Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2025 Volume: 8 Issue:1 January-June
1) Antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of synthetic 2-styrylchromones
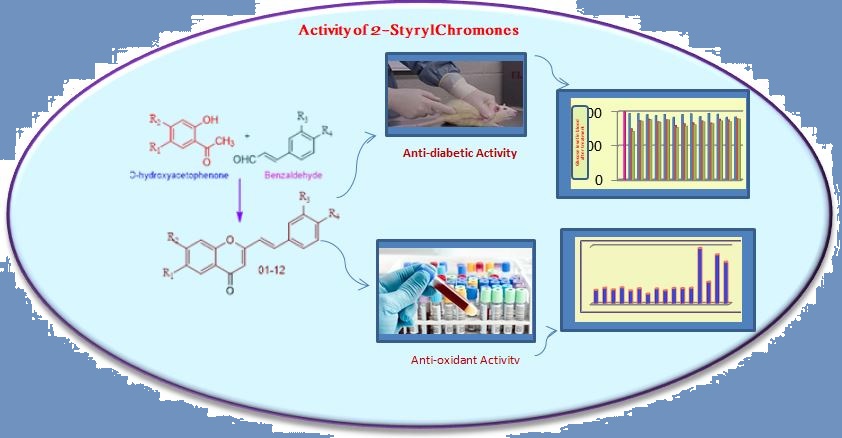
2-Styrylchromones are very potent bioactive substances showing innumerable activities like antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiviral, antiinflammatory, anticancer, anti-microbial etc. All these activities are due to their core structure (benz-γ-pyrone) containing styryl group at 2nd position. Substituents especially hydroxyl groups are responsible for anti-diabetic and antioxidant activities. 2-Styrylchromones with a greater number of –OH substituents showed high activity than the remaining compounds. Compounds 5, 6, 7 and 9 having significant activity where the nature and position of substituents play a vital role. The synthetic compound with –OH groups at 4', 6 and 7 positions competed with standard drugs in respective activities.
DOI doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.33.2505.3509 Keywords 2-styrylchromones antidiabetic Activity antioxidant Activity streptozotocin induced diabetic glibenclamide superoxide radical scavenging DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) In silico prediction of some peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists targeted drugs as potential SARS-Cov-2 inhibitors
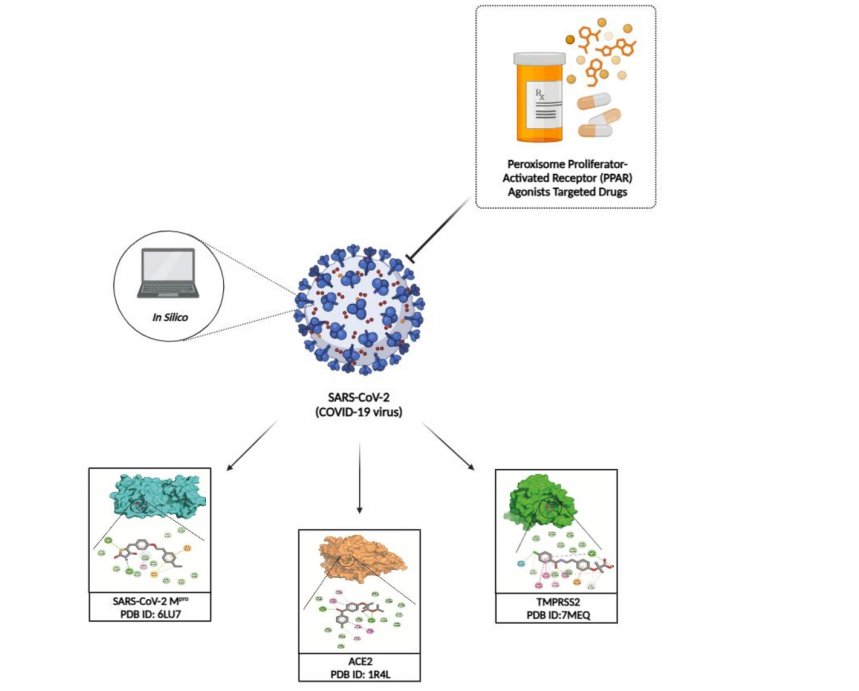
Since COVID-19 epidemic began, no effective medication have been found to treat this disease. In the current study, several peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonist drugs, including fenofibrate, binifibrate, bezafibrate, ciprofibrate, clofibrate, gemfibrozil, pioglitazone, and rosiglitazone were selected, and the molecular docking studies were applied by using main protease (Mpro), human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) targets. The chemical structures of selected drugs were retrieved from the PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). AutoDock 4.2 molecular docking program was used to obtain best binding interactions of selected drugs. Visualization of the docking results was performed using BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer and PyMol. As a result, rosiglitazone and binifibrate were found to be an effective drugs against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) with binding energies of –6.8 and -6.7 kcal/mol, respectively. Bezafibrate and binifibrate were found to be an effective drugs against ACE2 with binding energies of -8.6 kcal/mol, respectively. On the other hand, fenofibrate, bezafibrate and rosiglitazone showed highest binding energies against TMPRSS2 protein as compared with reference drugs favipiravir, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine. Our in silico results suggest that PPAR agonist drugs warrant further investigation as potential lead molecules for discovering more potent compounds in anti-CoV drug development research.
DOI doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.34.2502.3426 Keywords SARS-CoV-2 molecular docking ACE2 TMPRSS2 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.