JOURNAL 3478
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2025 Issue: 6 November-December
p.722 - 727
Viewed 1200 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
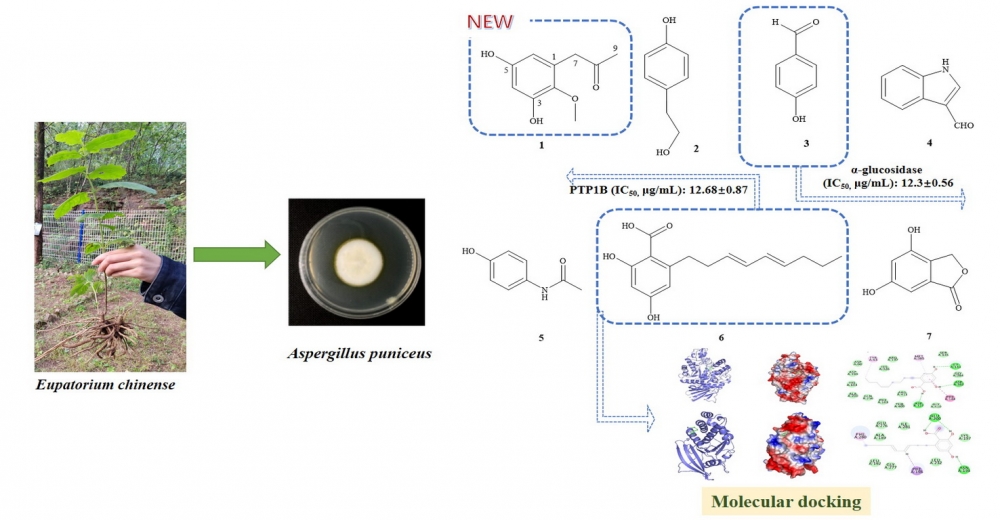
ABSTRACT
A novel polyketide, named Asperpropanol E, was found from the secondary metabolites of the endophytic fungus Aspergillus puniceus which was isolated from Eupatorium chinense L. In addition to this new compound, six known compounds were also identified. The structures of all compounds were elucidated through comprehensive chemical analysis utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) spectroscopic techniques. All isolated compounds were evaluated for biological activity by the MTT assay, compound 1 exhibited moderate inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), the IC50 (μg/mL) values of 31.63 ± 0.42 and 36.82 ± 0.54, respectively. Compound 3 demonstrated significant inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase (IC50 =12.3±0.56 μg/mL). Notably, compound 6 displayed potent dual inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and PTP1B with the IC50 (μg/mL) values of 26.72 ± 0.63 and 12.68 ± 0.87, respectively. However, none of the tested compounds showed significant inhibitory effects on HGC-27 gastric cancer cells and HepG2 liver cancer cells.
KEYWORDS- Aspergillus puniceus
- eupatorium chinense L
- endophytic fungi
- PTP1B Inhibition
- α-glucosidase