Records of Natural Products
Year: 2026 Volume: 20 Issue:1
1) A new chapter, 20th year
 DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3649
Keywords
Records of Natural Products
new format
quality
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3649
Keywords
Records of Natural Products
new format
quality
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
2) Nitric oxide inhibitory compounds from Thai medicinal plants Averrhoa bilimbi and Schinus terebinthifolia
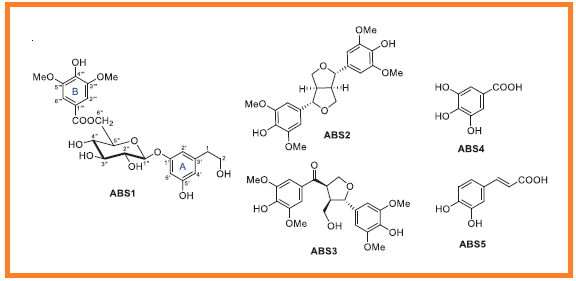
Nitric oxide (NO) overproduction by activated macrophages drives inflammatory responses via iNOS activation, prompting the search for natural NO inhibitors. A bioassay-guided investigation targeting NO inhibition was conducted on Averrhoa bilimbi and Schinus terebinthifolia, two Thai medicinal plants. The most active fractions, derived from the branches of A. bilimbi and the stems of S. terebinthifolia, were subjected to chemical analysis. Seventeen compounds were isolated, five (ABS1–ABS5) from A. bilimbi and twelve (ST1–ST12) from S. terebinthifolia, with bilimoside A (ABS1) identified as a new compound. Structural elucidation of all isolated compounds was accomplished through detailed spectroscopic analysis, including NMR and HRESIMS. Their in vitro NO inhibitory activity was evaluated, revealing 3-oxoursolic acid (ST2) as the most potent compound (IC50 28.00 µg/mL), surpassing the positive control L-NMMA (IC50 41.30 µg/mL), while exhibiting minimal cytotoxicity. These findings suggest that ST2 could serve as a promising candidate for further development as an anti-inflammatory agent.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2507.3593 Keywords Averrhoa bilimbi Schinus terebinthifolia bilimoside A nitric oxide inhibition. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Windienoic acid, a new compound from themedicinal plant Wikstroemia indica
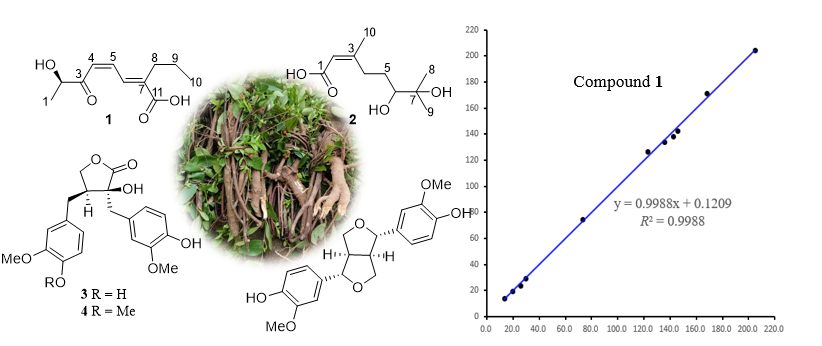
A phytochemical investigation of the roots of the medicinal plant Wikstroemia indica (Linn.) C. A. Mey led to the isolation of five compounds (1–5), comprising one previously undescribed metabolite (1), named windienoic acid, and four reported compounds (2–5). The structural elucidation of these compounds was accomplished through comprehensive analysis of spectroscopic data, including 1D (¹H and ¹³C NMR) and 2D NMR techniques (HSQC, COSY, and HMBC). Compounds 2–5 were identified as the monoterpene 6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenoic acid (2), the dibenzylbutyrolactone-type lignans (-)-nortrachelogenin (3) and (-)-trachelogenin (4), and the furofuran-type lignan pinoresinol (5) by comparing with literature data. Notably, the structure of compound 1 incorporated an extended conjugated system comprising a dienone moiety linked to a carboxylic acid group, which is rarely in acyclic compound, its structure was confirmed by 13C NMR calculation. The NMR assignment of dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenoic acid (2) is reported herein for the first time in methanol-d4. The cytotoxic screening assay against the A549 human lung cancer cell line of all compounds revealed that compound 3 exhibited weak activity with an IC₅₀ value of 42.3 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3621 Keywords Wikstroemia indica windienoic acid cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and application of Clitoria ternatea L.: a review

Clitoria ternatea L. (Fabaceae) is a leguminous plant with a long history of medicinal use and multifaceted applications, widely distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Oceania. In traditional medicine, particularly within the Ayurvedic system, C. ternatea has been employed to treat various ailments such as diabetes, cognitive impairment, and respiratory disorders. With advancing research into its chemical composition and pharmacological activity, C. ternatea has been found to possess a rich array of bioactive constituents, including flavonoids, anthocyanins, lignans, and triterpenoids. It exhibits diverse pharmacological effects such as hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic properties, memory enhancement, antibacterial and insecticidal action, anti-inflammatory effects, cough suppression, and antitumor activity. Moreover, C. ternatea demonstrates broad application prospects across agriculture, cosmetics, food additives, and pesticides. This article aims to provide a systematic review of the plant's botanical characteristics, chemical constituents, pharmacological activities, and practical applications, thereby offering a reference framework for subsequent in-depth research and comprehensive development.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3634 Keywords Clitoria ternatea L. Fabaceae phytochemistry pharmacology applications DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) LC-MS/MS characterization of phenolic compounds and in vitro assessment of antioxidant, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, and anti-Alzheimer activities of Echium creticum L.

The present work provides the first comprehensive LC–MS/MS phytochemical profiling and pharmacological investigation of Echium creticum L., Boraginaceae, native to the Mediterranean region, used in folk medicine, The aerial parts were sequentially extracted using petroleum ether (PEEEC), chloroform (CEEC), ethyl acetate (EAEEC), and n-butanol (BEEC). LC-MS/MS profiling of the polar extracts identified 25, 22, and 24 bioactive compounds, with rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid, salicylic acid, and gentisic acid as major phenolics. Several flavonoid glycosides (cosmosiin, nicotiflorin, genistin) are reported for the first time in the Echium genus. Antioxidant activity was evaluated using DPPH, ABTS FRAP, and Fe³⁺-phenanthroline assays, was strongest in the ethyl acetate fraction. Antidiabetic potential was confirmed via α-amylase inhibition, where EAEEC demonstrated effective inhibition (IC₅₀ = 207.20 ± 2.58 µg/mL), comparable to quercetin and Acarbose. The antibacterial activity was also evaluated through the disc diffusion methods and MIC tests against a panel of 10 gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (-) bacterial strains (references and isolates multi-drug resistant bacteria) (MIC 32- 80 μg/mL). The n-butanol extract (BEEC) displayed the strongest anticholinesterase activity (IC₅₀ = 68.98 ± 1.33 µg/mL), consistent with its flavonoid glycoside enrichment. Altogether, these results highlight E. creticum as an underexplored source of phenolic compounds with multi-target in vitro bioactivities and expand the phytochemical diversity of the Echium genus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3611 Keywords Echium creticum LC–MS/MS phenolic compounds antioxidant anti-diabetic anticholinesterase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Anti-phytopathogenic himeic acid derivatives produced by the Nicotiana tabacum symbiotic fungus Aspergillus sp. TE-65L
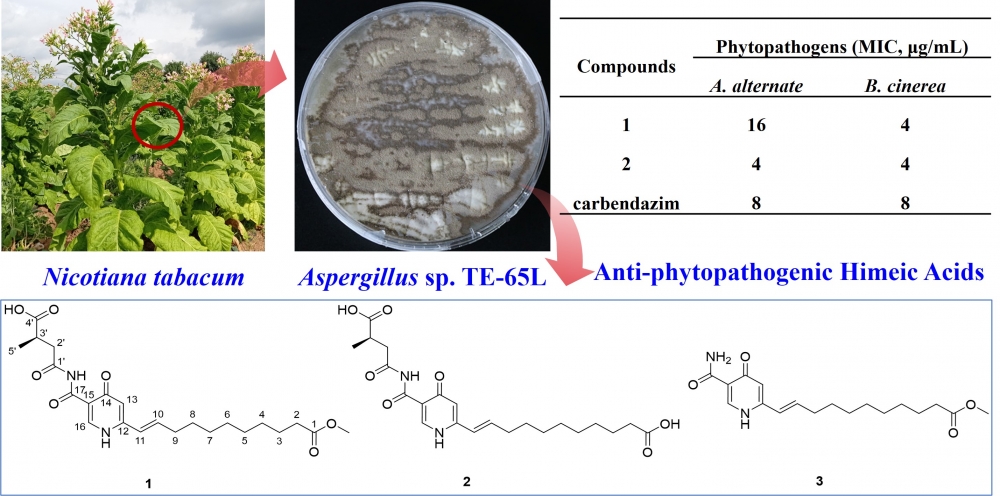
In our study, chemical exploration of the Nicotiana tabacum L. symbiotic fungus Aspergillus sp. TE-65L led to the discovery of a new himeic acid derivative, japonimeic acid J (1), along with two previously reported compounds 2 and 3. The structure of the new compound was unequivocally elucidated using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Furthermore, compounds 1 and 2 displayed strong anti-phytopathogenic potency against Alternaria alternata and Botrytis cinerea, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 4 μg/mL. This result suggests that they have considerable potential as new, naturally sourced agro-antibiotics for controlling fungal plant diseases.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3628 Keywords symbiotic fungus natural product secondary metabolite himeic acids anti-phytopathogenic potency DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Kaempferol enhances hair growth by regulating JAK3/STAT6 and TGF-β/Smad signaling in human dermal papilla cells and a C57BL/6 mousemodel
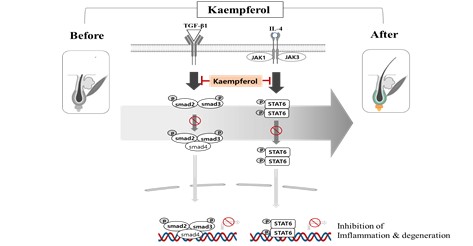
Kaempferol, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in hair growth-promoting plants, was investigated for its direct effects on hair loss prevention. This study assessed its impact on human dermal papilla (HDP) cells, essential regulators of hair follicle activity. Kaempferol significantly enhanced HDP cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, exceeding the effect of minoxidil. It markedly inhibited TGF-β1-induced Smad-binding activity (65.8%) and IL-4-induced STAT6 activity (72.5%), compared to finasteride (35%) and tofacitinib (96%), respectively. Western blot analysis showed suppression of phosphorylated Smad2/3 and STAT6, along with upregulation of CDK2, CDK4, cyclin D3, ERK1/2, IGF-1R, and VEGFR-2. In vivo, topical application of Kaempferol in C57BL/6 mice significantly promoted hair growth, increased follicle numbers, and improved hair thickness. These findings suggest that Kaempferol enhances hair growth through modulation of TGF-β/Smad and JAK3/STAT6 pathways and may serve as a promising natural therapeutic agent for hair loss treatment.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3629 Keywords Kaempferol hair growth IL-4/JAK3/STAT6 TGF β1/Smad/SBE HDP cells C57BLmouse model DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A new isoflavone from the ethyl acetate extracts of Apios fortunei Maxim and anti-inflammatory activity
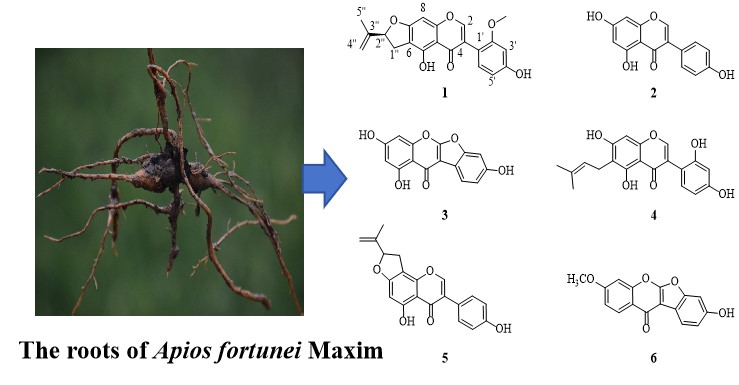
A new isoflavone apiosisoflavone A (1) and five known isoflavones (2–6) were isolated fromthe ethanol extracts of Apios fortuneiMaxim. The structures were elucidated by spectroscopic data analysis of NMR, HR-ESI-MS, and experimental and calculated ECD. All compounds were evaluated on the anti-inflammatory activity against RAW264.7 cell lines. The levels of NO and TNF-α released by RAW264.7 cells were detected by the kit. All the compounds displayed moderate anti-inflammatory activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2506.3553 Keywords Apios fortunei Maxim isoflavone structure elucidation anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Phytochemical and antileismanial activity studies on the tubers of Cyclamen rohlfsianum Asch

Antileishmanial activity guided studies on the methanolic extract of the tubers of Cyclamen rohlfsianum Asch. resulted in the isolation and characterization of six saponins. All saponins were established as tri-, tetra-, and pentaglycosidic derivatives of 13β-28- epoxy-oleanane-type triterpenic sapogenols. Two of them were found to be newly described saponins, rohlfsianosides A and B. Their structures were identified as 3-O-β-{[β-Dxylopyranosyl-( 1→2)-β-D-lucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)]-α-L-arabinopyranosyl}- 13β,28-epoxy-16α-hydroxy-30-acetoxy-oleanane (rohlfsianoside A), and 3-O- β-{{[β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)]-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4) ]}-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)]-α-L-arabinopyranosyl}-protoprimulagenin A (rohlfsianoside B), respectively. Additionally, three known compounds, cyclamiretin A (3β,16α- dihydroxy-13β-28-epoxy-oleanan-30-al) glycosides; cyclaminorin, deglucocyclamin and cyclamen, and protoprimulagenin A (13β-28-epoxy-3β,16α-dihydroxy-oleanane) derivative, lysikoianoside I, were identified. The structure elucidation of the saponins was established by means of spectroscopic methods (1D and 2D NMR, HR-MS). All the saponins showed notable growth inhibitory activity against Leishmania ropica, with IC50 values ranging from 17.5 to 21.9/mL.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3646 Keywords Cyclamen rohlfsianum 13β-28-epoxy-oleanan-type saponins rohlfsianosides A and B antileishmanial activity Leishmania tropica DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Cytotoxic activities and in silico study of carbazole alkaloids isolated from Murraya koenigii against HL-60 and HeLa cancer cell lines
.jpg)
Carbazole alkaloids from Murraya koenigii exhibit diverse structural features and promising anticancer potential. This study evaluated the cytotoxic activity and structure–activity relationship (SAR) of 24 carbazole alkaloids against HL-60 and HeLa cancer celllines, alongside molecular docking studies against the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 (PDB ID: 2W3L).The SAR analysis revealed that electron-donating and redox-active substituents, particularly formyl groups, significantly enhanced cytotoxicity, while dimerization generally reduced potency. Docking results showed binding energies ranging from −5.49 to −9.37 kcal/mol, with key interactions mainly involving Phe63, Asp70, Phe71, Met74, Val92,Glu95, Leu96, Asp99, Gly104, Phe109, Glu111 and Phe112 residues. Potent compounds such as mahanine (15) and murrayamine-J (18) exhibited both strong cytotoxicity (IC50 = 12.1 and 5.1 μg/mL for HL-60 and 12.8 and 7.7 μg/mL for HeLa, respectively) and favorable binding affinities (−7.66 and −7.25 kcal/mol), suggesting that Bcl-2 inhibition contributes to their activity. Conversely, murrayafolline-A (2) displayed notable cytotoxicity (IC50 = 8.5 μg/mL forHL-60 and 4.6 μg/mL forHeLa) despite only moderate predicted affinity (−5.71 kcal/mol), indicating possible alternative mechanisms of action. Similarly, bisisomahanine (24) showed the strongest predicted binding (−9.37 kcal/mol) with lowest ligand efficiency but negligible cytotoxicity, suggesting that the high binding affinity is attributed to its bulky size. Overall, this study provides supportive computational insights into the cytotoxic potential of carbazole alkaloids and highlights their predictive relevance for future mechanistic and pharmacokinetic studies.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3616 Keywords Murraya koenigii carbazole alkaloids sturcture-activity relationship HL-60 HeLa Bcl-2 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Delving into the phytochemical constituents and biological activities of Scorzonera coriacea extracts: new perspectives from in vitro and in silico studies
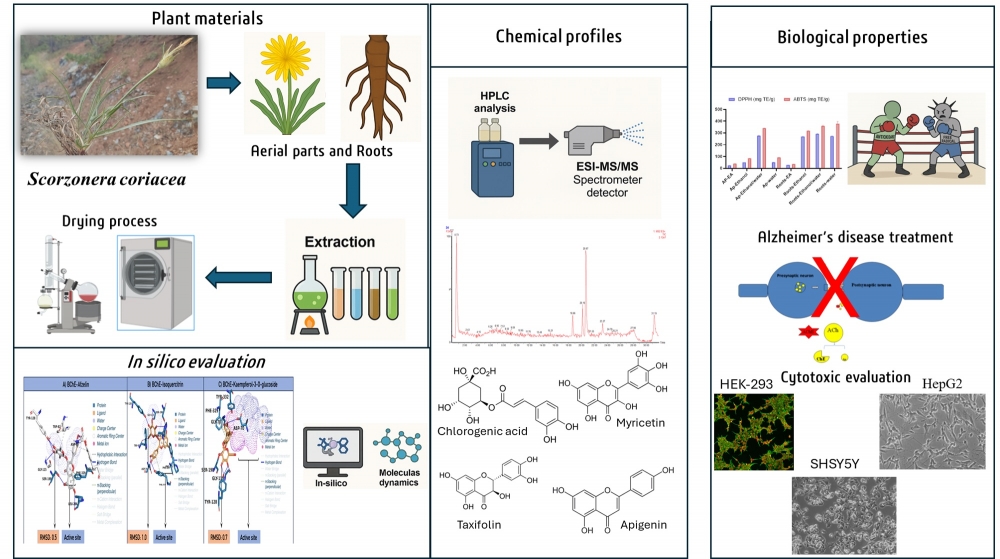
The current study was designed to investigate the chemical composition, antioxidant, enzyme inhibitory, and cytotoxic activities of Scorzonera coriacea A.Duran & Aksoy. Both organs were rich in total phenolic content, with the highest content recorded from the 70% EtOH (48.41 mg GAE/g) and aqueous (47.11 mg GAE/g) extracts of the roots. All aerial parts extracts accumulated higher total flavonoid content than their respective roots extracts, with the highest amount found in their EtOH extract (36.44 mg RE/g). Chemical analysis revealed the presence of 86 compounds belonging to organic acids, phenolic acids, flavonoids, coumarins, anthocyanins, terpenes, saponins, and fatty acids and their derivatives, with the aerial parts accumulating the highest number. The roots displayed the strongest antiradical and ion-reducing capacities. EtOH extract of both organs recorded the highest acetylcholinesterase activity (2.77 and 3.02 mg GALAE/g; p≥0.05), while that of the root showed the best butyrylcholinesterase activity (3.49 mg GALAE/g) and that of the aerial parts the best tyrosinase inhibitory (59.07 mg KAE/g). EtOAc of the root exhibited the best cytotoxicity towards the HepG2 cell line (cell viability = 29.30%), but was also toxic towards HEK293 cells (cell viability = 11.72%). In silico screening supported these findings by identifying multiple strong ligand–protein interactions. Molecular dynamics simulations further confirmed the structural stability of selected complexes. In silico profiling docked 26 phytochemicals against 14 therapeutic targets, generating 364 complexes, of which 62% showed ΔG ≤ −7.0 kcal·mol⁻¹. Binding energies ranged from −1.4 to −10.7 kcal·mol⁻¹, with PD-1–Eriodictyol-7-O-neohesperidoside the best. For metabolic enzymes, Eriodictyol-7-O-neohesperidoside yielded the top α-amylase score and Diosmetin-7-O-glucoside the top α-glucosidase score, while several flavonoids bound AChE/BChE strongly; in contrast, tyrosinase displayed poor affinity overall. 100-ns MD simulations on five top complexes indicated stable behavior for C1 and C4, whereas C2/C3/C5 showed loosening interactions over time. These findings showed that S. coriacea could be a promising source of bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic applications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3633 Keywords Scorzonera coriacea molecular docking molecular dynamics antioxidant enzyme inhibition cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) Mannodaidzein, a rare daidzein mannoside isolated froma rare actinomycete Saccharothrix sp. JS2
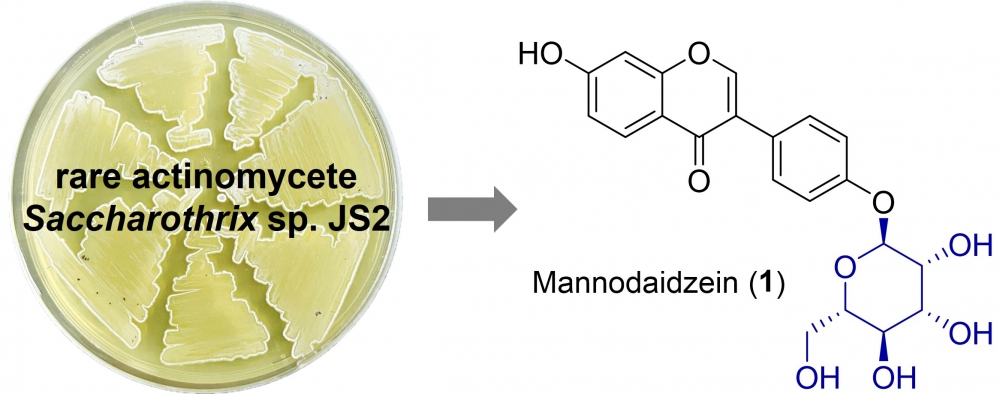
A rare isoflavone mannoside, mannodaidzein (1), along with three known isoflavones (2–4), was isolated from the culture broth of an actinomycete Saccharothrix sp.JS2. Their chemical structures were determined by 1D/2D NMR and HR(ESI)MS data analyses. Among them, only compound 2 exhibited weak anti-proliferative activity against HT1080 cells at 100 µM. The structure-activity relationship analysis revealed that modification of the C-4' hydroxyl group adversely affected cytotoxicity. Mannodaidzein (1) represents the first mannoside of flavone.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3614 Keywords Isoflavone mannoside actinomycete cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Vilmorinine G, a new quassinoid from Ailanthus altissima

A new quassinoid, named vilmorinine G (1), along with two known congeners (2 and 3), has been isolated from the root bark of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle. The structure of 1 was elucidated through spectroscopic evidence in NMR, HR-ESI-MS, and ECD. The absolute configuration of 1 was further confirmed by X-ray crystallography.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3645 Keywords Quassinoid Ailanthus altissima absolute configuration DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) Uvaol-28-D-(R)-pyroglutamic acid ester: a new triterpenoid compound from Circinellamuscae CGMCC 3.2695 and its activity assessment in transgenic zebrafish
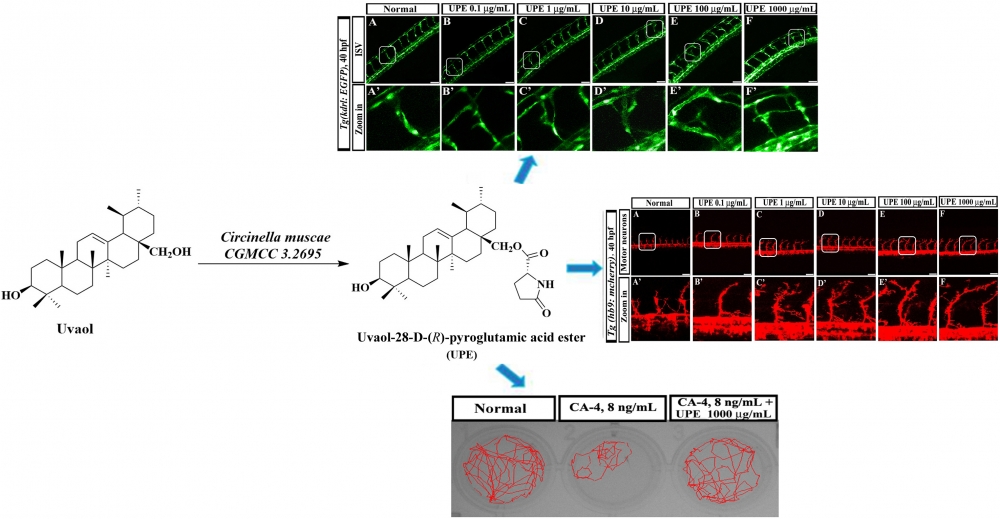
A novel triterpenoid compound named Uvaol-28-D-(R)-pyroglutamic acid ester (UPE) was obtained via microbial biotransformation of uvaol by Circinella muscae CGMCC 3.2695. Its structure was elucidated by spectroscopic and mass-spectrometric analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR and HR-ESI-MS. UPE administration promotes intersegmental vessel (ISV) growth and motor neuron development in transgenic zebrafish embryos in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, UPE significantly restored the swimming distance in zebrafish exposed to combretastatin A-4 (CA-4), as assessed by ESOvision behavioral analysis. These findings suggest that UPE holds promise for the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3620 Keywords Uvaol-28-D-(R)-pyroglutamic acid ester Circinella muscae CGMCC 3.2695 transgenic zebrafish intersegmental vessel motor neuronal axonal DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) Euphebranone F, a new acetophenone derivative fromthe Euphorbia fischeriana

Phytochemical investigation of the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana led to the isolation of a novel acetophenone derivative, named Euphebranone F (1), along with three known acetophenone analogs (2–4). The structure of the new compound, featuring a C-C linkage between the C-9 of the acetophenone unit and C-8′ of the phenylpropanoid moiety, was elucidated by extensive NMR and HRESIMS analysis, and its absolute configuration was determined by ECD calculations. Cytotoxic activity screening against human gastric cancer cell lines (MKN-45 and AGS) revealed that only compound 2 exhibited moderate antiproliferative activity against MKN-45 cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2511.3720 Keywords Euphorbia fischeriana Steud structure elucidation Euphebranone F acetophenone derivative DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.