Records of Natural Products
A scientific open access journal in the field of natural products.LATEST ARTICLES
Fusasolpolyol A, An Unreported Polyhydroxy Compound Isolated from the Sargassum thunbergii-Derived Endophytic Fungus Fusarium solani 2024f-xx
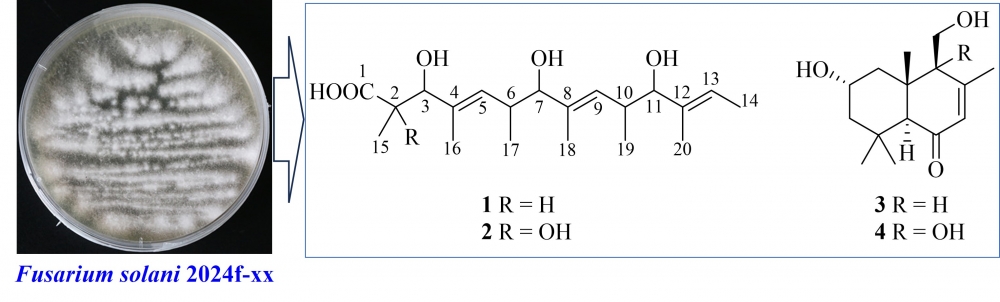
Fusarium solani 2024f-xx, an endophytic fungus derived from the marine brown algae Sargassum thunbergii, was chemically studied. As a result, two polyhydroxy compounds, namely fusasolpolyol A (1) and (4E,8E,12E)-2,3,7,11-tetrahydroxy-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexamethyltetradeca-4,8,12-trienoic acid (2), as well as two known drimane-type sesquiterpenoids (3 and 4) were isolated and identified. The structures of the isolated compounds were ascertained by means of specific spectroscopic methods (mainly determined by HRESIMS and 1D/2D NMR data). Compound 1 was identified as a new compound. In the cytotoxic assays, compound 2 revealed moderate activity against the human gastric carcinoma cell MKN-45 and the human pancreatic cancer cell PATU8988T, with the respective IC50 values of 19.6 ± 1.2 μM and 26.3 ± 0.9 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.520.2504.3506 Keywords Fusarium solani endophytic fungus secondary metabolites polyhydroxy compound cytotoxic activity Available online: May 29, 2025 DETAILS DOWNLOAD PDF © ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Chemical Constituents and Pharmacology of Fomes fomentarius: A Systematic Review
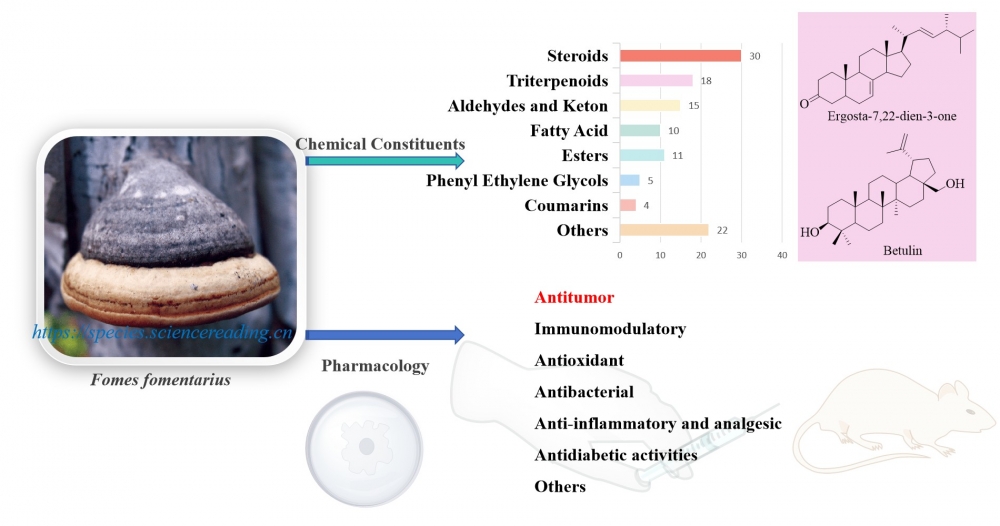
This paper mainly provides a systematic review of the chemical constituents and biological activities of Fomes fomentarius. As a widely distributed medicinal fungus, F. fomentarius has a long history of application in traditional medicine. Rich in chemical constituents, it contains over a hundred compounds such as steroids, triterpenes, and fatty acids. Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that this fungus exhibits multiple activities, including antitumor, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic, antidiabetic, anti-hypoxic, and hepatoprotective effects. However, our current understanding of its action mechanisms and the synergistic effect among components remains limited. This review provides crucial references for further research and development of F. fomentarius.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.521.2503.3466 Keywords Fomes fomentarius chemical constituents pharmacological activities Pyropolyporus fomentarius Available online: May 29, 2025 DETAILS DOWNLOAD PDF © ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, Acetylcholinesterase and β-Lactamase Inhibitory Activities of Essential Oils from Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum Turcz. and Clerodendrum fortunatum L.
(1).png)
Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum Turcz. and Clerodendrum fortunatum L. are traditional medicinal plants used for clearing heat, reducing fire, reducing inflammation and detoxification, and relieving cough and analgesia in China. In the current study, the essential oils (EOs) of C. cyrtophyllum and C. fortunatum were obtained by hydrodistillation. The chemical compositions and the contents of the EOs were measured by GC-MS and GC-FID methods. The antioxidant capacity was measured by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl radical (DPPH), 2'-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate) (ABTS) free radical scavenging capacity and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP). The GC and GC-MS analysis results identified 89 and 63 components in the EOs of C. cyrtophyllum and C. fortunatum, accounting for 94.9% and 96.2%, respectively. 1-octen-3-ol, linalool, and hexahydrofarnesyl acetone were reported as the same primary components. The inhibition rates of the DPPH radical scavenger assay were 43.49% ± 0.95% and 27.23% ± 0.40% at 20 mg/mL, while the ABTS radical scavenging assay showed capacities with the IC50 values 2.31 ± 0.05 mg/mL and 7.43 ± 1.80 mg/mL, respectively. The FRAP values (Trolox equivalent antioxidant concentration) were 55.61 ± 2.56 µmol/g and 23.39 ± 1.58 µmol/g, respectively. The C. cyrtophyllum and C. fortunatum EOs showed anti-acetylcholinesterase activity with the IC50 values 289.10 ± 0.43 µg/mL and 1060.00 ± 0.82 µg/mL, and β-lactamase inhibitory activity with the IC50 values 41.34 ± 0.84 µg/mL and 673.50 ± 1.27 μg/mL, respectively. This study makes a substantial contribution to the chemical and biological knowledge expansion on Clerodendrum species EOs from China.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.518.2501.3418 Keywords Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum Turcz. Clerodendrum fortunatum L. essential Oil GC-MS cemical compositions biological activities Available online: May 25, 2025 DETAILS DOWNLOAD PDF © ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Structures and Biological Evaluation of 8,4′-oxyneolignans from the Roots of Platycodon grandifloras
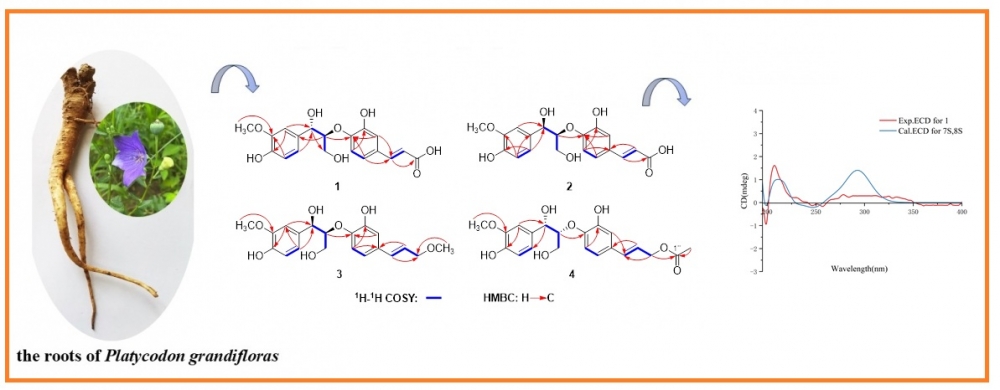
Chemical investigations of Platycodon grandiflorus have resulted in the isolation and identification of seven 8,4'-oxyneolignans, including four undescribed compounds (1-4). The structures of these novel compounds were determined using HR-ESI-MS and NMR (1D and 2D) spectroscopic analyses, combined with ECD calculations. The inhibitory activity of these terpenoids against α-glucosidase was also evaluated, and the results revealed that none of the compounds exhibited significant α-glucosidase inhibitory activity at a concentration of 50 μM. Compared with the positive control, all the compounds displayed weak inhibitory activity, with inhibition rates ranging from 1.06% to 7.31%.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.513.2501.3409 Keywords Platycodon Platycodon grandiflorus apha-glucosidase chemical constituents 8,4-oxyneolignan. Available online: May 25, 2025 DETAILS DOWNLOAD PDF © ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
