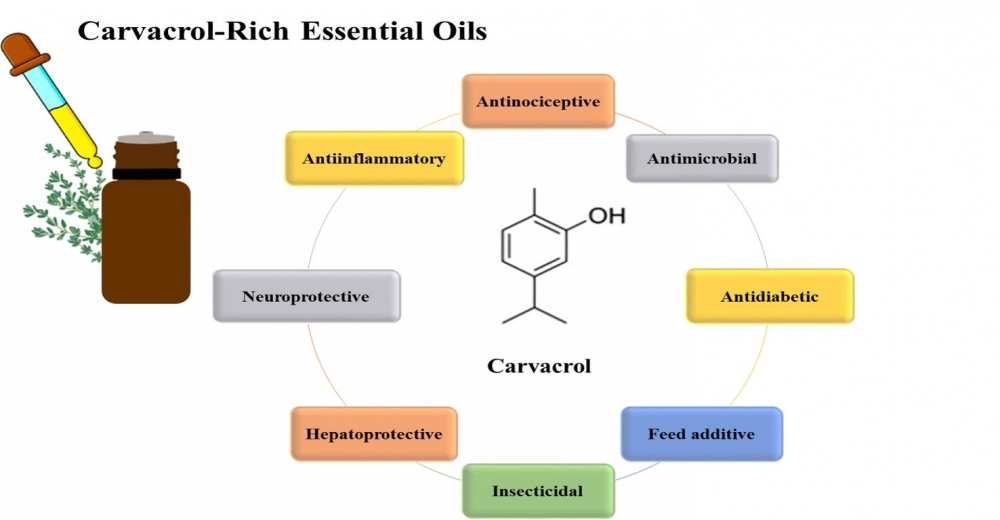
Carvacrol, a monoterpenic phenol found abundantly in essential oils of Origanum, Thymus, Satureja, Thymbra and Lippia genera, is recognized for its extensive range of biological and pharmacological activities. This bioactive compound, primarily responsible for the health-promoting properties of oregano essential oil, exhibits diverse functionalities including antimicrobial, antitumor, antimutagenic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects. Its therapeutic applications extend to managing gastrointestinal ailments, reducing oxidative stress, and serving as an insecticidal agent. Furthermore, carvacrol has demonstrated potential as a feed additive and in honeybee breeding. Advances in encapsulation and nanotechnology have enhanced its stability and bioavailability, broadening its utility across food, pharmaceutical, and agricultural industries. This review synthesizes the evidence for carvacrol's biological activities and explores its possible in vivo mechanisms of action, emphasizing its promise as a natural therapeutic agent.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.504.2502.3428 Keywords Oregano monoterpenic phenol biological activity carvacrol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) A Mini Review on the Chemodiversity of Lamiaceae plants That Are Native to Türkiye and Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus#
The Lamiaceae family, or mint family, is renowned for its aromatic oils, which have played a crucial role in culinary, medicinal, and horticultural practices throughout history. Many species hold significant economic value, serving as sources of wood, ornamental plants, cosmetics, and medicinal and culinary herbs. In Türkiye, Lamiaceae is represented by five of the 12 global subfamilies: Ajugoideae, Lamioideae, Nepetoideae, Scutellarioideae, and Viticoideae. Systematic studies highlight the family's rich diversity, particularly its medicinal and pharmaceutical potential, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic significance, biodiversity, conservation importance, and ecological roles. Their diverse secondary metabolites and extensive use in traditional medicine make them valuable for drug discovery, natural product chemistry, and sustainable resource management. Given their high endemism (~44.9%) and culinary applications—such as flavoring herbs and herbal teas—Lamiaceae species native to Turkey and the Mediterranean deserve priority in research. This study presents findings on the non-volatile phytochemicals of selected plants from each subfamily at the genus level.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.516.2503.3458 Keywords Lamiaceae ajugoideae lamioideae scutellarioideae viticoideae secondary metabolites DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) An Updated Review on Ziziphora L.: A Valuable Source of Phytoconstituents for Potential Health Benefits
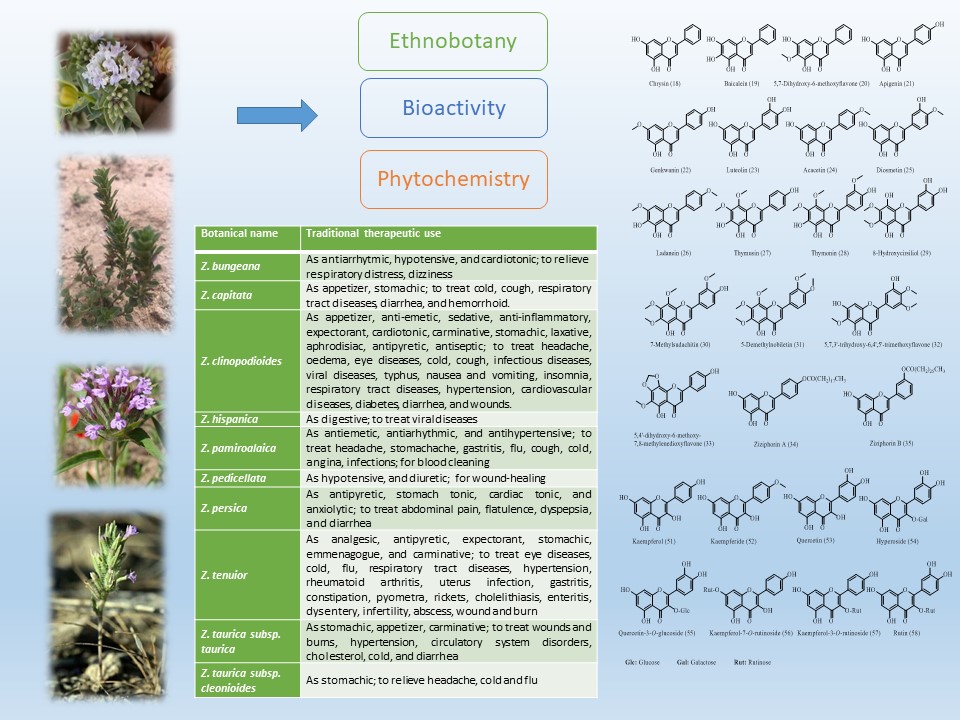
Abstract: Ziziphora L. (Lamiaceae) is a genus of annual or perennial medicinal plants. These species are characterized by their aromatic features and are widely distributed across Southern and Eastern Europe, Asia, and North-West Africa. In Türkiye, the genus comprises eleven taxa, namely Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam., Z. clinopodioides subsp. elbursensis, Z. clinopodioides subsp. filicaulis, Z. clinopodioides subsp. kurdica, Z. clinopodioides subsp. rigida, Z. capitata L., Z. persica Bunge, Z. tenuior L., Z. taurica M.Bieb., Z. taurica Bieb. subsp. taurica, and Z. taurica Bieb. subsp. cleonioides (Boiss.) Davis. Ziziphora species have been used in Turkish, Kazakh, and Iranian folk medicine, especially in the form of infusion, decoction, and maceration, owing to their antiseptic, expectorant, stomachic, carminative, and sedative effects. Ziziphora species have also been used against the common cold, coughing, migraine, fever, inflammation, diarrhea, and depression. There is a high number of studies documenting the phytochemical features and biological activities of Ziziphora species. Although the essential oil composition of the Ziziphora genus was the primary focus of earlier studies, these species also contain triterpenes, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. They were demonstrated to display antimicrobial, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities. Given their diverse biological activities and phytoconstituents, Ziziphora species represent a promising candidate for further pharmacological research. In the present review, ethnobotanical records, phytochemical profiles, and bioactivities of Ziziphora species will be extensively presented.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.523.2504.3496 Keywords Lamiaceae Ziziphora ethnobotany biological activity phytochemistry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Review on the Biological Activities and Phytochemistry of the Genus Satureja
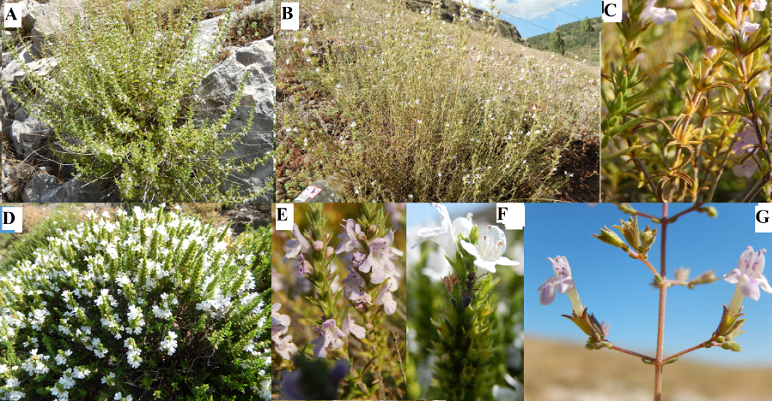

The genus of Satureja species belongs to the Lamiaceae family and has been used as culinary spice and condiment as well as in traditional medicine for the treatment of a variety of diseases such as gastrointestinal system disorders including cramps, nausea, indigestion, and diarrhea and respiratory system disorders, skin disorders, pain and inflammation. The genus is represented by 61 taxa worldwide, and 17 taxa are distributed in Türkiye. This paper reviews biological activity and phytochemical constituents of Satureja species. The related scientific and books, journals, articles and Pubmed, Scopus, Science Direct and Google Scholar databases were searched using the keyword “Satureja” related to the studies on the phytochemistry, secondary metabolites, essential oil, volatiles, phytochemisrty and/or biological activities were evaluated and reviewed. As a result of this current review, current data on the Satureja genus was assessed mainly for various biological activities. Especially the anticholinergic, anti-antioxidant, cytotoxic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic/antinociceptive, larvicidal, and insecticide activities of the genus are remarkable. However, only a limited number of the current literature focused on the isolated active compounds. As a result, the genus Satureja presents a significant potential as a natural resource for the development of agricultural products for new pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, veterinary products, and foods of different sectors. New research and in vivo bioactivity evaluations may open new avenues for the valorisation of Satureja preparations especially in the health and cosmetic industries.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.526.2504.3483 Keywords Satureja essential oil carvacrol flavonoids phenolics biological activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Thymus Species: A Powerful Tool for Conservation of Historical Art Craft

The application of conventional biocides to manage biodeterioration in cultural heritage is being progressively discouraged because of the hazards they present to human health, the environment, and the possible modification of historical materials. For this reason, research is focused on identifying alternative solutions that are more sustainable, innovative, and eco-friendly. This study aims to analyze the results of recent scientific investigations, identifying the most promising natural substances, highlighting knowledge gaps, and outlining future research directions. We carried out a systematic review of the literature, analysing peer-reviewed articles published between 2010 and 2025 that explore the application of natural biocides to counteract the biodeterioration of materials like stone, wood, textiles, and paper. Among the emerging solutions, essential oils have shown particular promise due to their antimicrobial effectiveness and lower environmental impact. Among the aromatic plants studied, belonging to the Lamiaceae family, Thymus pulegioides, Thymus serpyllum, Thymus vulgaris, Thymus mastichina, Thymus zygis, and Thymus capitatus (syn. Thymbra capitata) stand out, with their essential oils demonstrating significant antimicrobial properties. Experimental tests have employed various methodologies, predominantly in vitro studies, with fungi being the most frequently targeted organisms, followed by algae and cyanobacteria. However, the efficacy of these substances has shown considerable variability, mainly due to discrepancies in experimental protocols and dosages, making it challenging to establish clear guidelines. Furthermore, some studies have reported potential undesirable interactions between essential oils and the original materials, which require further investigation. Despite these limitations, the use of natural biocides offers an innovative and promising approach to preserving cultural heritage. Nevertheless, it is crucial for future research to adopt more standardized protocols to systematically evaluate the effectiveness and safety of these substances, ensuring a balance between conservation and sustainability.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.526.2503.3467 Keywords Biodeterioration essential oils Thymus species cultural heritage biocides DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Biological Activities of Diterpenoids Isolated from Anatolian Lamiaceae Plants II
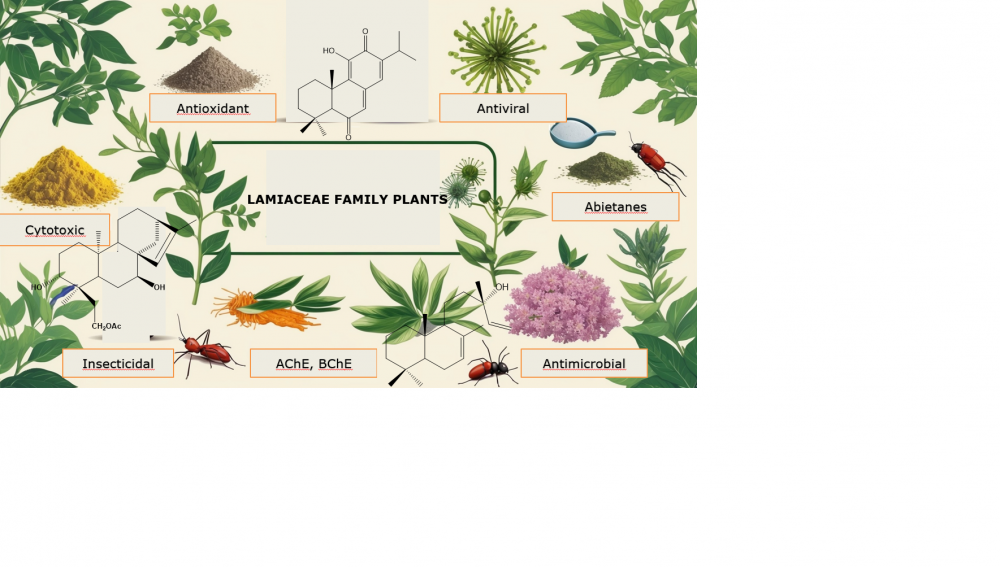
In this study, biological activity studies and their results on diterpenoids isolated from Lamiaceae plants in Türkiye between 2006-2025 were updated. When the studies conducted in the past twenty years were examined, it was observed that mainly cytotoxic and acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity tests were carried out on diterpenoids obtained from Lamiaceae family plants. However, in decreasing numbers of studies for antibacterial, antifungal, cytotoxic, antitumor, cardiovascular, antiviral, antiplasmodial, insecticidal and some other single activities were examined. In this study, researches on thirty-nine abietane diterpenoids isolated from Salvia species, thirteen kaurane type diterpenoids isolated from Sideritis species, and three labdane, one manoylxoide and one pimarane diterpenoids from different sources and their biological activities data were reported.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.524.2504.3490 Keywords Salvia Sideritis Teucrium cytotoxic activities anticholinesterase activities insecticidal activities. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) The Lamiaceae Family Plants Ethnobotanical Properties, Ethnopharmacological Uses, Phytochemical Studies and Their Utilization in Public or Current Clinical Practices: A Review
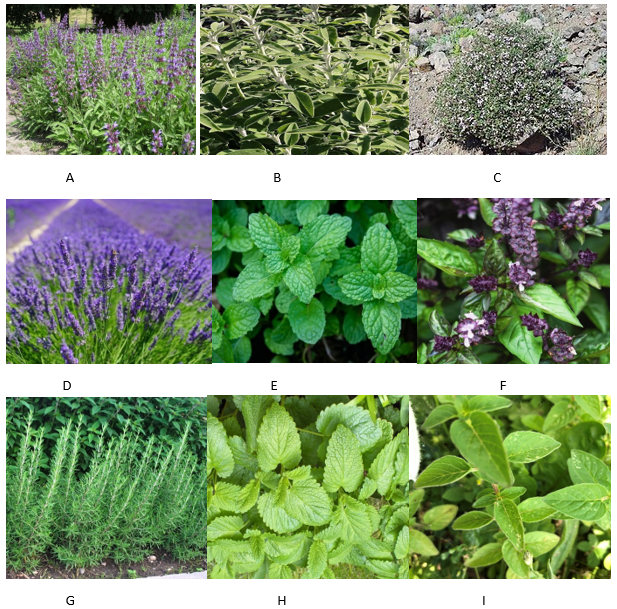

Through ethnobotanical, pharmacological, and phytochemical data of the Lamiaceae family of inflammatory, cardiovascular, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, cancer, and gastrointestinal disorders, this study aims to gather knowledge on traditional usage. The necessity to guarantee the safety, effectiveness, and purity of herbal medicines is underscored by the long tradition of folk medicine's use for therapeutic purposes. As this need has increased throughout the years, collective attempts have been made to conserve priceless information about therapeutic plants and to archive records of the past. The family Lamiaceae, sometimes known as Labiatae, is well known for its wide variety of medicinal herbs. The leaves, flowers, roots, bark, fruit, twigs, seeds, and other components of Lamiaceae species may be separately utilized for medicinal purposes. A multitude of plants in the Lamiaceae family have been used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of illnesses. The members of the Lamiaceae family are found across the Mediterranean area. Also, some biochemical and pharmacological analyses have been used to investigate the biological activity of Lamiaceae species. Its pharmacological qualities have been confirmed by the thorough study, which has shown that numerous bioactive characteristics of this plants possess wound healing, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-Alzheimer’s disease, enzymes inhibitory, antiviral, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antihypertensive, and antileishmanial effects. This thorough analysis provides a perceptive synopsis of the Lamiaceae family, clarifies the extraction techniques used to produce therapeutic organic compounds, investigates the phytoconstituents found in Lamiaceae medicinal plant species, and systematically describes the family's diverse range of pharmacological properties.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.529.2505.3521 Keywords Lamiaceae species antioxidants phytochemistry ethnobotany ethnopharmacology phenolic compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.