Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2025 Volume: 5 Issue:1 January-June
1) Essential Oil Compositions and Biological Activities of the Genus Chaerophyllum: An Updated Review
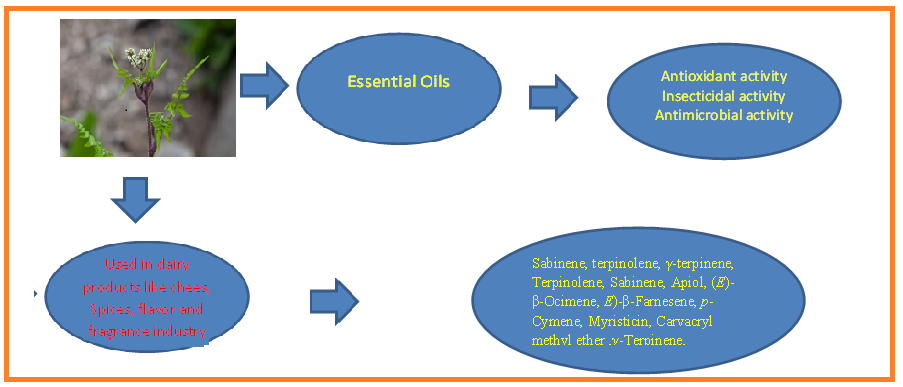
The genus Chaerophyllum has economic value-added species. Chaerophyllum belongs to the family, Apiaceae, which comprises about 110 species, including annual and perennial herbal plants widely distributed in temperate and sub-temperate zones of Asia, Africa, and Europe. Chaerophyllum species are used for flavor and fragrance in the food industry. In some countries, a species of this genus is used in cheese production for its strong aroma. Chaerophyllum species were characterized by lignans, polyacetylenes, essential oils, phenolic acids, and flavone derivatives. This review summarizes the essential oil components and isolates of various extracts and their biological activities. In addition, since ancient times, essential oils have been used in many different traditional healing systems worldwide because of their biological activities. Moreover, this review will attract the attention of scientists from the aroma industry, nutritionists, and pharmaceutical industries to improve the use of essential oils for nutraceutical purposes with commercialization to aid and promote a healthy lifestyle, wellness, and wellbeing.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.27.2501.3397 Keywords Apiaceae biological activities essential oils Chaerophyllum villosum DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Comparative Study on the Yield, Amino Acid Profile and Cowhide (Ponmo) Tenderization Efficiency of Papain from Different Parts of Papaya (Carica papaya)
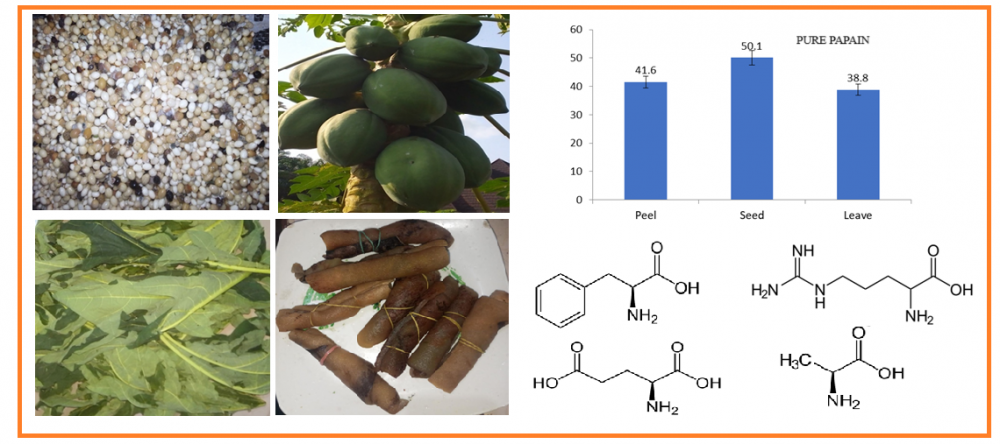
This study evaluated the yield, amino acid profile, and cowhide (Ponmo) (tenderization efficiency of papain from different parts of papaya (Carica papaya). The fresh leaves and fully grown but unripe pawpaw fruits were harvested from 1st to 7th August 2024. Papain was extracted from the peels, leaves, and seeds of papaya and purified. Ponmo from adult cattle was obtained from commercial producers after slaughtering and subjected to enzyme treatment, evaluation of amino acid profile, and meat tenderness. The highest yield of purified papain was obtained from the papaya seed (50.1%), while the lowest was obtained from the leaves (38.8%). Ponmo treated with papain from papaya peel recorded the highest values for all the essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids except for glycine (5.10%) and proline (5.18%), which were high in Ponmo treated with papain from papaya seed and control (animal fed with untreated diet) respectively. The shear force values of all the treated samples were significantly (p<0.05) lower than the control sample (5.41 kg/cm3). The study has clearly shown that when you treat ponmo with papain, more beta-pleated bonds are broken down, the meat becomes more tender and essential amino acids become more available and quantifiable than the control (untreated ponmo).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.26.2501.3398 Keywords Ponmo papain papaya amino acid profile tenderness DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Digital Agriculture Approaches for Resource Assessment of Blueberry Yield on Kozuf Mountain (R. of North Macedonia) Integrating Remote Sensing, GIS and Ground-Based Research Data
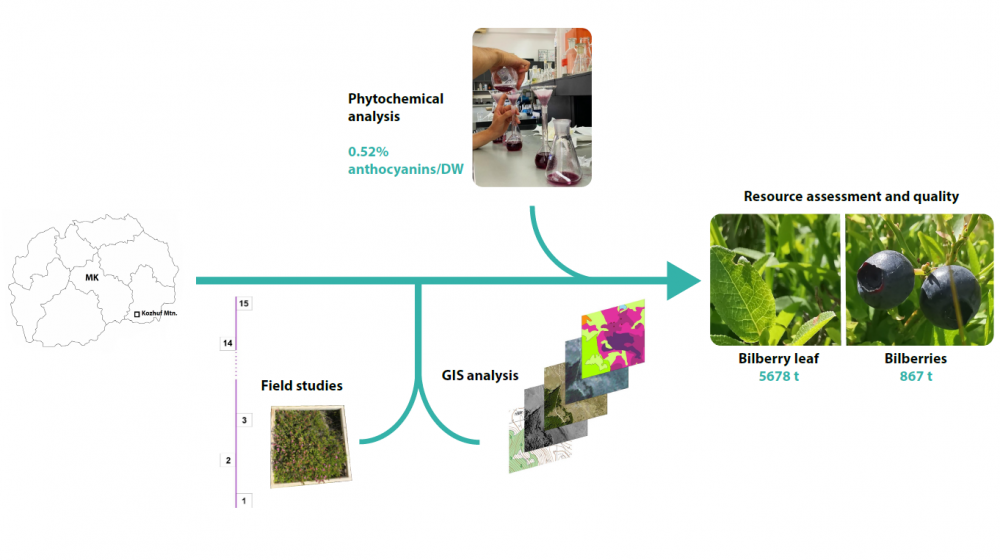
Blueberries are a valuable natural resource in North Macedonia, providing income for many people. However, underdeveloped collection, licensing, and monitoring systems result in unsustainable use. This study integrates GIS and field assessments of blueberry resources on Kozuf Mountain, analyzing annual fruit and leaf production and their chemical composition. Leaf and fresh fruit production averaged 48.30 g/m² and 30.70 g/m², respectively. The total biomass of dry leaves was estimated at 5186.70 t, mainly in heathlands. Anthocyanin content in fresh blueberries, determined according to Ph. Eur. 11, was 0.52%. The total phenolic content in Vaccinium myrtillus leaf extract averaged 174.55 mg GAE/g DW. Sustainable blueberry use could generate 3.55 million EUR from fruit and 5.44 million EUR from leaves. This could support nearly 1400 people based on average Macedonian salaries. To strengthen the licensing and monitoring system, resource management must align with the growing demand for bilberry collection while considering the region’s socioeconomic conditions. Establishing a protected area on Kozuf Mountain, promoting sustainable harvesting, and raising biodiversity awareness are crucial for long-term conservation. These efforts will help preserve natural resources while ensuring continued economic benefits for local communities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.28.2501.3419 Keywords Vaccinium myrtillus biomass production natural resources anthocyanins DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Antioxidant Activity of Satureja aintabensis P.H. Davis
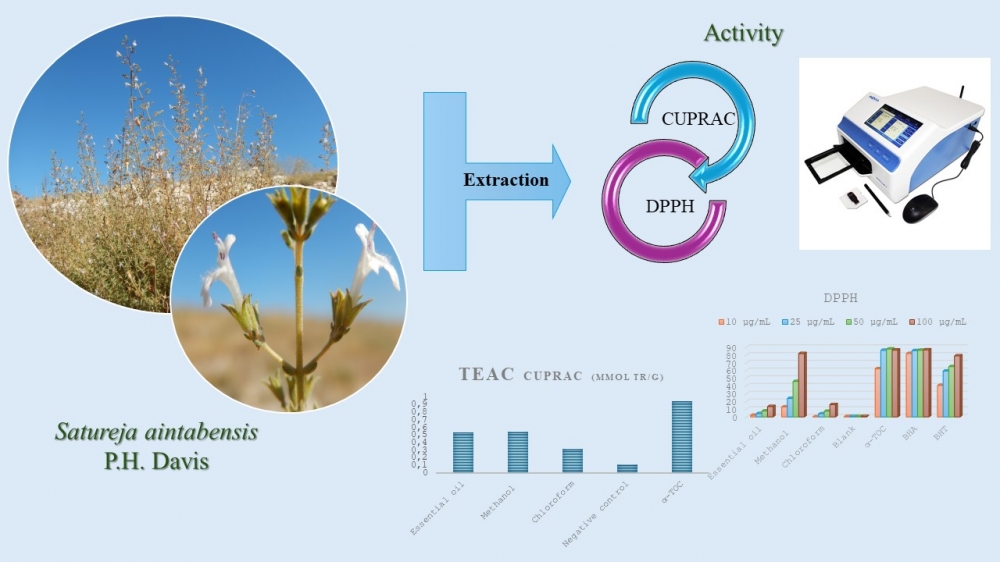
In this study, the antioxidant activity of the essential oil, methanol and chloroform extracts of Satureja aintabensis P.H. Davis, an endemic Turkish species traditionally consumed as tea and spice, was investigated for the first time using CUPRAC (cupric (Cu2+) ion reduction) and DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl free radical scavenging) assays. The aerial parts of the plant were extracted with methanol and chloroform and the essential oil was obtained by the hydrodistillation method using Clevenger apparatus. The methanol extract and essential oil exhibited comparable CUPRAC activity (0.55 ± 0.04 and 0.54 ± 0.03, respectively), while the methanol extract demonstrated the highest DPPH scavenging (13.0–82.0%), suggesting its dominance in neutralizing hydrophilic radicals. This result shows that S. aintabensis contains both hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants.
5) Effect of Selected Processing Methods on Nutrient, Phytochemical, and Carotenoid Profiles of Two Cultivars of Pterocarpus santalinoides
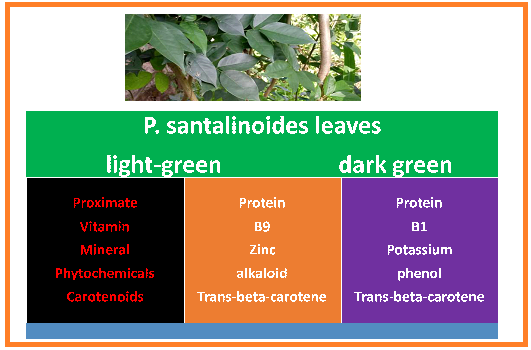
The aim of this research was to compare the nutrient and potential medicinal properties of two cultivars of Pterocarpus santalinoides leaves. Two cultivars of Pterocarpus santalinoides (Nturukpa) leaves (light green Avuo and dark green oseleukwu) were investigated for their nutrient composition, phytochemical content and carotenoid profiles. The effects of oven-drying at 550C for 1h 20 min; sauteeing in palm oil for 3 min and blanching in boiling water for 5 min on the nutrients and phytochemicals were evaluated. The leaves were rich in protein (14.0%) and vitamin B6 (73mg/100g). The leaves are also moderate sources of iron (6.2-7.4%), magnesium (42-44%), zinc (1.2%) and potassium (45.0-55.0%). Raw light green Avuo contained the highest amount of folate (vitamin B9). The phenolic contents, cyanogenic glycosides, anthocyanins, and phytates of the two P. santalinoides cultivars were statistically similar (p>0.05). Steroids, oxalate, tannins and alkaloids (7.7%) were higher in the light coloured cultivar (Avuo) while saponins and flavonoids (1.1%) were higher (p <0.5) in the dark green cultivar (Oseleukwu). The α-carotene, trans-β-carotene, and total β-carotene contents of the two P.santaniloides cultivars were statistically similar (P> 0.05). The most predominant peak in the chromatogram of the P. santalinoides was trans-beta-carotene. The nutrient and phytochemical composition of the two cultivars of P. santalinoides indicate that they are good sources of proteins and micronutrients and their phytochemical content suggest that they possess medicinal value.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.29.2505.3494 Keywords Pterocarpus santalinoides cultivars nturukpa nutrients phytochemicals carotenoid profile effects of processing DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Investigation of the Effect of Waste Polystyrene Modified with AlCl3 and FeCl₃ on BPA Removal and Optimisation with CCD-RSM Model

In this study, waste polystyrene (PS) was chemically modified using aluminium chloride (AlCl₃) and ferric chloride (FeCl₃) to enhance its adsorption performance for the removal of Bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solutions. The modification significantly improved the surface characteristics and adsorption capacity of the polystyrene. The removal efficiency of BPA was systematically evaluated under varying experimental conditions, including initial BPA concentration, solution pH, adsorbent dosage, temperature, and contact time. In order to optimise these parameters, central composite design under response surface methodology (CCD-RSM) was applied to design the experiments: The optimised conditions for the AlCl₃-modified polystyrene (PS/AlCl₃) were determined to be; initial concentration 40 mg/L, pH 4, adsorbent amount 0.1 g/L, temperature 40°C and contact time 30 min, while for FeCl₃-modified polystyrene (PS/FeCl₃) were initial concentration 40 mg/L, pH 6.3, adsorbent amount 0.1 g/L, temperature 20°C and contact time 90 min. As a result of the adsorption experiments carried out using the developed materials, it was determined that BPA was effectively removed from the simulated wastewater. The maximum adsorption capacities were determined to be 52.17 mg/g for PS/AlCl₃ and 54.95 mg/g for PS/FeCl₃. The results demonstrate that metal chloride modification is an effective approach for valorising waste
PS in environmental remediation applications.
7) Bioprospecting Terpenoid-Rich Himalayan Plants for Use in Food Preservation and Natural Flavouring Agents
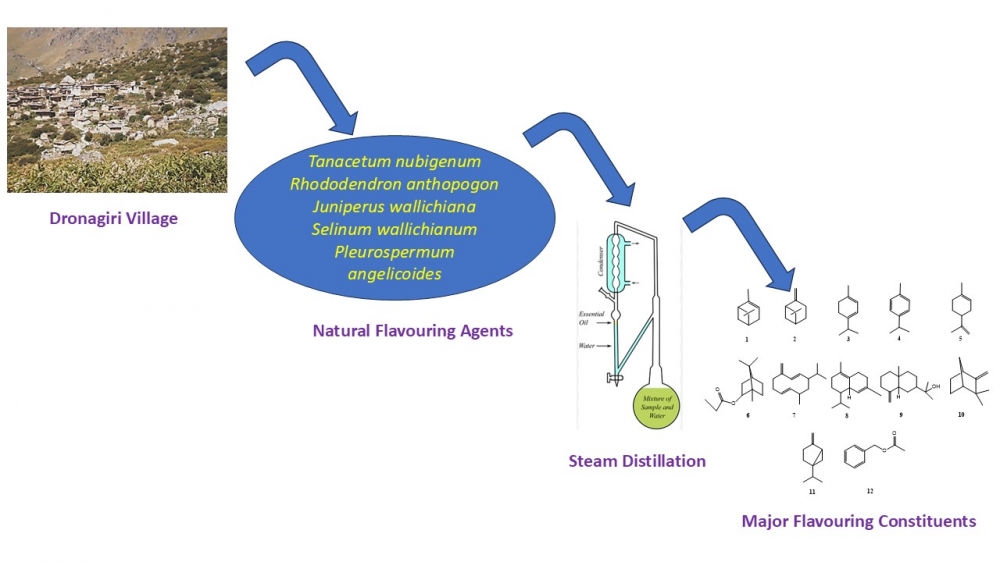
The Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) is known for its distinct flora and fauna. Many aromatic plants from IHR are used in food preservation, as ingredients in food items, and in folk herbal medicines, and their fragrance is used to improve mood and relieve depression. In continuation with this, essential oils (EOs) of five selected aromatic plants from Dronagiri hills of Uttaranchal (India) were analysed by gas chromatography (GC-FID) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Volatile oil of Tanacetum nubigenum Wall. contained β-eudesmol and isobornyl propionate as major compounds, Pleurospermum angelicoides (DC.) Klotzsch was found to contain p-cymene, camphene and α-asarone as major compounds; Rhododendron anthopogon D. Don was found rich in α-pinene, whereas germacrene-D and limonene were the major components of Selinum wallichianum (DC.) Raizada & Saxena, and Juniperus wallichiana Brandis were rich in β-pinene, sabinene, and α-pinene. Four out of five plant species were found to be rich in monoterpenoids, while one was noted for its abundance of oxygenated sesquiterpenoids. Tanacetum nubigenum, Pleurospermum angelicoides, and Selinum wallichianum are identified as chemotypes, while Juniperus wallichiana exhibits a composition similar to that previously reported. Several essential oils (EOs) derived from various traditional plants have demonstrated enhanced antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. They have also successfully extended the shelf lives of cereal products and improved the standard of food safety. Without compromising the quality, the main classes of essential oils (EOs), such as terpenes and aromatic volatile chemicals are crucial for food safety. Essential oils investigated may be used as alternative preservatives to extend the shelf life of grains and cereals, owing to their various properties, including antibacterial and antioxidant effects.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.31.2506.3551 Keywords Essential oils chemotype monoterpenoids food preservative Dronagiri plants DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Quality Assessment of Composite Flours from Blends of Acha (Digitaria exilis), African Breadfruit (Treculia africana), and Soybean Protein Concentrate (Glycine max)
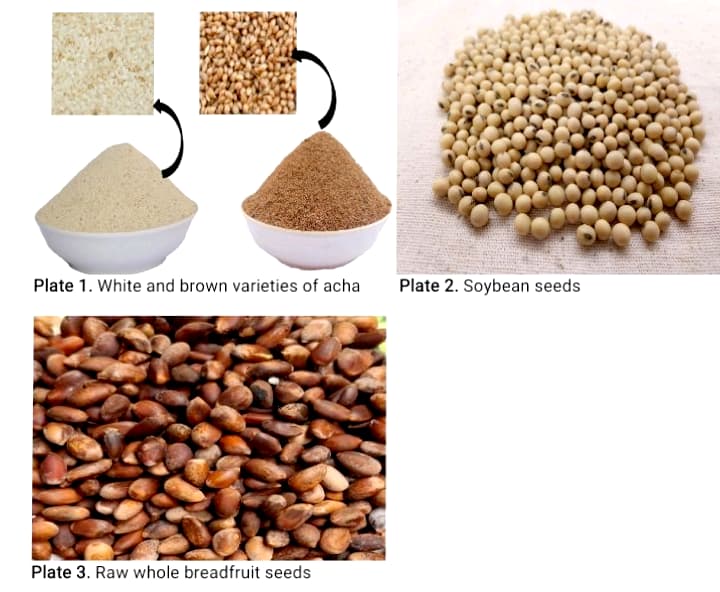

This research explored the quality characteristics of composite flour samples from two varieties of acha (brown and white) fortified with soybean concentrate and breadfruit flour. Acha and soybean concentrate flours were blended (%, w/w) at ratios 100:0, 90:10, 85:15, and 80:20. 5% breadfruit flour was added to each blend as a constant, and 100% of each of the two varieties of acha flour containing 5% breadfruit flour were used as the control samples. Proximate composition of the flours and their blends, and sensory evaluations of the swallow produced from the blends were determined. The replicated experimental data were analyzed using Analysis of Variance at a 0.05 level of significance and Pearson correlation coefficient at a 0.05 level of significance, employing one-way ANOVA. The results of the proximate compositions of the flours showed that protein concentrate recorded the highest values for moisture, ash, and protein. Breadfruit flour recorded the highest values for fibre, fat, and energy value. Brown acha flour had the least fat and protein, while white acha flour had the least ash and fibre. Significant (p < 0.05) increases in ash, fibre, fat, and protein contents, and decreases in carbohydrate content, were recorded in the flour blends with increasing concentrations of soybean protein concentrate and decreasing concentrations of acha flours. Overall, a blend of 80% white acha flour, 20% soybean concentrate, and 5% breadfruit flour showed a better proximate composition in terms of ash, fibre, fat, and protein than others. White acha variety recorded the highest values in aroma and texture. The sensory attributes were all above 5 for all the parameters studied, which indicates that they were acceptable to a reasonable degree to the panelists. The overall quality of the composite flour samples indicates that they are suitable for use in infant food formulations, baking, and the production of other food products.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.32.2505.3522 Keywords Nutritional enrichment breadfruit soybean concentrate composite flour sensory evaluation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Determination of Phenolic Content and Biological Activity of Aqueous Extracts of Origanum onites L. from Different Locations
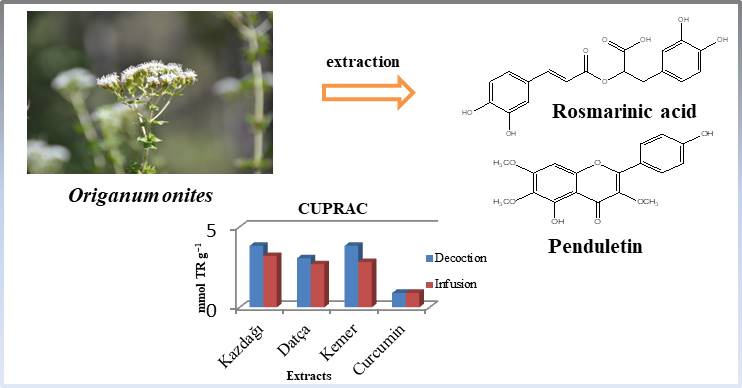
The phenolic content of the decoction and infusion extracts of Origanum onites from three different locations in Türkiye was evaluated using LC-MS/MS. The antioxidant capacity of the decoction and infusion was assessed using the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), β-carotene linoleic acid, and CUPRAC assays. Additionally, the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities of the both extracts of O. onites were investigated. The highest level of rosmarinic acid (935.79 mg/kg), penduletin (743.53 mg/kg), and kaempferol (506.14 mg/kg) were found in the decoction extract of O. onites from Kemer. In addition, Kemer had the highest DPPH free radical scavenging (61.43-75.59%) and lipid peroxidation (59.03-78.99%) activity of all the locations examined. Kazdağı sample had the highest value on the CUPRAC assay (3.83 mmol TR g-1 for decoction and 3.20 mmol TR g-1 for infusion, respectively). The study concludes that a quantitative relationship between phenolic content and antioxidant activity was established, which is important for understanding the role of phenolics in antioxidant activity. The location had an impact on the biological activities of both extracts of O. onites, as well as their phenolic content.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.33.2505.3547 Keywords Origanum onites different location phenolics antioxidant AChE BChE DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Chemical Properties of Wild Cistus creticus L. and Cistus salviifolius L. Species at Different Development Stages
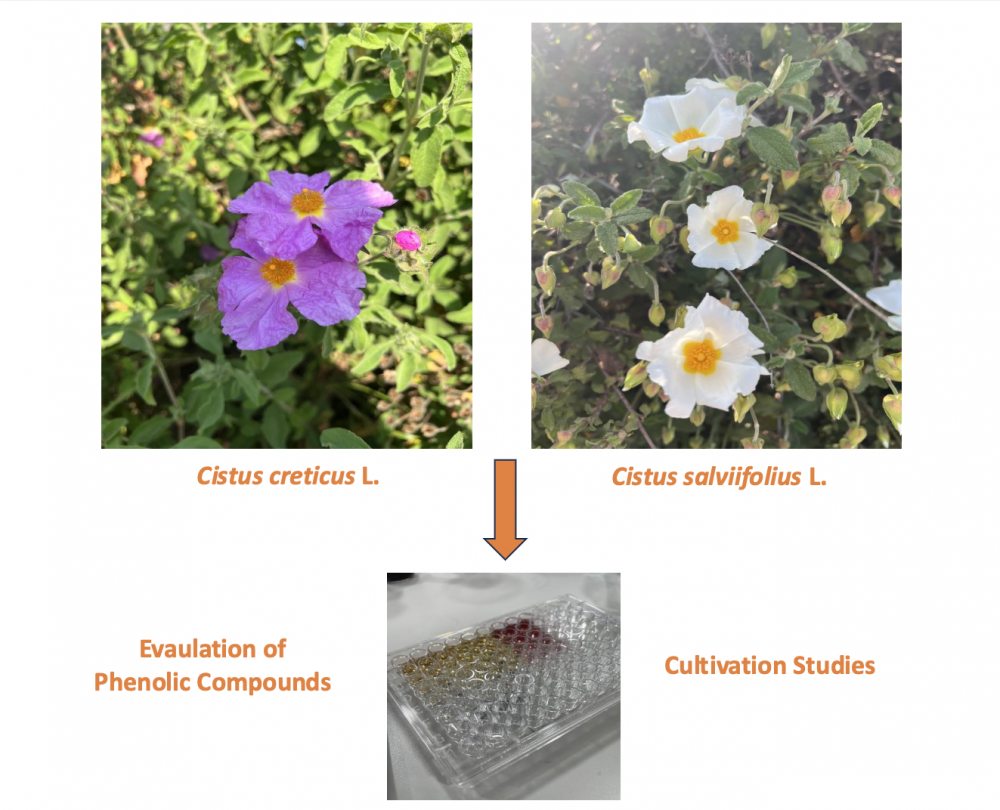
The seasonal variations are important exogenous factors that cause differences in the chemical properties of the plants. The primary objective of this study was to assess the chemical properties of two Cistus species (Cistus creticus L. and Cistus salviifolius L.), which are widely utilized in the pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, and veterinary industries, taking into account seasonal variations. The C. creticus and C. salviifolius plant samples were collected during the early flowering, full flowering, and fruit maturity stages. Then, the 50% EtOH extract of each plant was prepared, and their total phenolic and flavonoid contents were determined by the Folin-Ciocalteu and aluminum chloride colorimetric methods, respectively. In the early flowering stage period the C. creticus plant’s both total phenol (CC1: 105.695 ± 2.657 mg/g, CC2: 120.260 ± 3.986 mg/g, CC3: 123.739 ± 2.677 mg/g) and the flavonoid (CC1: 8.298 ± 0.481 mg/g, CC2: 10.116± 1.659 mg/g, 11.935 ± 1.120 mg/g) contents were the highest. The C. salviifolius plant’s total phenol content was the highest in the fruit maturity stage period (CS1: 151.565 ± 3.549 mg/g, CS2: 138.304 ± 2.551 mg/g, CS3: 132.652 ± 3.779 mg/g) while the total flavonoid content was the highest in the early flowering stage period (CS1: 10.896 ± 1.179 mg/g, CS2: 10.246 ± 1.196 mg/g, CS3: 9.077 ± 1.981 mg/g). To the best of our knowledge, the current study is the first to demonstrate the effect of seasonal variations on the total phenolic and total flavonoid compounds of C. creticus and C. salviifolius, specifically during the periods when they contained the highest levels.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.34.2506.3567 Keywords Cistus creticus L. Cistus salviifolius L. quality control phenolic compound flavonoids DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.